ESAB PSF 315 R User manual
- Category
- Welding System
- Type
- User manual
This manual is also suitable for

GB
Valid for serial no. 217, 6340457 342 101 GB 060822
PSFt 315 M
PSFt 315 R
Instruction manual

-- 2 --
TOCe
Rights reserved to alter specifications without notice.
1 DIRECTIVE 3........................................................
2SAFETY 3...........................................................
3 INTRODUCTION 4...................................................
4 TECHNICAL DATA 5.................................................
5 CONSUMABLES 5...................................................
5.1 Changing wire liner , replacing electrode conductors 5............................
5.2 Interchangeable connectors 6.................................................
5.3 Compressed air cleaning 6...................................................
5.4 Contact tip 7................................................................
5.5 Wire liners 7................................................................
5.6 Gas nozzles 7..............................................................
5.7 Gas protection 7............................................................
6 OPERATION 8.......................................................
7 MAINTENANCE 8....................................................
8 SPARE PARTS AND ACCESSORIES 8.................................
DIMENSION DRAWING 9................................................
ORDERING NUMBER 10.................................................
WEAR PARTS 12........................................................
ACCESSORIES 13.......................................................

-- 3 --
bg14e
1DIRECTIVE
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
ESAB Welding Equipment AB, S--695 81 Laxå, Sweden, gives its unreserved guarantee that welding
gun PSF 315 M / 315 R from serial number 217 complies with standard EN 60974--7, in accordance
with the requirements of directive (73/23/EEC) and addendum (93/68/EEC).
-- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --------
Henry Selenius
Vice President
ESAB Welding Equipment AB
695 81 LAXÅ
SWEDEN Tel: + 46 584 81000 Fax: + 46 584 411924
Laxå 2002--04--25
2SAFETY
WARNING
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE INSTALLING OR OPERATING.
ARC WELDING AND CUTTING CAN BE INJURIOUS TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS. TAKE PRECAU-
TIONS WHEN WELDING. ASK FOR YOUR EMPLOYER’S SAFETY PRACTICES WHICH SHOULD BE
BASED ON MANUFACTURERS’ HAZARD DATA.
ELECTRIC SHOCK -- Can kill
S Install and earth the welding unit in accordance with applicable standards.
S Do not touch live electrical parts or electrodes with bare skin, wet gloves or wet clothing.
S Insulate yourself from earth and the workpiece.
S Ensure your working stance is safe.
FUMES AND GASES -- Can be dangerous to health
S Keep your head out of the fumes.
S Use ventilation, extraction at the arc, or both, to take fumes and gases away from your breathing zone
and the general area.
ARC RAYS -- Can injure eyes and burn skin.
S Protect y our eyes and body. Use the correct welding screen and filter lens and wear protective
clothing.
S Protect bystanders with suitable screens or curtains.
FIRE HAZARD
S Sparks (spatter) can cause fire. Make sure therefore that there are no inflammable materials nearby.
NOISE -- Excessive noise can damage hearing
S Protect y our ears. Use earmuffs or other hearing protection.
S Warn bystanders of the risk.
MALFUNCTION -- Call for expert assistance in the event of malfunction.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS!
ESAB can provide you with all necessary welding protection an d accessories.
GB

-- 4 --
bg14e
Users of ESAB welding equipment have the ultimate responsibility for ensuring that anyone who
works on or near the equipment observes all the relevant safety precautions. Safety precautions
must meet the requirements that apply to this type of welding equipment. The following recommen-
dations should be observed in addition to the standard regulations that apply to the workplace.
All work must be carried out by trained personnel well--acquainted with the operation of the welding
equipment. Incorrect operation of the equipment may lead to hazardous situations which can result
in injury to the operator and damage to the equipment.
1. Anyone who uses the welding equipment must be familiar with:
S its operation
S location of emergency stops
S its function
S relevant safety precautions
S welding
2. The operator must ensure that:
S no unauthorized person is stationed within the working area of the equipment when it is
started up.
S no--one is unprotected when the arc is struck
3. The workplace must:
S be suitable for the purpose
S be free from drafts
4. Personal safety equipment
S Always wear recommended personal safety equipment, such as safety glasses, flame--proof
clothing, safety gloves.
S Do not wear loose--fitting items, such as scarves, bracelets, rings, etc., which could become
trapped or cause burns.
5. General precautions
S Make sure the return cable is connected securely.
S Work on high voltage equipment may only be carried out by a qualified electrician.
S Appropriate fire extinquishing equipment must be clearly marked and close at hand.
S Lubrication and maintenance must not be carried out on the equipment during operation.
3 INTRODUCTION
The PSFt 315M / 315 R is an self--cooled welding gun. The welding gun is
developed for use in robot applications or mechanised welding.
A range of accessories including welding tips, swan necks and contact nozzles are
also available.
Details of ESAB’s welding torches accessories can be found on page 13.
GB

-- 5 --
bg14e
4 TECHNICAL DATA
Welding gun PSF 315 M / 315 R
Permitted load at 60% intermittence
CO
2
MIX
315 A
285 A
Permitted load at 100% intermittence
CO
2
MIX
200 A
170 A
Electrode dimensions 0.8 -- 1.2 mm
Rec. gas flow l/min 10 -- 20 l/min
Weight, hose length
1.5 m
2.2 m
3m
2.0 kg
2.6 kg
3.2 kg
Duty cycle
The duty cycle refers to the time as a percentage of a ten--minute period that you can weld at a cer-
tain load without overloading.
5 CONSUMABLES
5.1 Changing wire liner, replacing electrode conductors
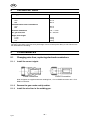
5.1.1 Install the correct nipple
ESAB Connection EURO Connection
Note! 2 nipples are supplied with each welding liner, 1 for an ESAB connection and 1 for a
EURO connection.
5.1.2 Remove the gas nozzle and tip adator.
5.1.3 Install the wire liner in the welding gun.
GB

-- 6 --
bg14e
5.1.4 Cut the wire liner to the correct length.
When cutting, the welding gun should be extended with the wire liner fully inserted in
the rear connection.
Cut the wire liner so that it protrudes by “X” in accordance with the table below.
Welding gun
Length
Adapter
Measu-
rement
X
Helix
Measu-
rement
X
PSF 315 M / 315 R
1.5 m 0368 145 001 27 mm 0368 683 001 22 mm
PSF 315 M / 315 R 2.2 m 0368 145 001 28 mm 0368 683 001 23 mm
PSF 315 M / 315 R 3.0 m 0368 145 001
31 mm 0368 683 001 26 mm
Sharp edges are not allowed on the inside of the wire liner guide after cutting.
5.1.5 Reinstall th e tip adaptor an d gas n o zzle.
5.1.6 Install the welding gun on the machine.
a) Turn the connecting piece clockwise when you encounter resistance
b) The welding rod goes in
5.2 Interchangeable connectors
Connectors are m anufactured with the same measurements between the mount and
the tip of the contact tip and are therefore directly interchangeable.
For dimensions and guaranteed tolerances, see diagram on page 9.
5.3 Compressed air cleaning
The connector has a connection and ducts for compressed air cleaning of the gas
nozzle.
GB

-- 7 --
bg14e
5.4 Contact tip
Contact tips are selected according to e lectrode diameter, type of shielding gas and
rating of the welding current being used. See table on page 13.
The contact tips are initially selected with the guidance of the CO
2
table. If seizing
occurs in the event of high welding data with Argon or mixed gas, select on the basis
of the MIX, AR table.
For HELIX, the table applies regardless of shielding gas type. HELIX contact tips
must be combined with a special tip adaptor, see spare parts list. Note that the item
number for HELIX includes 2 contact tips + 1 locking nut for installation.
5.5 Wire liners
In order to achieve good welding rod feed, the wire liner should be selected in
accordance with the table o n page 14. A PTFE--based wire liner produces less
friction and is kinder to the electrode, but normally has a shorter service life than a
steel spiral. It is suitable for all types of electrode, except for the majority of core wire
types thicker than 1.2 mm.
Steel spirals can be used for all except for stainless steel and aluminium electrodes.
For changing electrode guides – see the enclosed instructions.
Note! All welding guns are supplied with steel spirals for welding liner ∅1.0.
5.6 Gas nozzles
If you want a gas nozzle with a smaller opening diameter, this is available as an
accessory for each gun. See the spare parts list. Note that it is also possible to
exchange the connector type.
IMPORTANT! There is a spatter guard in the gas nozzle. T his must be in place to
prevent welding spatter penetrating the connector.
For good function, the gas nozzle must always be screwed in as far as it will go.
5.7 Gas protection
Several factors combine to provide good gas protection. T he most important of these
are:
1. Choice of shielding gas. -- Mixed gas and argon require a greater flow than
carbon dioxide
2. Set flow quantity. -- See technical data (should be measured at the gas nozzle).
3. Set welding current. -- High current requires a greater gas flow.
4. Position of the welding joint. -- A vertical position requires a greater gas flow.
5. Type of welding joint. -- An outer corner joint requires a greater gas flow than a
butt joint. A fillet weld joint requir e s a correspondingly sm aller gas flow.
6. The angle of the welding gun against the workpiece -- below 45° entails a risk of
poor gas protection.
GB

-- 8 --
bg14e
6 OPERATION
General safety regulations for the handling of the equipment can be found on
page 3. Read through before you start using the equipment!
The welding gun contains a lead for starting point searching. T his is connected to the
ring--shaped adapter plug in the welding gun’s feeder end. The connection lead from
starting point searching ( e.g. Smartac) is connected to the corresponding flat--pin
connection in the feeder’s terminal block.
7 MAINTENANCE
Note!
All guarantee undertakings from the supplier cease to apply if the customer himself
attempts any work in the product during the guarantee period in order to rectify any
faults.
Regular servicing reduces unnecessary and expensive operational stoppages.
1. Welding spray in the gas nozzle impairs the gas protection and increases the risk
of flash--over.
--Clean regularly and use a moderate amount of welding paste or welding spray.
2. The spray guard in the gas nozzle should be replaced when its front end has
become thin.
3. Every time the electrode bobbin is replaced, the welding hose should be
disconnected from the feeder and blown clean with compressed air.
4. The end of the electrode may not have any sharp edges when it is inserted into
the welding rod guide. This is particularly important in the case of PTFE--based
welding rod guides.
8 SPARE PARTS AND ACCESSORIES
PSF 315 M / 315 R is designed and tested in accordance with the international and Eu-
ropean standards IEC/EN 60974--7 and EN 60974--7. It is the obligation of the service
unit which has carried out the service or repair work to make sure that the product still
conforms to the said standard.
Spare parts may be ordered through your nearest ESAB dealer, see the last page of
this publication. When ordering, please state product type, serial number, designa-
tion and spare part number in accordance with the spare parts list.
This facilitates shipment and ensures correct delivery.
GB

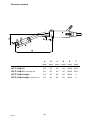
Dimension drawing
-- 9 --
bg14dim
A
(mm)
B
(mm)
C
(mm)
D
(mm)
E
(mm)
F
(mm)
PSFt 315M, 25˚ 3.5
20 22 94 196.3 63.4
PSFt 315M, 25˚ extended 100 3.5 20 22 94 296.3 63.4
PSFt 315M, straight 3.5
20 22 94 209.3 0
PSFt 315M, straight,
extended 100 3.5 20 22 94 309.3 0

We
l
d
i
ng gun
P
S
F
t 31
5
M
,
P
S
F
t 31
5
R
Edition 060822
Ordering number
-- 1 0 --
bg14or
Ordering numbers for Welding gun PSFt 315 M, PSFt 315 R
0367 233 894 PSFt 315 M / 315 R 1.5 m, 25˚
EURO Connection
0367 233 896 PSFt 315 M / 315 R 1.5 m, straight
EURO Connection
0367 233 898 PSFt 315 M / 315 R 3.0 m, 25˚
EURO Connection
0367 233 900 PSFt 315 M / 315 R 2.2 m, 25˚
EURO Connection
0367 233 901 PSFt 315 M / 315 R 2.2 m, straight
EURO Connection
0367 233 905 PSFt 315 M / 315 R 3.0 m, straight
EURO Connection

We
l
d
i
ng gun
P
S
F
t 31
5
M
,
P
S
F
t 31
5
R
Edition 060822
-- 1 1 --
bg14or
Ordering numbers for other lengths
When ordering please quote:
-- N e c k t y p e
-- Wire diameter
-- Cable assembly length
These ordering numbers apply only to standard torch variations. Other variations will be issued with
part numbers on receipt of order. Refer to order confirmation.
Order form for torch with extended swan neck or custom specific length 0367 233 90x
PSF 315M / R Item no 0367 233 xxx 1.5 m 2.2 m
3.0 m
Free
length*
X (mm)
Swan neck 25˚ (0368 155 890) 894 900 898 196.3
Swan neck straight (0368 155 894) 896 901 905 209.3
Swan neck 25˚ ext. 100 (0368 155 892) 296.3
Swan neck straight, ext. 100 (0368 155 896) 309.3
Length Y (± 20 mm) 1300 mm 2040 mm 3000 mm
* Specify length Y = in the correct column (swan neck)

We
l
d
i
ng gun
P
S
F
t 31
5
M
,
P
S
F
t 31
5
R
Edition 060822
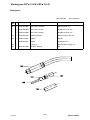
Wear p arts
-- 1 2 --
bg14wear
(W) = wear part (A) = accessory
Item
Qty Ordering no. Denomination Notes
102 1 0459 073 882 Gas nozzle, standard (W) D/d 20/16 mm
-- 1 0366 946 882 Gas nozzle, conical (A) (W) D/d 17/13 mm
-- 1 0468 194 882 Gas nozzle, straight (A) (W) D/d 18/13 mm
104 1 0366 396 003 Spatter protection (W) Included in item 102
105 1 0368 145 001 Adapter (W) M6
-- 0368 683 001 Adapter (A) HELIX, M7
106 1 Contact tip (W) See table on page 13
107 1 0366 397 002 Insulation bushing (W)

Edition 060822
We
l
d
i
ng gun
P
S
F
t 31
5
M
,
P
S
F
t 31
5
R
Accessories
-- 1 3 --
bg14a11a
NO TAG
Contact tip
The bore dimension of the contact tips is to be selected with regard to wire diameter,
type of shielding gas and actual intensity of the current -- we refer to the table below.
Standard M6 ESAB Standard M6 ABB
To start with, choose a contact tip as specified in the shortarc--table (CO
2
). Should
binding occur with high parameters when using Argon or gas mixture, choose contact
tip from the sprayarc table.
Welding wire Ordering No Marked Ordering No
Short arc
CO
2
Spray arc
MIX
Contact-
tip
hole Ø
M6x27ESAB
Wire
Ø
M6x30ABB
Contact
tip
hole Ø
(0.8) 0.6 0.9 0468 500 002 W0.8 ESAB 0.8 0153 500 202 1.0
0.8 (0.8) 1.0 0468 500 003 W0.8 ESAB 0.9 0153 500 203 1.1
0.9 0.8 1.1 0468 500 004 W0.9 ESAB 1.0 0153 500 204* 1.2
1.0 0.9 1.2 0468 500 005 W1.0 ESAB -- -- 1.2
1.1 (1.0) 1.3 0468 500 006 W1.2 ESAB -- -- 1.3
1.2 1.0--1.1 1.5 0468 500 007 W1.2 ESAB -- -- 1.5
Table 1
*)
Is delivered as standard
Helix M7
Helix M7 contact tip must be combined with special tip adapter. See spare parts list.
Ordering number Marked
M7
HELIX
0368 313 881 W0.8 --
0368 313 882 W0.9 --
0368 313 883 W1.0 --
0368 313 884 W1.2 --
Table 2

Edition 060822
We
l
d
i
ng gun
P
S
F
t 31
5
M
,
P
S
F
t 31
5
R
-- 1 4 --
bg14a11a
Wire liner
NO TAG
Welding wire *)
PTFE conduit incl.
wear insert (steel)
Wear insert separate
3m Steel PTFE (Al)
0.8 mm 0366 550 882 0366 545 880 0368 742 880
0.9--1.0 mm 0366 550 884 0366 545 881 0368 742 880
1.2 mm 0366 550 886 0366 545 882 0368 742 881
*) The wire guide aperture = 1.5 x wire diameter. The wire guide is marked with the max. wire diameter (stamped on the nipple).
Table 3
W
l
d
i
i
*
)
Steel spiral PTFE ceramic liner
Welding wire
*
)
3m 3 m **)
0.6--0.8 mm 0366 549 882 --
0.9--1.0 mm 0366 549 884 0457 969 882
1.2 mm 0366 549 886 0457 969 882
*) The wire guide aperture = 1.5 x wire diameter. The wire guide is marked with the max. wire diameter (stamped on the nipple).
**) To be cut to gun length. No wear insert needed.
Table 4
Gasflow meter
To measure the current gas flow a gasflow meter is available as option, ordering
number 0155 716 880.

-- 1 5 --
page

ESAB AB
SE--695 81 LAXÅ
SWEDEN
Phone +46 584 81 000
www.esab.co m
060517
ESAB subsidiaries and representative offices
Europe
AUSTRIA
ESAB Ges.m.b.H
Vienna--Liesing
Tel: +43 1 888 25 11
Fax: +43 1 888 25 11 85
BELGIUM
S.A. ESAB N.V.
Brussels
Tel: +32 2 745 11 00
Fax: +32 2 745 11 28
THE CZECH REPUBLIC
ESAB VAMBERK s.r.o.
Prague
Tel: +420 2 819 40 885
Fax: +420 2 819 40 120
DENMARK
Aktieselskabet ESAB
Herlev
Tel:+4536300111
Fax:+4536304003
FINLAND
ESAB Oy
Helsinki
Tel: +358 9 547 761
Fax: +358 9 547 77 71
FRANCE
ESAB France S.A.
Cergy Pontoise
Tel:+33130755500
Fax:+33130755524
GERMANY
ESAB GmbH
Solingen
Tel: +49 212 298 0
Fax: +49 212 298 218
GREAT BRITAIN
ESAB Group (UK) Ltd
Waltham Cross
Tel: +44 1992 76 85 15
Fax: +44 1992 71 58 03
ESAB Automation Ltd
Andover
Tel: +44 1264 33 22 33
Fax: +44 1264 33 20 74
HUNGARY
ESAB Kft
Budapest
Tel:+3612044182
Fax:+3612044186
ITALY
ESAB Saldatura S.p.A.
Mesero (Mi)
Tel:+3902979681
Fax:+390297289181
THE NETHERLANDS
ESAB Nederland B.V.
Utrecht
Tel: +31 30 2485 377
Fax: +31 30 2485 260
NORWAY
AS ESAB
Larvik
Tel:+4733121000
Fax:+4733115203
POLAND
ESAB Sp.zo.o.
Katowice
Tel: +48 32 351 11 00
Fax: +48 32 351 11 20
PORTUGAL
ESAB Lda
Lisbon
Tel: +351 8 310 960
Fax: +351 1 859 1277
SLOVAKIA
ESAB Slovakia s.r.o.
Bratislava
Tel:+421744882426
Fax:+421744888741
SPAIN
ESAB Ibérica S.A.
Alcalá de Henares (MADRID)
Tel: +34 91 878 3600
Fax: +34 91 802 3461
SWEDEN
ESAB Sverige AB
Gothenburg
Tel:+4631509500
Fax:+4631509222
ESAB international AB
Gothenburg
Tel:+4631509000
Fax:+4631509360
SWITZERLAND
ESAB AG
Dietikon
Tel: +41 1 741 25 25
Fax: +41 1 740 30 55
North and South America
ARGENTINA
CONARCO
Buenos Aires
Tel: +54 11 4 753 4039
Fax: +54 11 4 753 6313
BRAZIL
ESAB S.A.
Contagem--MG
Tel: +55 31 2191 4333
Fax: +55 31 2191 4440
CANADA
ESAB Group Canada Inc.
Missisauga, Ontario
Tel: +1 905 670 02 20
Fax: +1 905 670 48 79
MEXICO
ESAB Mexico S.A.
Monterrey
Tel: +52 8 350 5959
Fax: +52 8 350 7554
USA
ESAB Welding & Cutting Products
Florence, SC
Tel: +1 843 669 44 11
Fax: +1 843 664 57 48
Asia/Pacific
CHINA
Shanghai ESAB A/P
Shanghai
Tel: +86 21 5308 9922
Fax: +86 21 6566 6622
INDIA
ESAB India Ltd
Calcutta
Tel: +91 33 478 45 17
Fax: +91 33 468 18 80
INDONESIA
P.T. ESABindo Pratama
Jakarta
Tel: +62 21 460 0188
Fax: +62 21 461 2929
JAPAN
ESAB Japan
Tokyo
Tel: +81 3 5296 7371
Fax:+81352968080
MALAYSIA
ESAB (Malaysia) Snd Bhd
Selangor
Tel: +60 3 8027 9869
Fax:+60380274754
SINGAPORE
ESAB Asia/Pacific Pte Ltd
Singapore
Tel:+6568614322
Fax: +65 6861 31 95
SOUTH KOREA
ESAB SeAH Corporation
Kyungnam
Tel: +82 55 269 8170
Fax: +82 55 289 8864
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES
ESAB Middle East FZE
Dubai
Tel: +971 4 887 21 11
Fax: +971 4 887 22 63
Representative offices
BULGARIA
ESAB Representative Office
Sofia
Tel/Fax: +359 2 974 42 88
EGYPT
ESAB Egypt
Dokki--Cairo
Tel: +20 2 390 96 69
Fax: +20 2 393 32 13
ROMANIA
ESAB Representative Office
Bucharest
Tel/Fax: +40 1 322 36 74
RUSSIA
LLC ESAB
Moscow
Tel: +7 095 543 9281
Fax: +7 095 543 9280
LLC ESAB
St Petersburg
Tel: +7 812 336 7080
Fax: +7 812 336 7060
Distributors
For addresses and phone
numbers to our distributors in
other countries, please visit our
home page
www.esab.co m
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
ESAB PSF 315 R User manual
- Category
- Welding System
- Type
- User manual
- This manual is also suitable for
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
















