
Programming Environments Manual
for 32-Bit Implementations of the
PowerPC™ Architecture
MPCFPE32B
Rev. 3, 9/2005

Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. The PowerPC
name is a trademark of IBM Corp. and is used under license. All other product or service names are
the property of their respective owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc., 2005. All rights reserved.
Document Number: MPCFPE32B
Rev. 3, 9/2005
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software
implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are no express or
implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or fabricate any integrated
circuits or integrated circuits based on the information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further notice to
any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty, representation or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does
Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability arising out of the application or use of
any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without
limitation consequential or incidental damages. “Typical” parameters which may be
provided in Freescale Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do
vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals” must be validated for each customer application by
customer’s technical experts. Freescale Semiconductor does not convey any license
under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Freescale Semiconductor products are
not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for
surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life,
or for any other application in which the failure of the Freescale Semiconductor product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semiconductor products for any such unintended or
unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Freescale Semiconductor
and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all
claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of,
directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such
unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale
Semiconductor was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
email:
support@freescale.com
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, CH370
1300 N. Alma School Road
Chandler, Arizona 85224
(800) 521-6274
480-768-2130
support@freescale.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
support@freescale.com
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku
Tokyo 153-0064, Japan
0120 191014
+81 2666 8080
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate,
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 2666 8080
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor
Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
(800) 441-2447
303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor
@hibbertgroup.com

Overview
Register Set
Operand Conventions
Addressing Modes
Memory Management Unit
Instruction Set
Instruction Set Listings
Multiple-Precision Shifts
Floating-Point Models
Synchronization Programming Examples
Glossary
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
B
C
D
GLO
E
F
Cache
Exceptions
Simplified Mnemonics
PEM Revision History
Index IND

Overview
Register Set
Operand Conventions
Addressing Modes
Memory Management Unit
Instruction Set
Instruction Set Listings
Multiple-Precision Shifts
Floating-Point Models
Synchronization Programming Examples
Glossary
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A
B
C
D
GLO
E
F
Cache
Exceptions
Simplified Mnemonics
PEM Revision History
IndexIND

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor v
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
Chapter 1
Overview
1.1 PowerPC Architecture Overview..................................................................................... 1-2
1.1.1 The Levels of the PowerPC Architecture .................................................................... 1-3
1.1.2 Latitude within the Levels of the Architecture............................................................1-4
1.1.3 Features Not Defined by the PowerPC Architecture................................................... 1-4
1.2 The Architectural Models................................................................................................ 1-5
1.2.1 Registers and Programming Model ............................................................................. 1-5
1.2.2 Operand Conventions .................................................................................................. 1-7
1.2.2.1 Byte Ordering .......................................................................................................... 1-7
1.2.2.2 Data Organization in Memory and Data Transfers.................................................. 1-8
1.2.2.3 Floating-Point Conventions..................................................................................... 1-8
1.2.3 Instruction Set and Addressing Modes........................................................................ 1-8
1.2.3.1 Instruction Set..........................................................................................................1-8
1.2.3.2 Calculating Effective Addresses............................................................................ 1-10
1.2.4 Cache Model..............................................................................................................1-10
1.2.5 Interrupt Model.......................................................................................................... 1-10
1.2.6 Memory Management Model (MMU)....................................................................... 1-11
Chapter 2
Register Set
2.1 UISA Register Set............................................................................................................2-1
2.1.1 General-Purpose Registers (GPRs).............................................................................. 2-3
2.1.2 Floating-Point Registers (FPRs).................................................................................. 2-3
2.1.3 Condition Register (CR).............................................................................................. 2-5
2.1.3.1 Condition Register CR0 Field Definition................................................................2-5
2.1.3.2 Condition Register CR1 Field Definition................................................................2-6
2.1.3.3 Condition Register CRn Field—Compare Instruction ............................................2-6
2.1.4 Floating-Point Status and Control Register (FPSCR).................................................. 2-6
2.1.5 XER Register (XER) ................................................................................................... 2-9
2.1.6 Link Register (LR)..................................................................................................... 2-10
2.1.7 Count Register (CTR)................................................................................................ 2-11
2.2 VEA Register Set—Time Base...................................................................................... 2-12
2.2.1 Reading the Time Base.............................................................................................. 2-14
2.2.2 Computing Time of Day from the Time Base ...........................................................2-15
2.3 OEA Register Set........................................................................................................... 2-15
2.3.1 Machine State Register (MSR).................................................................................. 2-18

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
vi Freescale Semiconductor
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
2.3.2 Processor Version Register (PVR)............................................................................. 2-21
2.3.3 BAT Registers............................................................................................................ 2-21
2.3.4 SDR1..........................................................................................................................2-24
2.3.5 Segment Registers...................................................................................................... 2-25
2.3.6 Data Address Register (DAR) ................................................................................... 2-26
2.3.7 SPRG0–SPRG3 ......................................................................................................... 2-26
2.3.8 DSISR........................................................................................................................2-27
2.3.9 Machine Status Save/Restore Register 0 (SRR0)...................................................... 2-27
2.3.10 Machine Status Save/Restore Register 1 (SRR1)...................................................... 2-28
2.3.11 Floating-Point Exception Cause Register (FPECR).................................................. 2-28
2.3.12 Time Base Facility (TB)—OEA................................................................................2-29
2.3.12.1 Writing to the Time Base....................................................................................... 2-29
2.3.13 Decrementer Register (DEC)..................................................................................... 2-29
2.3.13.1 Decrementer Operation.......................................................................................... 2-30
2.3.13.2 Writing and Reading the DEC............................................................................... 2-30
2.3.14 Data Address Breakpoint Register (DABR )............................................................. 2-30
2.3.15 External Access Register (EAR)................................................................................ 2-32
2.3.16 Processor Identification Register (PIR)..................................................................... 2-32
2.3.17 Synchronization Requirements for Special Registers and for Lookaside Buffers..... 2-33
Chapter 3
Operand Conventions
3.1 Data Organization in Memory and Data Transfers..........................................................3-1
3.1.1 Aligned and Misaligned Accesses............................................................................... 3-1
3.1.2 Byte Ordering ..............................................................................................................3-2
3.1.3 Structure Mapping Examples....................................................................................... 3-2
3.1.3.1 Big-Endian Mapping ............................................................................................... 3-2
3.1.3.2 Little-Endian Mapping.............................................................................................3-3
3.1.4 Byte Ordering in PowerPC Architecture ..................................................................... 3-4
3.1.4.1 Aligned Scalars in Little-Endian Mode................................................................... 3-4
3.1.4.2 Misaligned Scalars in Little-Endian Mode.............................................................. 3-6
3.1.4.3 Nonscalars................................................................................................................3-7
3.1.4.4 Instruction Addressing in Little-Endian Mode........................................................ 3-7
3.1.4.5 Input/Output Data Transfer Addressing in Little-Endian Mode..............................3-8
3.2 Operand Placement and Performance—VEA.................................................................. 3-8
3.2.1 Summary of Performance Effects................................................................................ 3-8
3.2.2 Instruction Restart...................................................................................................... 3-10
3.3 Floating-Point Execution Models—UISA..................................................................... 3-10
3.3.1 Floating-Point Data Format ....................................................................................... 3-11
3.3.1.1 Value Representation ............................................................................................. 3-12

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor vii
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
3.3.1.2 Binary Floating-Point Numbers............................................................................. 3-13
3.3.1.3 Normalized Numbers (±NORM)........................................................................... 3-14
3.3.1.4 Zero Values (±0) .................................................................................................... 3-14
3.3.1.5 Denormalized Numbers (±DENORM).................................................................. 3-14
3.3.1.6 Infinities (±∞)........................................................................................................ 3-15
3.3.1.7 Not a Numbers (NaNs).......................................................................................... 3-15
3.3.2 Sign of Result.............................................................................................................3-16
3.3.3 Normalization and Denormalization.......................................................................... 3-17
3.3.4 Data Handling and Precision ..................................................................................... 3-17
3.3.5 Rounding....................................................................................................................3-19
3.3.6 Floating-Point Program Exceptions........................................................................... 3-21
3.3.6.1 Invalid Operation and Zero Divide Exception Conditions....................................3-27
3.3.6.1.1 Invalid Operation Exception Condition............................................................. 3-29
3.3.6.1.2 Zero Divide Exception Condition...................................................................... 3-30
3.3.6.2 Overflow, Underflow, and Inexact Exception Conditions.....................................3-31
3.3.6.2.1 Overflow Exception Condition.......................................................................... 3-33
3.3.6.2.2 Underflow Exception Condition........................................................................ 3-34
3.3.6.2.3 Inexact Exception Condition ............................................................................. 3-35
Chapter 4
Addressing Modes and Instruction Set Summary
4.1 Conventions ..................................................................................................................... 4-2
4.1.1 Sequential Execution Model........................................................................................ 4-2
4.1.2 Classes of Instructions ................................................................................................. 4-2
4.1.2.1 Definition of Boundedly Undefined........................................................................ 4-3
4.1.2.2 Defined Instruction Class ........................................................................................ 4-3
4.1.2.2.1 Preferred Instruction Forms................................................................................. 4-3
4.1.2.2.2 Invalid Instruction Forms .................................................................................... 4-3
4.1.2.2.3 Optional Instructions ........................................................................................... 4-4
4.1.2.3 Illegal Instruction Class........................................................................................... 4-4
4.1.2.4 Reserved Instructions............................................................................................... 4-5
4.1.3 Memory Addressing .................................................................................................... 4-5
4.1.3.1 Memory Operands ................................................................................................... 4-5
4.1.3.2 Effective Address Calculation ................................................................................. 4-6
4.1.4 Synchronizing Instructions.......................................................................................... 4-6
4.1.4.1 Context Synchronizing Instructions ........................................................................ 4-7
4.1.4.2 Execution Synchronizing Instructions..................................................................... 4-7
4.1.5 Interrupt Summary....................................................................................................... 4-7
4.1.6 Recommended Simplified Mnemonics........................................................................ 4-8
4.2 UISA Instructions ............................................................................................................4-8

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
viii Freescale Semiconductor
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
4.2.1 Integer Instructions ...................................................................................................... 4-8
4.2.1.1 Integer Arithmetic Instructions................................................................................ 4-9
4.2.1.2 Integer Compare Instructions ................................................................................ 4-12
4.2.1.3 Integer Logical Instructions................................................................................... 4-13
4.2.1.4 Integer Rotate and Shift Instructions..................................................................... 4-15
4.2.1.4.1 Integer Rotate Instructions................................................................................. 4-15
4.2.1.4.2 Integer Shift Instructions ................................................................................... 4-16
4.2.2 Floating-Point Instructions ........................................................................................ 4-17
4.2.2.1 Floating-Point Arithmetic Instructions.................................................................. 4-18
4.2.2.2 Floating-Point Multiply-Add Instructions............................................................. 4-20
4.2.2.3 Floating-Point Rounding and Conversion Instructions .........................................4-21
4.2.2.4 Floating-Point Compare Instructions..................................................................... 4-22
4.2.2.5 Floating-Point Status and Control Register Instructions .......................................4-22
4.2.2.6 Floating-Point Move Instructions.......................................................................... 4-23
4.2.3 Load and Store Instructions ....................................................................................... 4-24
4.2.3.1 Integer Load and Store Address Generation..........................................................4-24
4.2.3.1.1 Register Indirect with Immediate Index Addressing
for Integer Loads and Stores.......................................................................... 4-25
4.2.3.1.2 Register Indirect with Index Addressing for Integer Loads and Stores............. 4-25
4.2.3.1.3 Register Indirect Addressing for Integer Loads and Stores...............................4-26
4.2.3.2 Integer Load Instructions....................................................................................... 4-27
4.2.3.3 Integer Store Instructions....................................................................................... 4-29
4.2.3.4 Integer Load and Store with Byte-Reverse Instructions........................................ 4-30
4.2.3.5 Integer Load and Store Multiple Instructions........................................................4-31
4.2.3.6 Integer Load and Store String Instructions............................................................ 4-31
4.2.3.7 Floating-Point Load and Store Address Generation.............................................. 4-32
4.2.3.7.1 Register Indirect with Immediate Index Addressing for Floating-Point
Loads and Stores............................................................................................ 4-32
4.2.3.7.2 Register Indirect with Index Addressing for Floating-Point
Loads and Stores............................................................................................ 4-33
4.2.3.8 Floating-Point Load Instructions........................................................................... 4-34
4.2.3.9 Floating-Point Store Instructions........................................................................... 4-35
4.2.4 Branch and Flow Control Instructions....................................................................... 4-36
4.2.4.1 Branch Instruction Address Calculation................................................................ 4-37
4.2.4.1.1 Branch Relative Addressing Mode.................................................................... 4-37
4.2.4.1.2 Branch Conditional to Relative Addressing Mode............................................ 4-38
4.2.4.1.3 Branch to Absolute Addressing Mode............................................................... 4-39
4.2.4.1.4 Branch Conditional to Absolute Addressing Mode...........................................4-40
4.2.4.1.5 Branch Conditional to Link Register Addressing Mode...................................4-41
4.2.4.1.6 Branch Conditional to Count Register Addressing Mode.................................4-41

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor ix
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
4.2.4.2 Conditional Branch Control................................................................................... 4-42
4.2.4.3 Branch Instructions................................................................................................ 4-45
4.2.4.4 Simplified Mnemonics for Branch Processor Instructions.................................... 4-45
4.2.4.5 Condition Register Logical Instructions................................................................ 4-46
4.2.4.6 Trap Instructions.................................................................................................... 4-46
4.2.4.7 System Linkage Instruction—UISA......................................................................4-47
4.2.5 Processor Control Instructions—UISA ..................................................................... 4-47
4.2.5.1 Move to/from Condition Register Instructions...................................................... 4-47
4.2.5.2 Move to/from Special-Purpose Register Instructions (UISA)...............................4-47
4.2.6 Memory Synchronization Instructions—UISA .........................................................4-48
4.3 VEA Instructions ........................................................................................................... 4-49
4.3.1 Processor Control Instructions—VEA....................................................................... 4-50
4.3.2 Memory Synchronization Instructions—VEA .......................................................... 4-51
4.3.3 Memory Control Instructions—VEA ........................................................................ 4-51
4.3.3.1 User-Level Cache Instructions—VEA .................................................................. 4-52
4.3.4 External Control Instructions (Optional)................................................................... 4-54
4.4 OEA Instructions ........................................................................................................... 4-55
4.4.1 System Linkage Instructions—OEA ......................................................................... 4-55
4.4.2 Processor Control Instructions—OEA....................................................................... 4-56
4.4.2.1 Move to/from Machine State Register Instructions...............................................4-56
4.4.2.2 Move to/from Special-Purpose Register Instructions (OEA)................................4-56
4.4.3 Memory Control Instructions—OEA ........................................................................ 4-57
4.4.3.1 Supervisor-Level Cache Management Instruction ................................................4-57
4.4.3.2 Segment Register Manipulation Instructions.........................................................4-58
4.4.3.3 Translation Lookaside Buffer Management Instructions ......................................4-59
Chapter 5
Cache Model and Memory Coherency
5.1 Overview..........................................................................................................................5-1
5.2 The Virtual Environment ................................................................................................. 5-1
5.2.1 Memory Access Ordering............................................................................................ 5-2
5.2.1.1 Enforce In-Order Execution of I/O Instruction (eieio)............................................ 5-2
5.2.1.2 Synchronize Instruction........................................................................................... 5-3
5.2.2 Atomicity ..................................................................................................................... 5-3
5.2.3 Cache Model................................................................................................................5-4
5.2.4 Memory Coherency ..................................................................................................... 5-4
5.2.4.1 Memory/Cache Access Modes................................................................................ 5-4
5.2.4.1.1 Pages Designated as Write-Through....................................................................5-5
5.2.4.1.2 Pages Designated as Caching-Inhibited ..............................................................5-5
5.2.4.1.3 Pages Designated as Memory Coherency Required............................................5-5

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
x Freescale Semiconductor
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
5.2.4.1.4 Pages Designated as Memory Coherency Not Required..................................... 5-5
5.2.4.1.5 Pages Designated as Guarded.............................................................................. 5-6
5.2.4.2 Coherency Precautions ............................................................................................ 5-6
5.2.5 VEA Cache Management Instructions ........................................................................ 5-6
5.2.5.1 Data Cache Instructions........................................................................................... 5-7
5.2.5.1.1 Data Cache Block Touch (dcbt) and
Data Cache Block Touch for Store (dcbtst) Instructions................................ 5-7
5.2.5.1.2 Data Cache Block Set to Zero (dcbz) Instruction ...............................................5-7
5.2.5.1.3 Data Cache Block Store (dcbst) Instruction........................................................5-8
5.2.5.1.4 Data Cache Block Flush (dcbf) Instruction......................................................... 5-8
5.2.5.2 Instruction Cache Instructions................................................................................. 5-9
5.2.5.2.1 Instruction Cache Block Invalidate Instruction (icbi)......................................... 5-9
5.2.5.2.2 Instruction Synchronize Instruction (isync)......................................................5-10
5.2.6 Shared Memory.......................................................................................................... 5-10
5.2.6.1 Memory Access Ordering...................................................................................... 5-10
5.2.6.1.1 Programming Considerations ............................................................................ 5-12
5.2.6.1.2 Programming Examples .................................................................................... 5-14
5.2.6.2 Lock Acquisition and Import Barriers................................................................... 5-14
5.2.6.2.1 Acquire Lock and Import Shared Memory........................................................ 5-14
5.2.6.2.2 Obtain Pointer and Import Shared Memory ...................................................... 5-15
5.3 The Operating Environment .......................................................................................... 5-15
5.3.1 Memory/Cache Access Attributes ............................................................................. 5-16
5.3.1.1 Write-Through Attribute (W) ................................................................................5-17
5.3.1.2 Caching-Inhibited Attribute (I).............................................................................. 5-17
5.3.1.3 Memory Coherency Attribute (M)......................................................................... 5-18
5.3.1.4 W, I, and M Bit Combinations............................................................................... 5-18
5.3.1.5 The Guarded Attribute (G) .................................................................................... 5-19
5.3.1.5.1 Definition of Speculative and Out-of-Order Memory Accesses .......................5-19
5.3.1.5.2 Performing Operations Speculatively................................................................ 5-19
5.3.1.5.3 Guarded Memory............................................................................................... 5-20
5.3.1.5.4 Speculative Accesses to Guarded Memory .......................................................5-21
5.3.2 I/O Interface Considerations......................................................................................5-21
5.3.3 OEA Cache Management Instruction—Data Cache Block Invalidate (dcbi)........... 5-22
Chapter 6
Interrupts
6.1 Overview..........................................................................................................................6-1
6.2 Interrupt Classes ..............................................................................................................6-2
6.2.1 Precise Interrupts .........................................................................................................6-4
6.2.2 Context Synchronization.............................................................................................. 6-4

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor xi
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
6.2.2.1 Execution Synchronization...................................................................................... 6-5
6.2.2.2 Synchronous/Precise Interrupts............................................................................... 6-5
6.2.2.3 Asynchronous Interrupts.......................................................................................... 6-6
6.2.2.3.1 System Reset and Machine Check Interrupts...................................................... 6-6
6.2.2.3.2 External and Decrementer Interrupts................................................................... 6-6
6.2.3 Imprecise Interrupts..................................................................................................... 6-7
6.2.3.1 Imprecise Interrupt Status Description.................................................................... 6-7
6.2.3.2 Recoverability of Imprecise Floating-Point Interrupts............................................6-8
6.2.4 Partially Executed Instructions.................................................................................... 6-8
6.2.5 Interrupt Priorities........................................................................................................6-9
6.3 Interrupt Processing ....................................................................................................... 6-11
6.3.1 Enabling and Disabling Interrupts............................................................................. 6-13
6.3.2 Steps for Interrupt Processing.................................................................................... 6-14
6.3.3 Returning from an Interrupt Handler......................................................................... 6-14
6.4 Process Switching.......................................................................................................... 6-15
6.5 Interrupt Definitions ...................................................................................................... 6-15
6.5.1 System Reset Interrupt (0x00100).............................................................................6-16
6.5.2 Machine Check Interrupt (0x00200)..........................................................................6-17
6.5.3 Data Storage Interrupt (0x00300).............................................................................. 6-18
6.5.4 Instruction Storage Interrupt (0x00400) .................................................................... 6-20
6.5.5 External Interrupt (0x00500) ..................................................................................... 6-21
6.5.6 Alignment Interrupt (0x00600)..................................................................................6-22
6.5.6.1 Integer Alignment Interrupts ................................................................................. 6-23
6.5.6.1.1 Page Address Translation Access Considerations.............................................6-23
6.5.6.2 Little-Endian Mode Alignment Interrupts.............................................................6-24
6.5.6.3 Interpretation of the DSISR as Set by an Alignment Interrupt.............................. 6-24
6.5.7 Program Interrupt (0x00700) .................................................................................... 6-25
6.5.8 Floating-Point Unavailable Interrupt (0x00800) .......................................................6-27
6.5.9 Decrementer Interrupt (0x00900).............................................................................. 6-28
6.5.10 System Call Interrupt (0x00C00)............................................................................... 6-28
6.5.11 Trace Interrupt (0x00D00)......................................................................................... 6-29
6.5.12 Floating-Point Assist Interrupt (0x00E00) ................................................................6-30
Chapter 7
Memory Management
7.1 Overview..........................................................................................................................7-1
7.2 MMU Features.................................................................................................................7-2
7.3 MMU Overview............................................................................................................... 7-2
7.3.1 Memory Addressing .................................................................................................... 7-3
7.3.1.1 Predefined Physical Memory Locations.................................................................. 7-3

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
xii Freescale Semiconductor
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
7.3.2 MMU Organization...................................................................................................... 7-4
7.3.3 Address Translation Mechanisms................................................................................ 7-5
7.3.4 Memory Protection Facilities.......................................................................................7-6
7.3.5 Page History Information............................................................................................. 7-8
7.3.6 General Flow of MMU Address Translation............................................................... 7-8
7.3.6.1 Real Addressing Mode and Block Address Translation Selection..........................7-8
7.3.6.2 Page and Direct-Store Address Translation Selection............................................. 7-9
7.3.6.2.1 Selection of Page Address Translation.............................................................. 7-10
7.3.7 MMU Interrupts Summary ........................................................................................ 7-11
7.3.8 MMU Instructions and Register Summary................................................................ 7-12
7.3.9 TLB Entry Invalidation.............................................................................................. 7-15
7.4 Real Addressing Mode................................................................................................... 7-15
7.5 Block Address Translation............................................................................................. 7-16
7.5.1 BAT Array Organization............................................................................................ 7-16
7.5.2 Recognition of Addresses in BAT Arrays.................................................................. 7-18
7.5.3 BAT Register Implementation of BAT Array............................................................7-20
7.5.4 Block Memory Protection.......................................................................................... 7-23
7.5.5 Block Physical Address Generation .......................................................................... 7-25
7.5.6 Block Address Translation Summary........................................................................ 7-26
7.6 Memory Segment Model ............................................................................................... 7-26
7.6.1 Recognition of Addresses in Segments ..................................................................... 7-26
7.6.1.1 Selection of Memory Segments............................................................................. 7-27
7.6.1.2 Selection of Direct-Store Segments....................................................................... 7-27
7.6.2 Page Address Translation Overview.......................................................................... 7-28
7.6.2.1 Segment Register Definitions................................................................................ 7-28
7.6.2.1.1 Segment Register Format .................................................................................. 7-29
7.6.2.2 Page Table Entry (PTE) Definitions ...................................................................... 7-29
7.6.2.2.1 PTE Format........................................................................................................ 7-30
7.6.3 Page History Recording............................................................................................. 7-30
7.6.3.1 Reference Bit ......................................................................................................... 7-31
7.6.3.2 Change Bit ............................................................................................................. 7-32
7.6.3.3 Scenarios for Reference and Change Bit Recording ............................................. 7-32
7.6.3.4 Synchronization of Memory Accesses and Reference and Change
Bit Updates ........................................................................................................ 7-33
7.6.4 Page Memory Protection ........................................................................................... 7-34
7.6.5 Page Address Translation Summary.......................................................................... 7-36
7.7 Hashed Page Tables ....................................................................................................... 7-38
7.7.1 Page Table Definition ................................................................................................7-38
7.7.1.1 SDR1 Register Definitions .................................................................................... 7-39
7.7.1.2 Page Table Size...................................................................................................... 7-40
7.7.1.3 Page Table Hashing Functions............................................................................... 7-41

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor xiii
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
7.7.1.4 Page Table Addresses ............................................................................................ 7-42
7.7.1.5 Page Table Structure Summary.............................................................................. 7-45
7.7.1.6 Page Table Structure Examples ............................................................................. 7-45
7.7.1.7 PTEG Address Mapping Examples ....................................................................... 7-47
7.7.2 Page Table Search Operation..................................................................................... 7-50
7.7.2.1 Flow for Page Table Search Operation.................................................................. 7-50
7.7.3 Page Table Updates.................................................................................................... 7-51
7.7.3.1 Adding a Page Table Entry.................................................................................... 7-53
7.7.3.2 Deleting a Page Table Entry .................................................................................. 7-53
7.7.4 Segment Register Updates......................................................................................... 7-53
7.8 Direct-Store Segment Address Translation.................................................................... 7-53
7.8.1 Segment Registers for Direct-Store Segments...........................................................7-54
7.8.2 Direct-Store Segment Accesses................................................................................. 7-54
7.8.3 Direct-Store Segment Protection ............................................................................... 7-55
7.8.4 Instructions Not Supported in Direct-Store Segments...............................................7-55
7.8.5 Instructions with No Effect in Direct-Store Segments .............................................. 7-55
7.8.6 Direct-Store Segment Translation Summary Flow.................................................... 7-55
Chapter 8
Instruction Set
8.1 Instruction Formats..........................................................................................................8-1
8.1.1 Split-Field Notation ..................................................................................................... 8-1
8.1.2 Instruction Fields .........................................................................................................8-2
8.1.3 Notation and Conventions ........................................................................................... 8-3
8.2 Instruction Set................................................................................................................. 8-7
Appendix A
Instruction Set Listings
A.1 Instructions Sorted by Mnemonic (Decimal and Hexadecimal)..................................... A-1
A.2 Instructions Sorted by Primary Opcodes (Decimal and Hexadecimal)........................ A-17
A.3 Instructions Sorted by Mnemonic (Binary) .................................................................. A-26
A.4 Instructions Sorted by Opcode (Binary) ....................................................................... A-42
A.5 Instruction Set Legend.................................................................................................. A-51
Appendix B
Multiple-Precision Shifts
B.1 Overview..........................................................................................................................B-1
B.2 Multiple-Precision Shifts in 32-Bit Implementations......................................................B-1

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
xiv Freescale Semiconductor
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
Appendix C
Floating-Point Models
C.1 Execution Model for IEEE Operations............................................................................C-1
C.2 Multiply-Add Type Instruction Execution Model ...........................................................C-3
C.3 Floating-Point Conversions .............................................................................................C-4
C.3.1 Conversion from Floating-Point Number to Signed Fixed-Point Integer Word..........C-4
C.3.2 Conversion from Floating-Point Number to Unsigned Fixed-Point
Integer Word............................................................................................................C-5
C.4 Floating-Point Models .....................................................................................................C-5
C.4.1 Floating-Point Round to Single-Precision Model........................................................C-5
C.4.2 Floating-Point Convert to Integer Model.....................................................................C-9
C.4.3 Floating-Point Convert from Integer Model..............................................................C-11
C.5 Floating-Point Selection ................................................................................................C-12
C.5.1 Comparison to Zero ...................................................................................................C-13
C.5.2 Minimum and Maximum...........................................................................................C-13
C.5.3 Simple If-Then-Else Constructions ...........................................................................C-13
C.5.4 Notes..........................................................................................................................C-13
C.6 Floating-Point Load Instructions ...................................................................................C-14
C.7 Floating-Point Store Instructions...................................................................................C-15
Appendix D
Synchronization Programming Examples
D.1 General Information........................................................................................................ D-1
D.2 Synchronization Primitives............................................................................................. D-2
D.2.1 Fetch and No-Op......................................................................................................... D-2
D.2.2 Fetch and Store ........................................................................................................... D-2
D.2.3 Fetch and Add............................................................................................................. D-2
D.2.4 Fetch and AND........................................................................................................... D-3
D.2.5 Test and Set................................................................................................................. D-3
D.3 Compare and Swap......................................................................................................... D-3
D.4 Lock Acquisition and Release ........................................................................................ D-4
D.5 List Insertion................................................................................................................... D-5

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor xv
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number
Appendix E
Simplified Mnemonics for PowerPC Instructions
E.1 Overview..........................................................................................................................E-1
E.2 Subtract Simplified Mnemonics ......................................................................................E-2
E.2.1 Subtract Immediate......................................................................................................E-2
E.2.2 Subtract........................................................................................................................E-2
E.3 Rotate and Shift Simplified Mnemonics..........................................................................E-2
E.3.1 Operations on Words ...................................................................................................E-3
E.4 Branch Instruction Simplified Mnemonics......................................................................E-3
E.4.1 Key Facts about Simplified Branch Mnemonics.........................................................E-5
E.4.2 Eliminating the BO Operand .......................................................................................E-5
E.4.3 Incorporating the BO Branch Prediction .....................................................................E-7
E.4.4 The BI Operand—CR Bit and Field Representations..................................................E-7
E.4.4.1 BI Operand Instruction Encoding............................................................................E-8
E.4.4.1.1 Specifying a CR Bit.............................................................................................E-8
E.4.4.1.2 The crS Operand ...............................................................................................E-10
E.4.5 Simplified Mnemonics that Incorporate the BO Operand.........................................E-10
E.4.5.1 Examples that Eliminate the BO Operand.............................................................E-12
E.4.6 Simplified Mnemonics that Incorporate CR Conditions (Eliminates BO
and Replaces BI with crS).....................................................................................E-14
E.4.6.1 Branch Simplified Mnemonics that Incorporate CR Conditions: Examples.........E-16
E.4.6.2 Branch Simplified Mnemonics that Incorporate CR Conditions: Listings............E-16
E.5 Compare Word Simplified Mnemonics .........................................................................E-19
E.6 Condition Register Logical Simplified Mnemonics......................................................E-20
E.7 Trap Instructions Simplified Mnemonics ......................................................................E-20
E.8 Simplified Mnemonics for Accessing SPRs..................................................................E-22
E.9 Recommended Simplified Mnemonics..........................................................................E-23
E.9.1 No-Op (nop) ..............................................................................................................E-23
E.9.2 Load Immediate (li)...................................................................................................E-23
E.9.3 Load Address (la) ......................................................................................................E-24
E.9.4 Move Register (mr)...................................................................................................E-24
E.9.5 Complement Register (not).......................................................................................E-24
E.9.6 Move to Condition Register (mtcr)...........................................................................E-24
E.10 Comprehensive List of Simplified Mnemonics.............................................................E-24
Appendix F
Revision History
F.1 Changes From Revision 2 to Revision 3 .........................................................................F-1
F.2 Changes From Revision 1 to Revision 2 .........................................................................F-2

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
xvi Freescale Semiconductor
Contents
Paragraph
Number Title
Page
Number

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor xvii
Figures
Figure
Number Title
Page
Number
1-1 Programming Model—PowerPC Registers ............................................................................ 1-6
1-2 Big-Endian Byte and Bit Ordering.......................................................................................... 1-7
2-1 UISA Programming Model—User-Level Registers............................................................... 2-2
2-2 General-Purpose Registers (GPRs)......................................................................................... 2-3
2-3 Floating-Point Registers (FPRs) ............................................................................................. 2-4
2-4 Condition Register (CR) ......................................................................................................... 2-5
2-5 Floating-Point Status and Control Register (FPSCR).............................................................2-7
2-6 XER Register .......................................................................................................................... 2-9
2-7 Link Register (LR)................................................................................................................ 2-10
2-8 Count Register (CTR)........................................................................................................... 2-11
2-9 VEA Programming Model—User-Level Registers Plus Time Base .................................... 2-13
2-10 Time Base (TB)..................................................................................................................... 2-14
2-11 OEA Programming Model—All Registers........................................................................... 2-16
2-12 Machine State Register (MSR) ............................................................................................. 2-18
2-13 Processor Version Register (PVR)........................................................................................ 2-21
2-14 Format of Upper BAT Register............................................................................................. 2-22
2-15 Format of Lower BAT Register ............................................................................................ 2-22
2-16 SDR1 Register Format..........................................................................................................2-24
2-17 Segment Register Format (T = 0) ......................................................................................... 2-25
2-18 Segment Register Format (T = 1) ......................................................................................... 2-25
2-19 Data Address Register (DAR)............................................................................................... 2-26
2-20 SPRG0–SPRG3..................................................................................................................... 2-26
2-21 DSISR ...................................................................................................................................2-27
2-22 Machine Status Save/Restore Register 0 (SRR0) ................................................................. 2-27
2-23 Machine Status Save/Restore Register 1 (SRR1) ................................................................. 2-28
2-24 Decrementer Register (DEC)................................................................................................ 2-29
2-25 Data Address Breakpoint Register (DABR)......................................................................... 2-30
2-26 External Access Register (EAR)........................................................................................... 2-32
2-27 Processor Identification Register (PIR) ................................................................................ 2-33
3-1 C Program Example—Data Structure S.................................................................................. 3-2
3-2 Big-Endian Mapping of Structure S........................................................................................ 3-3
3-3 Little-Endian Mapping of Structure S..................................................................................... 3-3
3-4 Little-Endian Mapping of Structure S —Alternate View........................................................ 3-4
3-5 Modified Little-Endian Structure S as Seen by the Memory Subsystem................................ 3-5
3-6 Modified Little-Endian Structure S as Seen by the Processor ................................................3-6
3-7 True Little-Endian Mapping, Word Stored at Address 05 ......................................................3-6
3-8 Word at Little-Endian Address 05 as Seen by the Memory Subsystem .................................3-7
3-9 Floating-Point Single-Precision Format................................................................................ 3-11
3-10 Floating-Point Double-Precision Format.............................................................................. 3-11

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
xviii Freescale Semiconductor
Figures
Figure
Number Title
Page
Number
3-11 Approximation to Real Numbers.......................................................................................... 3-13
3-12 Format for Normalized Numbers.......................................................................................... 3-14
3-13 Format for Zero Numbers .....................................................................................................3-14
3-14 Format for Denormalized Numbers...................................................................................... 3-15
3-15 Format for Positive and Negative Infinities.......................................................................... 3-15
3-16 Format for NaNs ................................................................................................................... 3-15
3-17 Representation of Generated QNaN ..................................................................................... 3-16
3-18 Single-Precision Representation in an FPR .......................................................................... 3-18
3-19 Relation of Z1 and Z2 ...........................................................................................................3-19
3-20 Selection of Z1 and Z2 for the Four Rounding Modes.........................................................3-20
3-21 Rounding Flags in FPSCR.................................................................................................... 3-21
3-22 Floating-Point Status and Control Register (FPSCR)...........................................................3-21
3-23 Initial Flow for Floating-Point Exception Conditions .......................................................... 3-28
3-24 Checking of Remaining Floating-Point Exception Conditions.............................................3-32
4-1 Register Indirect with Immediate Index Addressing for Integer Loads/Stores..................... 4-25
4-2 Register Indirect with Index Addressing for Integer Loads/Stores.......................................4-26
4-3 Register Indirect Addressing for Integer Loads/Stores.........................................................4-27
4-4 Register Indirect with Immediate Index Addressing for Floating-Point Loads/Stores......... 4-33
4-5 Register Indirect with Index Addressing for Floating-Point Loads/Stores........................... 4-34
4-6 Branch Relative Addressing.................................................................................................. 4-38
4-7 Branch Conditional Relative Addressing.............................................................................. 4-39
4-8 Branch to Absolute Addressing ............................................................................................ 4-40
4-9 Branch Conditional to Absolute Addressing ........................................................................ 4-40
4-10 Branch Conditional to Link Register Addressing................................................................. 4-41
4-11 Branch Conditional to Count Register Addressing...............................................................4-42
5-1 Memory Barrier when Coherency is Required (M = 1)........................................................ 5-11
5-2 Cumulative Memory Barrier................................................................................................. 5-12
6-1 Machine Status Save/Restore Register 0 (SRR0) ................................................................. 6-11
6-2 Machine Status Save/Restore Register 1 (SRR1) ................................................................. 6-11
6-3 Machine State Register (MSR) ............................................................................................. 6-12
7-1 MMU Conceptual Block Diagram.......................................................................................... 7-4
7-2 Address Translation Types......................................................................................................7-5
7-3 General Flow of Address Translation (Real Addressing Mode and Block) ........................... 7-9
7-4 General Flow of Page and Direct-Store Address Translation............................................... 7-10
7-5 MMU Registers..................................................................................................................... 7-14
7-6 BAT Array Organization.......................................................................................................7-17
7-7 BAT Array Hit/Miss Flow..................................................................................................... 7-19
7-8 Format of Upper BAT Register............................................................................................. 7-21
7-9 Format of Lower BAT Register ............................................................................................ 7-21
7-10 Memory Protection Violation Flow for Blocks..................................................................... 7-24
7-11 Block Physical Address Generation...................................................................................... 7-25

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
Freescale Semiconductor xix
Figures
Figure
Number Title
Page
Number
7-12 Block Address Translation Flow........................................................................................... 7-26
7-13 Page Address Translation Overview..................................................................................... 7-28
7-14 Segment Register Format for Page Address Translation......................................................7-29
7-15 Page Table Entry Format.......................................................................................................7-30
7-16 Memory Protection Violation Flow for Pages ...................................................................... 7-36
7-17 Page Address Translation Flow—TLB Hit........................................................................... 7-37
7-18 Page Memory Protection Violation Conditions
for Page Address Translation ........................................................................................... 7-38
7-19 Page Table Definitions.......................................................................................................... 7-39
7-20 SDR1 Register Format..........................................................................................................7-40
7-21 Hashing Functions for Page Tables....................................................................................... 7-42
7-22 Generation of Addresses for Page Tables ............................................................................. 7-44
7-23 Example Page Table Structure .............................................................................................. 7-46
7-24 Example Primary PTEG Address Generation....................................................................... 7-48
7-25 Example Secondary PTEG Address Generation................................................................... 7-49
7-26 Page Table Search Flow........................................................................................................7-51
7-27 Segment Register Format for Direct-Store Segments...........................................................7-54
7-28 Direct-Store Segment Translation Flow................................................................................ 7-56
8-1 Instruction Description............................................................................................................8-7
C-1 IEEE 64-Bit Execution Model................................................................................................C-1
C-2 Multiply-Add 64-Bit Execution Model...................................................................................C-3
E-1 Branch Conditional (bc) Instruction Format...........................................................................E-4
E-2 BO Field (Bits 6–10 of the Instruction Encoding)..................................................................E-5
E-3 BI Field (Bits 11–14 of the Instruction Encoding)..................................................................E-8

Programming Environments Manual for 32-Bit Implementations of the PowerPC Architecture, Rev. 3
xx Freescale Semiconductor
Figures
Figure
Number Title
Page
Number
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
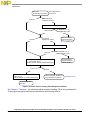 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
-
 125
125
-
 126
126
-
 127
127
-
 128
128
-
 129
129
-
 130
130
-
 131
131
-
 132
132
-
 133
133
-
 134
134
-
 135
135
-
 136
136
-
 137
137
-
 138
138
-
 139
139
-
 140
140
-
 141
141
-
 142
142
-
 143
143
-
 144
144
-
 145
145
-
 146
146
-
 147
147
-
 148
148
-
 149
149
-
 150
150
-
 151
151
-
 152
152
-
 153
153
-
 154
154
-
 155
155
-
 156
156
-
 157
157
-
 158
158
-
 159
159
-
 160
160
-
 161
161
-
 162
162
-
 163
163
-
 164
164
-
 165
165
-
 166
166
-
 167
167
-
 168
168
-
 169
169
-
 170
170
-
 171
171
-
 172
172
-
 173
173
-
 174
174
-
 175
175
-
 176
176
-
 177
177
-
 178
178
-
 179
179
-
 180
180
-
 181
181
-
 182
182
-
 183
183
-
 184
184
-
 185
185
-
 186
186
-
 187
187
-
 188
188
-
 189
189
-
 190
190
-
 191
191
-
 192
192
-
 193
193
-
 194
194
-
 195
195
-
 196
196
-
 197
197
-
 198
198
-
 199
199
-
 200
200
-
 201
201
-
 202
202
-
 203
203
-
 204
204
-
 205
205
-
 206
206
-
 207
207
-
 208
208
-
 209
209
-
 210
210
-
 211
211
-
 212
212
-
 213
213
-
 214
214
-
 215
215
-
 216
216
-
 217
217
-
 218
218
-
 219
219
-
 220
220
-
 221
221
-
 222
222
-
 223
223
-
 224
224
-
 225
225
-
 226
226
-
 227
227
-
 228
228
-
 229
229
-
 230
230
-
 231
231
-
 232
232
-
 233
233
-
 234
234
-
 235
235
-
 236
236
-
 237
237
-
 238
238
-
 239
239
-
 240
240
-
 241
241
-
 242
242
-
 243
243
-
 244
244
-
 245
245
-
 246
246
-
 247
247
-
 248
248
-
 249
249
-
 250
250
-
 251
251
-
 252
252
-
 253
253
-
 254
254
-
 255
255
-
 256
256
-
 257
257
-
 258
258
-
 259
259
-
 260
260
-
 261
261
-
 262
262
-
 263
263
-
 264
264
-
 265
265
-
 266
266
-
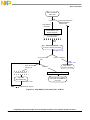 267
267
-
 268
268
-
 269
269
-
 270
270
-
 271
271
-
 272
272
-
 273
273
-
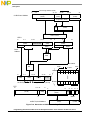 274
274
-
 275
275
-
 276
276
-
 277
277
-
 278
278
-
 279
279
-
 280
280
-
 281
281
-
 282
282
-
 283
283
-
 284
284
-
 285
285
-
 286
286
-
 287
287
-
 288
288
-
 289
289
-
 290
290
-
 291
291
-
 292
292
-
 293
293
-
 294
294
-
 295
295
-
 296
296
-
 297
297
-
 298
298
-
 299
299
-
 300
300
-
 301
301
-
 302
302
-
 303
303
-
 304
304
-
 305
305
-
 306
306
-
 307
307
-
 308
308
-
 309
309
-
 310
310
-
 311
311
-
 312
312
-
 313
313
-
 314
314
-
 315
315
-
 316
316
-
 317
317
-
 318
318
-
 319
319
-
 320
320
-
 321
321
-
 322
322
-
 323
323
-
 324
324
-
 325
325
-
 326
326
-
 327
327
-
 328
328
-
 329
329
-
 330
330
-
 331
331
-
 332
332
-
 333
333
-
 334
334
-
 335
335
-
 336
336
-
 337
337
-
 338
338
-
 339
339
-
 340
340
-
 341
341
-
 342
342
-
 343
343
-
 344
344
-
 345
345
-
 346
346
-
 347
347
-
 348
348
-
 349
349
-
 350
350
-
 351
351
-
 352
352
-
 353
353
-
 354
354
-
 355
355
-
 356
356
-
 357
357
-
 358
358
-
 359
359
-
 360
360
-
 361
361
-
 362
362
-
 363
363
-
 364
364
-
 365
365
-
 366
366
-
 367
367
-
 368
368
-
 369
369
-
 370
370
-
 371
371
-
 372
372
-
 373
373
-
 374
374
-
 375
375
-
 376
376
-
 377
377
-
 378
378
-
 379
379
-
 380
380
-
 381
381
-
 382
382
-
 383
383
-
 384
384
-
 385
385
-
 386
386
-
 387
387
-
 388
388
-
 389
389
-
 390
390
-
 391
391
-
 392
392
-
 393
393
-
 394
394
-
 395
395
-
 396
396
-
 397
397
-
 398
398
-
 399
399
-
 400
400
-
 401
401
-
 402
402
-
 403
403
-
 404
404
-
 405
405
-
 406
406
-
 407
407
-
 408
408
-
 409
409
-
 410
410
-
 411
411
-
 412
412
-
 413
413
-
 414
414
-
 415
415
-
 416
416
-
 417
417
-
 418
418
-
 419
419
-
 420
420
-
 421
421
-
 422
422
-
 423
423
-
 424
424
-
 425
425
-
 426
426
-
 427
427
-
 428
428
-
 429
429
-
 430
430
-
 431
431
-
 432
432
-
 433
433
-
 434
434
-
 435
435
-
 436
436
-
 437
437
-
 438
438
-
 439
439
-
 440
440
-
 441
441
-
 442
442
-
 443
443
-
 444
444
-
 445
445
-
 446
446
-
 447
447
-
 448
448
-
 449
449
-
 450
450
-
 451
451
-
 452
452
-
 453
453
-
 454
454
-
 455
455
-
 456
456
-
 457
457
-
 458
458
-
 459
459
-
 460
460
-
 461
461
-
 462
462
-
 463
463
-
 464
464
-
 465
465
-
 466
466
-
 467
467
-
 468
468
-
 469
469
-
 470
470
-
 471
471
-
 472
472
-
 473
473
-
 474
474
-
 475
475
-
 476
476
-
 477
477
-
 478
478
-
 479
479
-
 480
480
-
 481
481
-
 482
482
-
 483
483
-
 484
484
-
 485
485
-
 486
486
-
 487
487
-
 488
488
-
 489
489
-
 490
490
-
 491
491
-
 492
492
-
 493
493
-
 494
494
-
 495
495
-
 496
496
-
 497
497
-
 498
498
-
 499
499
-
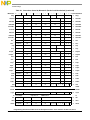 500
500
-
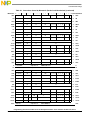 501
501
-
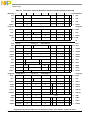 502
502
-
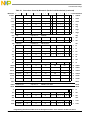 503
503
-
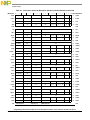 504
504
-
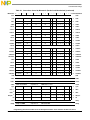 505
505
-
 506
506
-
 507
507
-
 508
508
-
 509
509
-
 510
510
-
 511
511
-
 512
512
-
 513
513
-
 514
514
-
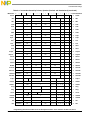 515
515
-
 516
516
-
 517
517
-
 518
518
-
 519
519
-
 520
520
-
 521
521
-
 522
522
-
 523
523
-
 524
524
-
 525
525
-
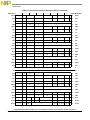 526
526
-
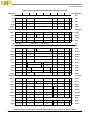 527
527
-
 528
528
-
 529
529
-
 530
530
-
 531
531
-
 532
532
-
 533
533
-
 534
534
-
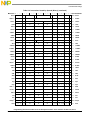 535
535
-
 536
536
-
 537
537
-
 538
538
-
 539
539
-
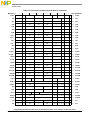 540
540
-
 541
541
-
 542
542
-
 543
543
-
 544
544
-
 545
545
-
 546
546
-
 547
547
-
 548
548
-
 549
549
-
 550
550
-
 551
551
-
 552
552
-
 553
553
-
 554
554
-
 555
555
-
 556
556
-
 557
557
-
 558
558
-
 559
559
-
 560
560
-
 561
561
-
 562
562
-
 563
563
-
 564
564
-
 565
565
-
 566
566
-
 567
567
-
 568
568
-
 569
569
-
 570
570
-
 571
571
-
 572
572
-
 573
573
-
 574
574
-
 575
575
-
 576
576
-
 577
577
-
 578
578
-
 579
579
-
 580
580
-
 581
581
-
 582
582
-
 583
583
-
 584
584
-
 585
585
-
 586
586
-
 587
587
-
 588
588
-
 589
589
-
 590
590
-
 591
591
-
 592
592
-
 593
593
-
 594
594
-
 595
595
-
 596
596
-
 597
597
-
 598
598
-
 599
599
-
 600
600
-
 601
601
-
 602
602
-
 603
603
-
 604
604
-
 605
605
-
 606
606
-
 607
607
-
 608
608
-
 609
609
-
 610
610
-
 611
611
-
 612
612
-
 613
613
-
 614
614
-
 615
615
-
 616
616
-
 617
617
-
 618
618
-
 619
619
-
 620
620
-
 621
621
-
 622
622
-
 623
623
-
 624
624
-
 625
625
-
 626
626
-
 627
627
-
 628
628
-
 629
629
-
 630
630
-
 631
631
-
 632
632
-
 633
633
-
 634
634
-
 635
635
-
 636
636
-
 637
637
-
 638
638
-
 639
639
-
 640
640
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
Related papers
-
NXP MPC821 User guide
-
NXP MPC7400 Reference guide
-
NXP MPC601 User guide
-
NXP MPC8275 Reference guide
-
NXP MPC5200 Reference guide
-
NXP MPC603E Reference guide
-
NXP MPC862 Reference guide
-
NXP MPC860 Reference guide
-
NXP MPC885 Reference guide
-
NXP QorIQ® T4240/T4160/T4080 Multicore Communications Processors Reference guide
Other documents
-
IBM 750GX User manual
-
Xilinx Virtex-II Pro PPC405 User manual
-
Bull AIX 5.3 Programming Guide
-
Motorola MPC823E Reference guide
-
Hitachi SH7750 series Programming Manual
-
Freescale Semiconductor MPC850 User manual
-
Apple PowerPC G5 User manual
-
Intel 253666-024US User manual
-
AFC CPU-06-G Datasheet
-
Toshiba TX39 User manual































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































