Page is loading ...

M~IIer
March
1995
Form:
OM-1584E
Effective
With
Serial
No.
KF785422
OWNERS
MANUAL
U
Read
and
follow
these
instructions
and
all
safety
blocks
carefully.
Have
only
trained
and
qualified
persons
install,
operate,
or
service
this
unit.
Call
your
distributor
if
you
do
not
understand
the
directions.
Give
this
manual
to
the
operator.
1I~fl
U
For
help,
call
your
distributor
U
or:
MILLER
Electric
Mfg.
Co.,
P0.
Box
1079,
Appleton,
WI
54912
414-734-9821
SWINGARCTM
DS-12
And
DS-16
24
Volts,
10
Amperes,
50/60
Hertz
Boom
Mounted
Wire
Feeder
U
For
Use
With
C
V/DC
Welding
Power
Source
With
Contactor
For
GMAW
And
FCAW
Welding
Rated
At
100
Volts,
750
Amperes,
100%
Duty
Cycle
Wire
Feed
Speed
Range:
50
To
780
ipm
(1.3
To
19.8
mpm)
Wire
Diameter
Range:
.023
To
1/8
in
(0.6
To
3.2
mm)
Vertical
Lift
Of
Boom:
Honzontal
To
60
Above
Horizontal
See
Rear
Cover
For
Options
And
Accessones
cover
5/94
ST-142 595-B
'
1995
MILLER
Electric
Mfg.
Co.
PRINTED
IN
USA

MILLERS
TRUE
BLUETM
LIMITED
WARRANTY
Effective
January
1,
1995
(Equipment
with
a
serial
number
preface
of
KD
or
newer)
This
limited
wsrrsnty
supersedes
eli
previous
MILLER
warranties
snd
is
exclusive
with
no
other
gusrsntees
or
wsrranties
expressed
or
implied.
LIMITED
WARRANTY
Subject
to
the
terms
end
conditions
below,
MILLER
Electric
Mtg.
Co.,
Appleton,
Wisconsin,
warrants
to
its
original
retell
purcheser
thst
new
MILLER
equipment
sold
after
the
effective
date
ot
this
limited
warranty
is
tree
of
de
tects
in
material
end
workmanship
at
the
time
it
is
shipped by
MILLER.
THIS
WAR
RANTY
IS
EXPRESSLY
IN
LIEU
OF
ALL
OTHER
WARRANTIES,
EXPRESS
OR
IMPUED,
INCLUDING
THE
WARRANTIES
OF
MERCHANTABILITY
AND
FIT
NESS.
Within
the
warranty
periods
listed
below,
MILLER
will
repair
or
replace
eny
war
ranted
pans
orcomponents
that
tail
due
to
such
detects
in
materiel
orwortcmanahip.
MILLER
must
be
notitied
in
writing
within
thirty
(30)
days
ct
such
detect
or
tailure,
at
which
time
MILLER
will
provide
instructions
on
the
warranty
claim
procedures
to
be
tollowed.
MILLER
shall
honor
warranty
claims
on
warranted
equipment
listed
below
in
the
event
ot
such
a
tailure
within
the
warranty
time
periods.
All
warranty
time
periods
start
on
the
dete
thet
the
equipment
was
delivered
to
the
original
retail
purchaser,
or
one
year
after
the
equipment
is
sent
to
a
North
American
distributor
or
eighteen
months
eher
the
equipment
is
sent
to
en
Intemational
distributor.
5
Years
Pans
3
Years
Labor
Original
main
power
rectiffem
2.
3
Years
Parts
and
Labor
TmnstormerfRectitier
Power
Sources
*
Plasma
Arc
CuBing
Power
Sources
*
Semi-Automatic
end
Automatic
Wire
Feeders
*
Robots
3.
2
Years
Pans
and
Labor
Engine
Driven
Welding
Generators
(NOTE:
Engines
are
warranted
separately
by
the
engine
manutacturer.)
*
Air
Compressors
4.
1
Year
Pens
and
Labor
Motor
Driven
Guns
Process
Controllers
Water
Coolant
Systems
HF
Units
Grids
Spot
Welders
Load
Banks
SDX
Tmnatormem
Running
Gear/Trailers
Plasma
Cutting
Torches
(except
APT,
ZIPCUT
&
PLAZCUT
Models)
Tecumaeh
Engines
Deutz
Engines
(outside
North
America)
Field
Options
(NOTE:
Field
options
are
covered
under
True
BIueTM
tor
the
remaining
warranty
period
ot
the
product
they
are
installed
in,
or
tor
a
minimum
ot
one
year
whichever
is
greater.)
6
Months
Batteries
90
Days
Pans
and
Labor
MIG
GunslflG
Torches
APT,
ZIPCUT
&
PLAZCUT
Model
Plasma
Cutting
Torches
a]
Remote
Controls
*
Accessory
Kits
Replacement
Pans
MILLERS
True
BIueTM
Limited
Warranty
shall
not
apply
to:
1.
Items
tumiahed
by
MILLER,
but
manutactured
by
cthers,
such
as
engines
or
trade
accessories.
These
items
are
covered
by
the
manutacturera
warranty,
it
any.
2.
Consumable
components;
such
as
contact
tips,
cutting
nozzles,
contactors
and
relays
or
pans
that
tail
due
to
normal
wear.
3.
Equipment
that
has
been
moditied
by
any
party
other
than
MILLER,
or
equip
ment
that
has
been
improperty
installed,
improperty
operated
or
misused
based
upon
industry
standards,
or
equipment
which
has
not
had
reasonable
and
necessary
maintenance,
orequipment
which
has
been
used
tor
operation
outside
ot
the
apecitications
tor
the
equipment.
MILLER
PRODUCTS
ARE
INTENDED
FOR
PURCHASE
AND
USE
BYCOMMER
CIALIINDUSTRIAL
USERS
AND
PERSONS
TRAINED
AND
EXPERIENCED
IN
THE
USE
AND
MAINTENANCE
OF
WELDING
EQUIPMENT.
In
the
event
ot
a
warranty
claim
covered
by
this
warranty,
the exclusive
remedies
shall
be,
at
MILLERS
option:
(1)
repair;
or
(2)
replacement;
or,
where
authorized
in
writing
by
MILLER
in
appropriate
cases,
(3)
the
reasonable
coat
ot
repair
or
replace
ment
at
an
authorized
MILLER
service
station;
or
(4)
payment
ot
orcmdit
torthe
pur
chase
price
(less
reasonable
depreciation
based
upon
actual
use)
upon
retum
otthe
goods
at
customers
risk
and
expense.
MILLERS
option
ot
repair
or
replacement
will
be
FOB.,
Factoryat
Appleton,
Wisconsin,
or
FOB.
at
a
MILLER
authorized
ser
vice
tacility
an
determined
by
MILLER.
Theretore
no
compensation
or
reimburse
ment
for
transportation
costs
ot
any
kind
will
be
allowed.
TO
THE
EXTENT
PERMITTED
BY
LAW,
THE
REMEDIES
PROVIDED
HEREtN
ARE
THE SOLE
AND
EXCLUSIVE
REMEDIES.
IN
NO
EVENT
SHALL
MILLER
BE
UABLE
FOR
DIRECT,
INDIRECT,
SPECIAL,
INCIDENTALOR
CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES
(INCLUDING
LOSS OF
PROFIT),
WHETHER
BASED
ON
CON
TRACT,
TORT
OR
ANY
OTHER
LEGAL
THEORY.
ANY
EXPRESS
WARRANTY
NOT
PROVIDED
HEREIN
AND
ANY
IMPLIED
WAR
RANTY,
GUARANTY
OR
REPRESENTATION
AS
TO
PERFORMANCE,
AND ANY
REMEDY
FOR
BREACH
OF
CONTRACT
TORT
OR
ANY
OThER
LEGAL
THEORY
WHICH,
BUT
FOR
THIS
PROVISION,
MIGHTARISE
BY
IMPLICATtON,
OPERATION
OF
LAW,
CUSTOM
OF
TRADE
OR
COURSE
OF
DEALING,
IN
CLUDING
ANY
IMPLIED
WARRANTY
OF
MERCHANTABILITY
OR
FITNESS
FOR
PARTICULAR
PURPOSE,
WITH
RESPECTTO
ANY
AND
ALL
EQUIPMENT
FURNISHED
BY
MILLER
IS
EXCLUDED
AND
DISCLAIMED
BY
MILLER.
Some
states
in
the
U.S.A.
do
not
allow
limitations ot
how
long
an
implied
warranty
lasts,
or
the
exclusion
ot
incidental,
indirect,
special
or
consequential
damages,
so
the
above
limitation
or
exclusion
may
not
apply
to
you.
This
warranty
provides
ape
citic
legal
rights,
end
other
rights
may
be
available,
but
may
vary
trom
state
to
state.
In
Canada,
legislation
in
some
provinces
provides
tor
certain
additional
warranties
or
remedies
other
than
as
stated
herein,
and
to
the
extent
that
they
may
not
be
waived,
the
limitations
and
exclusions
set
out
above
may
not
apply.
This
Umited
Warranty
provides
specific
legal
rights,
and
other
rights
may
be
available,
but
may
vary
trom
province
to
province.
5.
6.
fu
RECEIVING-HANDLING
Before
unpacking
equipment,
check
carton
for
any
damage
that
may
have
occurred
during
shipment.
File
any
claims
for
loss
or
damage
with
the
delivering
carrier,
Assistance
for
filing
or
settling
claims
may
be
obtained
from
distributor
and/or
equipment
manufacturers
Transportation
Department.
When
requesting
information
about
this
equipment,
always
provide
Model
Designation
and
Serial
or
Style
Number.
Use
the
following
spaces
to
record
Model
Designation
and
Serial
or
Style
Numberof
your
unit.
The
information
is
located
on
the
rating
label
or
nameplate.
Model
_________
Serial
or
Style
No.
Date
of
Purchase
miller
1/95

ERRATA
SHEET
March
29,
1995
FORM:
OM-1584E
Use
above
FORM
number
when
ordering
extra
manuals.
After
this
manual
was
printed,
refinements
in
equipment
design
occurred.
This
sheet
lists
exceptions
to
data
appearing
later
in
this
manual.
CHANGES
TO
SECTION
6
ELECTRICAL
DIAGRAMS
Replace
Figure
6-2.
Circuit
Diagram
For
Wire
Feeder
With
Optional
Equipment
(See
Pages
2
and
3
on
this
Errata
Sheet)

Figure
6-2.
Circuit
Diagram
For
Wire
Feeder
With
Optional
Equipment
72
VaTA~
SEbEE
RIGlI
~
LEAD
(DRTI~4AL
TO
DRIVE
IO~SINI3
~d
p
LEFT
RCI-3>
RCI-6>>~
)
Rd-a>
RCI-7
>>f-i
Rd-I
>>~
Rd-A>
I
)
Rd-S
>>
72
76
-
___
---_-
~–ii~
~i~i
iii
Rd2-4
)
RC2-5
)
802-2
)
Rd2-6
)
802-I
)
RC2-3
)
/
Z4
8023-4
8053-S
Rd53-2
R053-6
Rd53-I
Rd53-3
P05
~ER
BOARD
RC~G53
RCSI/PLGS4
Rd56/PLGRa
DR
CDI
PLGI
I
r
~
1Pt~034
RC27
P1027
~
~
Pt..G124
4,
4,
I
4-
4
4PLG33~
I~
I~ I~
I
A
A
ARc371
845
I
P1G371
~
99y
y
yRCAOI
I
i~
I
L
J~_
_~PIQ;3%
845
4
4
4PLGI8
44Z?<7
W!<I
WiEN
DIGITAL
V~TA~
C~4TR~
IS
LEED
WITH
A
CDRVENTIDRAL
POWER
SOIRCE
14A1(E
TIE
Fou..OWI~G
d~ECTI~
AT
PcAO,
Rd41-P1641
8C42-P1G42
Rd43-PIG43
RC44-N/C
RC4S-P1..G6
I
W1EN
DIGITAL
V~TA~
CDRTRa.
IS
LEED
WITH
AN
IPNERTER
POWER
SO.RCE
MAKE
TIE
F~L0WDG
~1~ECTIOE
AT
PC4O,
RCII-PLD6I
RC42-N/C
RC43-P1G43
RC44PLGA2
8C45-PLG4
I
r
~
RC3O
P1012
~r<61EL.<A
~6>-!<6I~
<
cR101
HI~1
~II4Z_<II.E~4II>~~(
i~_4
<
PIGI
ii
RC27
P1028
P10291
P1033
P1037
RC4O
I
_1r
7
P1018
,<6lE~-<6
E~6
>(6I
A11
I
-.
cR101
~
IiE~L(II~II,2~<Ii~tsJ-
P1017
8027
P1038
P1039
W
'
TcRI
I
DETAPI
DRTIDR
L
J
~
PIG
I
9
<2
C
(
0
(
E
<
P05
RELAY
BOARD
Rc90,Pl-G9O
RC9I/PIG9I
RC92/P1G92
RC93/P1093
RCV4/PLG94
RC95/PLG9~
RC96/PLG96
RC97/P1G97
RC98/P1G98
RC99/PL.G99
I
a
RC4-6
P050
RC53/PI~G53
RcSA/PLGS4
RCS6/P1056
RCG4-
I
TAOETER
BOARD
RC4-I
IDRTIDRAII
>~-0
1
I~
k
I~ I~
9054-4
>><RC98-
~
~RC54-5
>>~3~<RC98-3
~
-
7
7
0
~
0
~
~-l~~
,~
.~
PCI
-
~RCS4-2_>>~(<RC98-6
BOARD
66
10~~
RCI/P10I
~
I
69<AZRC9A-2
RC2/P1G2
I
724Z<RC96-3
RC3/PL.G3
4
4
RC4/PLG4
3.....
L.
7
~
.&
~
-
8CC/PIGS
r~
~tb~i~7
v
RCA/Pt_GB
I
0
I~
I~
I~
I%
($TIDR1
A~c~o
A
A
A~0
3
2
~P1ED8
~
,~,
~FLG38
r
~=_d(<pcg4IS
I~
I~
I~
I~
I
2
~
~
~
~
P1037
<OAC94-7
VRC27
V
y
yRC37
ZRC6-I
~
~
j,~
~
-<<RC94-14
L
2
.2
7
.i
<RC94-8
RCA
~
V
~jcj~
V V
VPL~T7
-
PL
~
CCI
4
4
kp1657
lJj,~oI~_
,.J~
2
1Pt.057
~
~
~P1G57
RCA-A
~ ~
~
~
I~
~
~
~
~
~
RC6-2
I
PCCI
II
P052
I
I
i
I2T2J~2T~Y7Y~~0
~
I
LET
II
8112ff
I
I
~
RC4-9
ITAPOETER
I I
TACIOETER
I
L~cR-IP
PIO(-LP
I
~
RCA
I.E02
RC8A
A
A
A
805-I
>~~
r
~
3
2
I
4
3
2
I
RC3-2>>17
I
RC3-3
>>
I
i
P1024
A
A A
A
4321 4321
RC4-2
>)~
L
RC43
>)~~
I
10
~
/0
RC3-4
)~
~
I
DETAOlDRTIDR
T~P
~
RC4-4
>>~
~
6J
~
-
Rd4-5
>)~~-
l~T~,
~
~
I
RdS-8
>>-~-
I
/0
805-4
>>
RC9-5~
-
________I
A~
I
RdS-I
>>~
<<RC62-3
Rd64I
>
Rd5-2>
/
I
)
~-<
RC62-2
~
~
/0
Pd60
<<RC62-4
8054-3>
I
I
RC62/PLG62
I
805-6
>>~
<<
8C62-
I
Rc63/PLG63
PCA~-4
>
I
66
RC64P1G64
8054-5
>>~
RCG-7>>
<<RC62-5
DIGITAL
~
I
~
BOARD
(DRTITJIAL)
8054-6
>
I
IRIOAT~
ti
~
~
I
~jL~1
~11I
/0
ji
~
________
LEFT
I
I
~ETER
~
____________________
L_T~.Jfl
I
I
P1044
I
>~-<<RC43-6
0.~a
>~.I~<
RC43-5
~
111
111
I
DIGiTAL
VOLTAGE
-
11
~
(1
RC4I-2>)
<
RC43-a
(DRTI124AL)
F~
Rd/PIG
~dTI~
Rd42-2>>
SEE
ICTES
RC42-3>>
>.~<<
RC43-2
RC42-I>>
>~<<
Rd43-I
.3
Ga
I
vv~v
OM-1584D
Page
2

P1G22
--
2
~-i
<
RC3I-2
PC3O
~~EFT)
1
<RC3I-3
PREFLOW
PGETFLOW
6
<
RC3I-6
SPOTTIjE
<
RC3I-8
TRIGGER
I~
~
~j
<
~
I
8C31-7
~
<Rc3(~(
<RC3I-4
~
.L
~,
I
v_v~v_v
971
9~~$RY
SP~
(0.0
~F
C~T
22I
RC76-6
>
<<Rc78-2
2
RC76-S
>
<<RC78-I
87
PL.G80
__~~_~<
(/
RC76-4>
~
<RC79-4
RC76-2>
<RC79-S
9/
RC76-3
>
<<RC79-2
RE76-I
>
<<RC79-I
/0
<<RC79-3
r
_I~1Tj
DIGITAL.
(hAL
a
(<RC78-4
I
(~TIGHAL)
SOEDLLE
42
RC72-2
>
2)/~~0
MIT
<<RC78-3
I
RC72-I
>1
(>1/1
~LED7(~
I
~~W2~--
9
0
90O
701PR5SS
80
8p~~
~
TOSET
I
WIRE
FEED
70
/07
6
0
6~~1
SPEED
B
50
~
~
cw
40
I40~
30I30~
PC7O
20
I
c~4iRQ.
(0
(RIGHT)
/0/
70T
~TI0N
I
INTERFACE
~
DIGITAL_DiAL
2o~L~~<
I
~
(CPTIC)(AL)
I
~
I
0/
3
~
I
RC72/P1G72
I
PL668
PL049
~
I
RC1G/PLG86
I
VQTAGE
RC76/P1G76
cGHTRa.
AI
RC78/P1G78
L
~
(FRGHDVC)
~
RC79/P1G79
~L3~I
i
RC7S-3
3
~
RIGHT
__________
VD.TAGE
8C75-2
12
(
~
1!i
RE(OTE
I
o
~
I
RC75-)
II
(
~
C(~IPTI
ALl
-I
RC76-6
>
RC78-2
RC76-5
>
<<RC79-I
/0
RC76-4
>
<<RC79-3
65
RC76-2>
<<RC7a-4
RC76-3
>
<<RC78-3
RC76-I
>
(<RC78-
I
<RC79-4
DIGITAL
DUAL
I
(~TID4AL)
~
RC72-2
>
I
2)~
~
<RC79-2
I
RC72-P
>1
Y1
~LED8I
PLG7~,
9
0
0~~_058I
~PRESS
80
I/~43
ITO
GET
70
7
/27
WIRE FEED
60
6
SPEED
8
~
~
40
l4o~
3
0
I
20
I
PC7O
(LEFT)
I
0
I
/2/
lOT
~TIO4
INTERFACE
I3~>(LL<~3
I
I
DIGITAL
~
20~~<
12
/522
~JI
RC72/PtG72
I
PL.G48
P1047
~
I
RC75/P1G84
RC76/PLGI6
VILTAGE
C)RITRa.
AI
RC78/P1G88
L
~.
(FRGHDVC(
~
RC79/P1G89
~
,
RC75-3
13
(
LEFT
___________
V(h.
I
AGE
12
(
52
REPOTE
I
I
CGHTRO..
I
~j
CW
A
:Rv75-I
Ii
(SPTIOIALI
L___
-I
TRIGGER
~F
_4~JIIiI~S~0T
I(RI~{T)
A
<RC3I-2
<RC3I-3~
-
RC3I-6
PC30
~GHT)
(~TIcP4AL(
<RC3I-8
PREFLOW
<RC3I-5
P0STFt~OW
SPOTTI(
<
RC3I-7
&SP8AD(
TRIG~
(ILD
<
RC3I-I
RC3I/PLG3)
<RC3I-4
RC3S/PLG3G
RC98-
(4
>
5c98-13>:
RC9R-
IO)~
RC98-4>
RC98-I
RC98-8)
Rc987>;
RC98-
(2
>~
RC98-
(>:
RC98-5>
Rc98-2>:
-
I)
~TAGE~A~
IVOLTAGE
~(TR0L.
LEFT
CW
IPLGI7
/2J
2/~j,,cu
~,ap
PLGR4y3
I
54
52J51-J54
(~_
5/
a
5,
54
I
52
ii
~PLG85
~2
PIG7O
(C75-2
SD-173
731
OM-1584D
Page
3


ARC
WELDING
SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS
ELECTRIC
SHOCK
can
kill.
Touching
live
electrical
parts
can
cause
fatal
shocks
or
severe
burns.
The
electrode
and
work
circuit
is
electrically
live
whenever
the
output
is
on.
The
input
power
circuit
and
machine
internal
circuits
are
also
live
when
power
is
on.
In
semiautomatic
or
automatic
wire
welding,
the
wire,
wire
reel,
drive
roll
housing,
and
all
metal
parts
touching
the
welding
wire
are
electrically
live,
Incorrectly
installed
or
improperly
grounded
equipment
is
a
hazard.
1.
Do
not
touch
live
electrical
parts.
2.
Wear
dry,
hole-free
insulating
gloves
and
body
protection.
3.
Insulate
yourself
from
work
and
ground
using
dry
insulating
mats
or
covers
big
enough
to
prevent
any
physical
contact
with
the
work
or
ground.
4.
Disconnect
input
power
or
stop
engine
before
installing
or
servicing
this
equipment.
Lockout/tagout
input
poweraccording
to
OSHA
29
CFR
1910.147
(see
Safety
Standards).
5.
Properly
install
and
ground
this
equipment
according
to
its
Owners
Manual
and
national,
state,
and
local
codes.
6.
Always
verify
the
supply
ground
check
and
be
sure
that
input
power
cord
ground
wire
is
properly
connected
to
ground
terminal
in
disconnect
box
or
that
cord
plug
is
connected
to
a
properly
grounded
receptacle
outlet.
7.
When
making
input
connections,
attach
proper
grounding
conductor
first
double-check
connections.
8.
Frequently
inspect
input
powercord
fordamage
or
bare
wiring
replace
cord
immediately
if
damaged
bare
wiring
can
kill.
9.
Turn
off
all
equipment
when
not
in
use.
10.
Do
not
use
worn,
damaged,
undersized,
or
poorly
spliced
cables.
11.
Do
not
drape
cables
over
your
body.
12.
If
earth
grounding
of
the
workpiece
is
required,
ground
it
directly
with
a
separate
cable
do
not
use
work
clamp
or
work
cable.
13.
Do
not
touch
electrode
if
you
are
in
contact
with
the
work,
ground,
or
another
electrode
from
a
different
machine.
14.
Use
only
well-maintained
equipment.
Repair
or
replace
damaged
parts
at
once.
Maintain
unit
according
to
manual.
15.
Wear
a
safety
harness
if
working
above
floor
level.
16.
Keep
all
panels
and
covers
securely
in
place.
17.
Clamp
work
cable
with
good
metal-to-metal
contact
to
workpiece
or
worktable
as
near
the
weld
as
practical.
a
WARNING
ARC
WELDING
can
be
hazardous.
PROTECT
YOURSELF
AND
OTHERS
FROM
POSSIBLE
SERIOUS
INJURY
OR
DEATH.
KEEP
CHILDREN
AWAY.
PACEMAKER
WEARERS
KEEP
AWAY
UNTIL
CONSULTING
YOUR
DOCTOR.
In
welding,
as
in
most
jobs,
exposure
to
certain
hazards
occurs.
Welding
is
safe
when
precautions
are
taken.
The
safety
information
given
below
is
only
a
summary
of
the
more
complete
safety
information
that
will
be
found
in
the
Safety
Standards
listed
on
the
next
page.
Read
and
follow
all
Safety
Standards.
HAVE
ALL
INSTALLATION,
OPERATION,
MAINTENANCE,
AND
REPAIR
WORK
PERFORMED
ONLY
BY
QUALIFIED
PEOPLE.
ARC
RAYS
can
burn
eyes
and
skin;
ARC
RAYS
NOISE
can
damage
hearing;
FLYING
f/~
SLAG
OR
SPARKS
can
injure
eyes.
2.
Wear
a
welding
helmet
fitted
with
a
proper
shade
of
filter
to
protect
yourface
and
eyes
when
welding
orwatching
(see
ANSI
Arc
rays
from
the
welding
process
produce
intense
Z49.1
and
Z87.1
listed
in
Safety
Standards).
visible
and
invisible
(ultraviolet
and
infrared)
rays
that
3.
Wear
approved
safety
glasses
with
side
shields.
can
bum
eyes
and
skin.
Noise
from
some
processes
can
damage
hearing.
Chipping,
grinding,
and
welds
4.
Use
protective
screens
or
barriers
to
protect
others
from
flash
cooling
throw
off
pieces
of
metal
or
slag.
and
glare;
warn
others
not
to
watch
the
arc.
NOISE
5.
Wear
protective
clothing
made
from
durable,
flame-resistant
1.
Use
approved
ear
plugs
or
ear
muffs
if
noise
level
is
high.
material
(wool
and
leather)
and
foot
protection.
,~
FUMES
AND
GASES
can
be
hazardous
5.
Work
in
a
confined
space
only
if
it
is
well
ventilated,
or
while
to
your
health.
wearing
an
air-supplied
respirator.
Always
have
a
trained
Welding
produces
fumes
and
gases.
Breathing
watchperson
nearby.
Welding
fumes
and
gases
can
displace
these
fumes
and
gases
can
be
hazardous
to
your
air
and
lower
the
oxygen
level
causing
injury
or
death.
Be
sure
health.
the
breathing
air
is
safe.
6.
Do
not
weld
in
locations
near
degreasing,
cleaning,
or
spraying
1.
Keep
your
head
out
of
the
fumes.
Do
not
breathe
the
fumes.
operations.
The
heat
and
rays
of
the
arc
can
react
with
vapors
to
2.
If
inside,
ventilate
the
area
and/or
use
exhaust
at
the
arc
to
form
highly
toxic
and
irritating
gases.
remove
welding
fumes
and
gases.
7.
Do
not
weld
on
coated
metals,
such
as
galvanized,
lead,
or
3.
If
ventilation
is
poor,
use
an
approved
air.supplied
respirator.
cadmium
plated
steel,
unless
the
coating
is
removed
from
the
4.
Read
the
Material
Safety
Data
Sheets
(MSDSs)
and
the
weld
area,
the
area
is
well
ventilated,
and
if
necessary,
while
manufacturers
instruction
for
metals,
consumables,
coatings,
wearing
an
air-supplied
respirator.
The
coatings
and
any
metals
cleaners,
and
degreasers.
containing
these
elements
can
give
off
toxic
fumes
if
welded.
I
CYLINDERS
can
explode
if
damaged.
4.
Never
drape
a
welding
torch
over
a
gas
cylinder.
Shielding
gas
cylinders
contain
gas
under
high
5.
Never
allow
a
welding
electrode
to
touch
any
cylinder.
pressure.
If
damaged,
a
cylinder
can
explode.
Since
6.
Never
weld
on a
pressurized
cylinder
explosion
will
result.
process,
be
sure
to
treat
them
carefully.
fittings
designed
for
the
specific
application;
maintain
them
and
I
gas
cylinders
are
normally
part
of
the
welding
~
Useonlycorrectshieldinggascylinders,
regulators,hoses,and
associated
parts
in
good
condition.
1.
Protect
compressed
gas
cylinders
from
excessive
heat,
8.
Tum
face
away
from
valve
outlet
when
opening
cylinder
valve.
mechanical
shocks,
slag,
open
flames,
sparks,
and
arcs.
9.
Keepprotectivecapinplaceovervalveexceptwhencylindoris
2.
lnstallcylindersinanuprightpositionbysecuringtoastationary
in
use
or
connected
for
use.
support
or
cylinder
rack
to
prevent
falling
or
tipping.
io.
Read
and
follow
instructions
on
compressed
gas
cylinders,
3.
Keep
cylinders
away
from
any
welding
or
other
electrical
associated
equipment,
and
CGA
publication
P-i
listed
in
Safety
circuits.
Standards.
Sri
.1.1
2/94

WELDING
can
cause
fire
or
explosion.
Welding
on
closed
containers,
such
as
tanks,
drums,
or
pipes,
can
cause
them
to
blow
up.
Sparks
can
fly
off
from
the
welding
arc.
The
flying
sparks,
hot
workpiece,
and
hot
equipment
can
cause
fires
and
burns.
Accidental
contact
of
electrode
to
metal
objects
can
cause
sparks,
explosion,
overheating,
or
lire.
Check
and
be
sure
the
area
is
sate
betore
doing
any
welding.
1.
Protect
yourself
and
others
from
flying
sparks
and
hot
metal.
2.
Do
not
weld
where
flying
sparks
can
strike
flammable
material.
3.
Remove
all
flammables
within
35
ft
(10.7
m)
of
the
welding
arc.
If
this
is
not
possible,
tightly
cover
them
with
approved
covers.
4.
Be
alert
that
welding
sparks
and
hot
materials
from
welding
can
easily
go
through
small
cracks
and
openings
to
adjacent
areas.
5.
Watch
for
fire,
and
keep
a
fire
extinguisher
nearby.
6.
Be
aware
that
welding
on
a
ceiling,
floor,
bulkhead,
or
partition
can
cause
fire
on
the
hidden
side.
7.
Do
not
weld
on
closed
containers
such
as
tanks,
drums,
or
pipes,
unless
they
are
properly
prepared
according
to
AWS
F4.1
(see Safety
Standards).
8.
Connect
work
cable
to
the
work
as
close
to
the
welding
area
as
practical
to
prevent welding
current
from
traveling
long,
possibly
unknown
paths
and
causing
electric
shock
and
fire
hazards.
9.
Do
not
use
welder
to
thaw
frozen
pipes.
10.
Remove
stick
electrode
from
holder
or
cut
off
welding
wire
at
contact
tip
when
not
in
use.
11.
Wear
oil-free
protective
garments
such
as
leather
gloves,
heavy
shirt,
cuffless
trousers,
high
shoes,
and
a
cap.
12.
Remove
any
combustibles,
such
as
a
butane
lighter
or
matches,
from
your
person
before
doing
any
welding.
ENGINES
can
be
hazardous.
ENGINE
EXHAUST
GASES
can
kill.
1.
Use
equipment
outside
in
open,
well-ventilated
areas.
Engines
produce
harmful
exhaust
gases.
2.
If
used
in
a
closed
area,
vent
engine
exhaust
outside
and
away
from
any
building
air
intakes.
SPARKS
can
cause
BA11ERY
GASES
TO
EXPLODE;
BATTERY
ACID
can
burn
eyes
and
skin.
3.
Do
not
allow
tools
to
cause
sparks
when
working
on
a
battery.
Do
not
use
welder
to
charge
batteries
or
jump
start
vehicles.
Observe
correct
polarity
(+
and
)
on
batteries.
STEAM
AND
PRESSURIZED
HOT
1.
If
the
engine
is
warm
and
checking
is
needed,
follow
steps
2
COOLANT
can
burn
face,
eyes,
and
and
3.
skin.
2.
Wear
safety
glasses
and
gloves
and
put
a
rag
over
cap.
It
is
best
to
check
coolant
level
when
engine
is
cold
3.
Turn
cap
slightly
and
let
pressure
escape
slowly
before
to
avoid
scalding.
completely
removing
cap.
PRINCIPAL
SAFETY
STANDARDS
Safely
in
Welding
and
Cutting,
ANSI
Standard
Z49.
1,
from
American
Welding
Society,
550
NW.
LeJeune
Rd,
Miami
FL
33126
Safety
and
Health
Standards,
OSHA
29
CFR
1910,
from
Superinten
dent
of
Documents,
U.S.
Government
Printing
Office,
Washington,
D.C.
20402.
Recommended
Safe
Practices
for
the
Preparation
for
Welding
and
Cutting
of
Containers
That
Have
Held
Hazardous
Substances,
Ameri
can
Welding
Society
Standard
AWS
F4.1
,from
American
Welding
So
ciety,
550
NW.
LeJeune
Rd,
Miami,
FL
33126
National
Electrical
Code,
NFPA
Standard
70,
from
National
Fire
Pro
tection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
Safe
Handling
of
Compressed
Gases
in
Cylinders,
CGA
Pamphlet
P-i,
from
Compressed
Gas
Association,
1235
Jefferson
Davis
High
way,
Suite
501,
Arlington,
VA
22202.
Code
for
Safely
in
Welding
and
Cutting,
CSA
Standard
Wi
17.2,
from
Canadian
Standards
Association,
Standards
Sales,
178
Rexdale
Bou
levard,
Rexdale,
Ontario,
Canada
M9W
1
R3.
Safe
Practices
ForOccupation
And
Educational
EyeAndFace
Protec
tion,
ANSI
Standard
Z87.i,
from
American
National
Standards
Institute,
1430
Broadway,
New
York,
NY
10018.
Cutting
And
Welding
Processes,
NFPA
Standard
51
B,
from
National
Fire
Protection
Association,
Batterymarch
Park,
Quincy,
MA
02269.
A~
WARNING
I~
~
ENGINE
FUEL
can
cause
fire
or
3.
Do
not
overfill
tank
allow
room
for
fuel
to
expand.
explosion.
-
Engine
fuel
is
highly
flammable,
4.
Do
not
spill
fuel.
engine.
If
fuel
is
spilled,
clean
up
before
starting
1.
Stop
engine
and
let
it
cool
off
before
checking
or
adding
fuel.
2.
Do
not
add
fuel
while
smoking
or
if
unit
is
near
any
sparks
or
open
flames.
MOVING PARTS
can
cause
injury.
3.
Have
only
qualified
people
remove
guards
or
covers
for
maintenance
and
troubleshooting
as
necessary.
Moving
parts,
such
as
fans,
rotors,
and
belts
can
cut
fingers
and
hands
and
catch loose
clothing,
4.
To
prevent
accidental
starting
during
servicing,
disconnect
negative
()
battery
cable
from
battery.
5.
Keep
hands,
hair,
loose
clothing,
and
tools
away
from
moving
1.
Keep
all
doors,
panels,
covers,
and
guards
closed
and
securely
in
place.
6.
parts.
Reinstall
panels
or
guards
and
close
doors
when
servicing
is
2.
Stop
engine
before
installing
or
connecting
unit.
finished
and
before
starting
engine.
1.
2.
Battenes
contain
acid
and
generate
explosive
iases.
Always
wear
a
face
shield
when
working
on
a
battery.
Stop
engine
before
disconnecting
or
connecting
battery
cables.
4.
5.
Sri
.1.1
2/94

EMF
INFORMATION
TABLE
OF
CONTENTS
SECTION
1
SAFETY
INFORMATION
1
SECTION
2
SPECIFICATIONS
1
SECTION
3INSTALLATION
3-1.
Equipment
Connection
Diagrams
3-2.
Installing
Swivel
Into
Pipe
Post
3-3.
Installing
Control
Box
Onto
Swivel
3-4.
Installing
Boom
And
Reel
Support
3-5.
Installing
Wire
Guide
Extension
3-6.
Wire
Guide
And
Drive
Roll Installation
3-7.
Welding
Gun
Connections
3-8.
Wire
Feed
Motor
And
Gas
Valve
Control
Connections
3-9.
14-Pin
Plug
Connection
3-10.
Shielding
Gas
And
Weld
Cable
Connections
3-11.
Voltage
Sensing
Lead
(Optional)
3-12.
Removing
Safety
Collar
And
Adjusting
Boom
3-13.
Welding
Wire
Installation
3-14.
Motor
Start
Control
3-15.
DIP
Switches
Options
3-16.
Changing
Optional
Digital
Voltage
Control
For
Use
With
A
MILLER
Inverter-Type
Power
Source
3-17.
Threading
Welding
Wire
SECTION
4OPERATION
18
SECTION
5-
MAINTENANCE
&
TROUBLESHOOTING
24
5-1.
Routine
Maintenance
24
5-2.
Replacing
The
Hub
Assembly
25
5-3.
Overload
Protection
25
5-4.
Troubleshooting
26
CM-i
584E
-
3/95
NOTE
~
Considerations
About
Welding
And
The
Effects
Of
Low
Frequency
Electric
And
Magnetic
Fields
The
following
is
a
quotation
from
the
General
Conclusions
Section
of
the
U.S.
Congress,
Office
of
Technology
Assessment,
Biological
Effects
of
Power
Frequency
Electric
&
Magnetic
Fields
Background
Paper~
OTA-BP-E-53
(Washington,
DC:
U.S.
Government
Printing
Office,
May
1989):
.
.
.
there
is
now
a
very
large
volume
of
scientific
findings
based
on
experiments
at
the
cellularlevel
and
from
studies
with
animals
and
people
which
clearly
establish
that
low
frequency
magnetic
fields
can
interact
with,
and
produce
changes
in,
biological
systems.
While
most
of
this
work
is
of
very
high
quality,
the
results
are
complex.
Current
scientific
understanding
does
not
yet
allow
us
to
interpret
the
evidence
in
a
single
coherent
framework.
Even
more
frustrating,
it
does
not
yet
allow
us
to
draw
definite
conclusions
about
questions
of
possible
risk
or
to
offer
clear
science-based
advice
on
strategies
to
minimize
or
avoid
potential
risks.
To
reduce
magnetic
fields
in
the
workplace,
use
the
following
procedures:
1.
Keep
cables
close
together
by
twisting
or
taping
them.
2.
Arrange
cables
to
one
side
and
away
from
the
operator.
3.
Do
not
coil
or
drape
cables
around
the
body.
4.
Keep
welding
power
source
and
cables
as
far
away
as
practical.
5.
Connect
work
clamp
to
workpiece
as
close
to
the
weld
as
possible.
About
Pacemakers:
The
above
procedures
are
among
those
also
normally
recommended
for
pacemaker
wearers.
Consult
your
doctor
for
complete
information.
modiO
i
4/93
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
6
7
7
8
9
9
9
11
12
15
16

SECTION
6
ELECTRICAL
DIAGRAMS
29
SECTION
7
PARTS
LIST
34
Figure
7-1.
Main
Assembly
34
Figure
7-2.
Support,
Hub &
Reel
37
Figure
7-3.
Control
Box
38
Figure
7-4.
Panel,
Front
w/Components
40
Figure
7-5.
Boom
Assembly
42
Figure
7-6.
Drive
Assembly,
Wire
44
Figure
7-7.
Control
Panel
46
Table
7-1.
Drive
Roll
And
Wire
Guide
Kits
49

SECTION
1
-
SAFETY
INFORMATION
Figure
1-1.
Safety
Information
modl.1
2/93
1
Safety
Alert
Symbol
2
Signal
Word
WARNING
means
possible
death
or
serious
injury
can
happen.
CAUTION
means
possible
minor
injury
or
equipment
damage
can
happen.
3
Statement
Of
Hazard
And
Result
4
Safety
Instructions
To
Avoid
Hazard
5
Hazard
Symbol
(If
Available)
6
Safety
Banner
Read
safety
blocks
for
each
sym
bol
shown.
7
NOTE
Special
instructions
for
best
oper
ation
not
related
to
safety.
SECTION
2-
SPECIFICATIONS
Table
2-1.
Wire
Feeder
12
ft
(3.7
m)
Boom
16
ft
(4.9
m)
Boom
Read
all
safety
messages
throughout
this
manual.
Obey
all
safety
messages
to
avoid
injury.
Learn
the
meaning
of
WARNING
and
CAUTION.
1
2
2
;1~II~e~
3
ELECTRIC
SHOCK
can
kill.
Do
not
touch
live
electrical
parts.
Disconnect
input
power
before
4
installing
or
servicing.
a
CAUTION
MOVING
PARTS
can
injure.
Keep
away
from
moving
parts.
Keep
all
panels
and
covers
closed
when
operating.
/
5
READ
SAFETY
BLOCKS
at
start
of
6
Section
3-1
before
proceeding
7~NOTE
-
~
Turn
Off
switch
when
using
high
frequency.
Specification
Description
Type
Of
Input
Power
From
Welding
Power
Source
Maximum
Weld
Circuit
Rating
Welding
Power
Source
Type
Wire
Feed
Speed
Range
Wire
Diameter
Range
Welding
Processes
Input
Power
Cord
Maximum
Height
With
4
ft
(1.2
m)
Post
Weight
Vertical
Lift
Of
Boom
Single-Phase
24
Volts
AC,
10
Amperes,
50/60
Hertz.
(It
115
Volts
AC
Is
The
Only
Power
Available,
Use
Optional
Power
Supply
Adapter
Model
PSA-2.)
100
Volts,
750
Amperes,
100%
Duty
Cycle
Constant
Voltage
(CV)
DC,
With Contactor
50
To
780
ipm
(1.31019.8
mpm);
Standard
Motor
90
To
1400
ipm
(2.3
To
35.6
mpm);
High
Speed
Motor
.023
Thru
1/8
in
(0.6
To
3.2
mm)
Gas
Metal
Arc
(GMAW)
And
Flux
Cored
Arc
Welding
(FCAW)
lOft(3.1
m)
17
ft
(5.2
m)
Net:
207
lb
(94
kg)
Ship:
318
lb
(144
kg)
Honzontal
To
60
Above
Horizontal
21
ft
(6.4
m)
Net:
280
lb
(127
kg)
Ship:
411
lb
(186
kg)
Honzontal
To
60
Above
Horizontal
OM-1
584
Page
1

SECTION
3-INSTALLATION
3-1.
Equipment
Connection
Diagrams
A~
WARNING
CYLINDERS
can
explode
if
damaged.
Keep
cylinders
away
from
welding
and
other
electrical
circuits.
Never
touch
cylinder
with
welding
electrode.
Always
secure
cylinder
to
running
gear,
wall,
or
other
stationary
support.
HOT
SURFACES
can
burn
skin.
Allow
gun
to
cool
before
touching.
ELECTRIC
SHOCK
can
kill.
Do
not
touch
live
electrical
parts.
Turn
Off
wire
feederand
welding
powersource,
and
disconnect
input
power
before
making
connections.
Stop
engine
on
welding
generator.
The
welding
wire,
drive
rolls,
drive
assembly,
and
all
metal
parts
touching
the
welding
wire
are
electrically
live
when
welding
or
feeding
wire
using
gun
trigger.
Have
only
qualified
persons
install
this
unit.
wfwarn9.1
2/93
2
13
4
5-
1
Welding
Power
Source
2
Remote
14
Connection
3
Negative
()
Weld
Output
Cable
4
Positive
(+)
Weld
Output
Cable
5
Workpiece
6
Voltage
Sensing
Clamp
7
Weld
Control
8
Boom
9
Gun
10
Swivel
11
Pipe
Post
And
Base
12
Gas
Hose
13
Gas
Supply
12
ST-153
176-A
10
Figure
3-1
.
Typical
System
Connections
OM-1584
Page
2

3-2.
Installing
Swivel
Into
Pipe
Post
____
a
WARNING
1*
RELEASE
OF
SPRING
PRESSURE
WITHOUT
BOOM
ATTACHED
can
cause
serious
personal
injury.
Do
not
remove
safety
collar
until
instructed
to
do
so.
FALLING
BOOM
can
cause
serious
personal
injury
and
equipment
damage.
Securely
mount
pipe
post
to
base
that
can
support
weight
of
unit
with
boom
in
horizontal
position.
Use
proper
equipment
for
lifting
swivel
and
boom
into
place.
4
1
Swingpak
Base
or
CBC
Cart
2
Pipe
Post
With
Base
3
Steel
Bolt
Secure
as
shown
using
as
a
mini
mum
1/2
in
diameter
SAE
grade
5
steel
bolts.
4
Swivel
Assembly
Insert
into
pipe
post.
Lubricate
swivel.
5
Safety
Collar
Do
not
remove
until
instructed
to.
Tools
Needed:
~
3/4in
ST-152
382
Figure
3-2.
Swivel
Installation
3-3.
Installing
Control
Box
Onto
Swivel
2
4
Tools
Needed:
3
c~zJ==n
3/8
in
1
Weld
Control
2
Bracket
3
Screws
Bracket
and
screws
are
installed
onto
bottom
of
control
at
factory.
4
Swivel
Loosen
screws.
Place
control
on
swivel
and
slide
forward.
Tighten
screws.
ST-153
174
Figure
3-3.
Control
Box
Installation
OM-1
584
Page
3

3-4.
Installing
Boom
And
Reel
Support
3-5.
Installing
Wire
Guide
Extension
READ
SAFETY
BLOCKS
at
start
of
Section
3-2
before
proceeding.
1
Swivel
Plates
2
Yoke
Remove
hardware
from
swivel
plates
and
yoke.
3
Boom
Set
boom
into
swivel
as
shown.
4
Yoke
Pin
Install
pin
through
yoke.
Install
cot
ter
pin
and
spread
ends.
5
Bolt
7
Install
bolt,
tighten
hardware,
and
back
bolt
off
one
half
turn.
6
Locking
Knob
Install
locking
knob
but
do
not
tight
en.
7
Reel
Support
Install
reel
support.
Ref.
ST-i
53
170
Tools
Needed:
~
3/4,3/8
in
Figure
3-4.
Boom
Installation
4
Tools
Needed:
3/8
in
1
Wire
Guide
Fitting
2
Bolt
3
Moriocoil
Liner
4
Wire
Guide
Extension
Tighten
bolt
to
secure
liner
in
wire
guide
fitting.
Do
not
overtighten
bolt
and
crush
liner.
Repeat
procedure
for
opposite
side.
ST-152
383
Figure
3-5.
Wire
Guide
Extension
Installation
OM-1
584
Page
4

3-6.
Wire
Guide
And
Drive
Roll
Installation
READ
SAFETY
BLOCKS
at
start
of
Section
3-1
before
proceeding.
B.
Drive
Roll
Installation
Figure
3-6.
Wire
Guide
Installation
Figure
3-7.
Drive
Roll
Installation
A.
Wire
Guide
Installation
When
changing
wire
size
or
type,
check
guide
size.
See
Table
7-1.
1
Drive
Rolls
Remove
drive
rolls
before
install
ing
wire
guides
(see
Figure
3-7).
2
Wire
Guide
Securing
Screws
Loosen
wire
guide
screws.
3
InletWireGuide
4
Intermediate
Wire
Guide
Insert
intermediate
guide
until
flange
on
guide
rests
against
cast
ing,
and
secure
with
guide
screw.
Install
drive
rolls
(see
Figure
3-7).
Repeat
procedure
for
opposite
side
of
wire
feeder.
ST-i
37
391-F/
ST-142
597-A
Tools
Needed:
1
When
changing
wire
size
or
type,
check
drive
roll
size.
See
Table
7-1
-
1
Spring
Shaft
Carrier
Close
spring
shaft
carrier.
2
Drive
Roll
Nut
3
Drive
Roll
Carrier
Turn
all
nuts
one
click
until
lobes
of
nut
line
up
with
lobes
of
drive
roll
carrier.
Open
spring
shaft
carrier.
4
Drive
Roll
Slide
drive
rolls
onto
drive
roll
carri
ers.
Close
spring
shaft
carrier.
Turn
nut
one
click.
5
Drive
Assembly
Cover
Close
cover.
Repeat
procedure
for
opposite
side
of
wire
feeder.
ST-142
597-A
2
3
OM-1
584
Page
5

3-7.
Welding
Gun
Connections
wfwarnl.1
2/93
1
Drive
Assembly
Cover
2
Gun
Securing
Knob
3
Gun
Connector
Loosen
securing
knob.
Insert
gun
connector,
and
position
as
close
as
possible
to
drive
rolls
without
touching.
lighten
knob.
4
Gun
Trigger
Plug
5
Gun
Trigger
Receptacle
Insert
plug
into
free-hanging
re
ceptacle
and
tighten
threaded
col
lar.
6
Trigger
Cord
7
Trigger
Plug
8
Weld
Control
Trigger
Recep
tacle
a
WARNING
ELECTRIC
SHOCK
can
kill.
Do
not
touch
live
electrical
parts.
Turn
Oft
wire
feeder
and
welding
power
source,
and
disconnect
input
power
before
inspecting
or
installing.
2
4
4
Insert
plug
into
receptacle
and
tighten
threaded
collar.
Repeat
procedure
forgun
on
oppo
site
drive
assembly.
Figure
3-8.
Gun
And
Trigger
Lead
Connections
ST-i
53
072/
Ref.
ST-153
172
/
Ref.
ST-142
598-C
OM-1
584
Page
6

3-8.
Wire
Feed
Motor
And
Gas
Valve
Control
Connections
3-9.
14-Pin
Plug
Connection
Figure
3-10.
14-Pin
Plug
With
Pin
Information
1
Wire
Feed
Motor
And
Gas
Valve
Control
Receptacle
2
Plug
From
Boom
3
Cord
From
Boom
Insert
plug
from
boom
cord
into
re
ceptacle
on
rear
of
control,
and
tighten
threaded
collar.
Repeat
procedure
for
opposite
side
of
weld
control.
Ref.
ST-142
598-C
Figure
3-9.
Boom
Connections
2
1
Plug
PLG1O
2
Keyway
3
Threaded
Collar
Connect
14-pin
plug
PLG1O
to
matching
receptacle
on
welding
powersource
as
follows:
align
key.
way,
insert
plug,
and
tighten
threaded
collar.
Pin
Information:
A,
B
Contact
closure
completes
the
24
volts
ac
contactor
control
circuit.
C
Command
signal;
+10
volts
dc.
D
Control
circuit
common.
E
Remote
power
source
voltage
command
signal
from
feeder
(potentiometerwiper
oro-1
0
volts
dc
source);
0
to
+10
volts
dc.
F
Current
feedback;
0-10
volts
dc,
1
volt
per
100
amperes.
G
Circuit
common
for
24
volts
ac
circuit.
H
Voltage
feedback;
0-10
volts
dc,
1
volt
per
10
arc
volts.
The
remaining
pins
in
the
plug
are
not
used
by
the
feeder.
Ref.
ST-143
260-A
/
Ref.
S-0512
OM-1584
Page
7

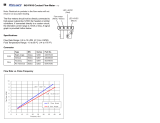
3-10.
Shielding
Gas
And
Weld
Cable
Connections
a
WARNING
CYLINDERS
can
explode
if
damaged.
Keep
cylinders
away
from
welding
and
other
electrical
circuits.
Never
touch
cylinder
with
welding
electrode.
Always
secure
cylinder
to
running
gear,
wall,
or
other
stationary
support.
ELECTRIC
SHOCK
can
kill.
Do
not
touch
live
electrical
parts.
Turn
Oft
wire
feederand
welding
power
source,
and
disconnect
input
power
before
inspecting
or
installing.
BUILDUP
OF
SHIELDING
GAS
can
harm
health
or
kill.
Shut
off
shielding
gas
supply
when
not
in
use.
The
weld
cables
and
shielding
gas
hoses
ex
tend
10
ft
(3m)
from
the
boom.
If
the
welding
power
source
or
gas
supply
are
further
from
the
boom,
extend
cables
and
hoses
as
follows:
1
Weld
Cables
2
Insulated
Sleeving
Bolt
together
weld
cables
from
welding
pow
er
source
and
boom.
Use
electrical
tape
and
insulated
sleeving
to
cover
connection.
3
Shielding
Gas
Extension
Hose
4
Boom
Shielding
Gas
Hose(s)
Connect
boom
shielding
gas
hoses
to
gas
supplies
or
extend
hoses.
The
hoses
from
the
boom
have
5/8-18
right-hand
threads.
5
Shielding
Gas
Y
Adapter
Connect
single
end
fitting
of
V
adapterto
gas
supply,
and
connect
boom
shielding
gas
hoses
to
fittings
on
V
end
of
adapter.
The
hoses
from
the
boom
have
5/8-18
right-hand
threads.
Figure
3-11.
Shielding
Gas
And
Weld
Cable
Connections
wam4.1
2/93
Tools
Needed:
Z~
5/8
in
Ref.
ST-153
175-B
OR
OM-1
584
Page
8

3-11.
Voltage
Sensing
Lead
(Optional)
A
35
ft
(10.6
m)
voltage
sensing
lead
is
provided
with
several
options.
Connect
voltage
sensing
lead
to
workpiece
(see
Figure
3-1).
3-12.
Removing
Safety
Collar
And
Adjusting
Boom
4~
WARNING
RELEASE
OF
SPRING
PRESSURE
FALLING
BOOM
can
cause
serious
WITHOUT
BOOM
ATTACHED
can
cause
serious
personal
injury.
personal
in
Adjustment
jury
and
equipment
damage.
rod
must
be
threaded
fully
through
Do
not
remove
safety
collar
until
instructed
to
do
so.
yoke.
1
Locking
Knob
Tighten
knob
to
prevent
boom
movement.
Loosen
knob
to
allow
boom
movement.
Change
knob
position
to
limit
upward
movement.
Tools
Needed:
O
\~,/
~
~1Jfr~J
~
LI~
~
Increasing
Spring
Pressure
ForA
Heavy
Gun
\~,1
1.J
~
~j1J1~
~
1
~
2
Decreasing
Spring
Pressure
ForA
Light
Gun
Pull
boom
down
slightly
and
re
move
safety
collar.
Boom
should
balance
in
any
position
from
hori
zontal
to
60
degrees
above
hori
zontal.
If
necessary,
adjust
boom
as
follows:
2
Threaded
Rod
3
Jam
Nut
Loosen
jam
nut
and
turn
threaded
rod
until
boom
balances.
Tighten
jam
nut.
Be
sure
several
full
threads
are
through
yoke
to
pre
vent
boom
falling.
4
Yoke
.
Retain
safety
collar
for
use
in
dis
1-1/8
in
assembling
or
moving
boom.
Ref.
ST-142
599-B
/
Ref
ST-152
380-A
Figure
3-12.
Boom
Adjustments
3-13.
Welding
Wire
Installation
A.
Installation
Of
Spool-Type
Wire
3
1
Retaining
Ring
2
Wire
Spool
3
Hub
Remove
retaining
nng
and
slide
spool
unto
hub.
4
Hub
Pin
Turn
spool
until
hub
pin
fits
in
spool.
Reinstall
retaining
ring.
Repeat
procedure
for
installing
spool-type
wire
on
opposite
side
of
wire
feeder.
E
ST-153
171
Figure
3-13.
Installation
Of
Spool-Type
Wire
OM-1
584
Page
9

B.
Installation
Of
Optional
Wire
Reel
And
Reel
Type
Wire
C.
Adjusting
Hub
Tension
Figure
3-14.
Installation
Of
Optional
Wire
Reel
And
Reel
Type
Wire
5
-4
1
Retaining
Ring
2
Spanner
Nut
3
Lock
4
Wire
Retainer
5
Wire
Reel
6
Hub
7
Hub
Pin
8 Reel
Support
Remove
retaining
ring.
Pull
lock
and
turn.
Remove
spanner
nut,
wire
retainer,
and
wire
reel
from
hub.
Lay
wire
reel
assembly
on
flat
sur
face,
and
install
wire
as
shown.
Tighten
spanner
nut
until
lock
is
in
position
over
hole
in
wire
retainer.
Pull
lock
and
turn
to
insert
locking
pin
into
wire
retainer.
Slide
wire
reel
assembly
onto
hub,
and
turn
assembly
until
hub
pin
is
seated
in
hole
in
reel.
Reinstall
re
taining
ring.
ST-143
478-A
/
ST-i
52463
__
4
S
/
Wire
Installation
Turn
Off
wire
feeder
and
welding
power
source.
1
Hex
Nut
2
Spool
Grasp
spool
in
one
hand
and
turn
while
using
a
wrench
to
adjust
hex
nut.
When
a
slight
force
is
needed
to
turn
spool,
tension
is
set.
Repeat
procedure
to
adjust
hub
tension
on
opposite
side
of
wire
feeder.
Tools
Needed:
I~
5/8in
ST-153
173
2
Figure
3-15.
Adjusting
Hub
Tension
OM-1
584
Page
10
/