
0740 801 004
0002
LTO 160/250
Mechtig 160/250
Service manual

-- 2 --conte
LIST OF CONTENTS Page
READ THIS FIRST 4................................................................
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION 5......................................................
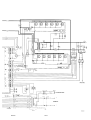
CONNECTION DIAGRAM LTO 160 8.................................................
CONNECTION DIAGRAM LTO 250 10.................................................
BLOCK DIAGRAM, CIRCUIT BOARD AP01 12.........................................
DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION, CIRCUIT BOARD AP01 14.............................
AP01:1 Power supply 14..........................................................
AP01:2 + 5 V Power supply monitoring 15...........................................
AP01:3 Start / Stop input 16.......................................................
AP01:4 Gas valve 16.............................................................
AP01:5 Shunt input with amplifier AP10 16..........................................
LTO 160 17..............................................................
LTO 250 17..............................................................
AP01:6 Arc voltage monitoring 18..................................................
AP01:7 HF Generator 18..........................................................
AP01:9 Machine type indicator 19..................................................
AP01:10 Thermal overload cutout 19.................................................
AP01:11 Welding process control 19.................................................
AP01:12 Motor control interface circuits 20...........................................
AP01:13 Pulse width modulator 21...................................................
AP01:14 Gate circuit LTO 160 22....................................................
Checking the gate pulses, LTO 160 23......................................
AP01:14 Gate circuit LTO 250 24...................................................
Checking the gate pulses, LTO 250 25......................................
Component positions, circuit board AP01 27...........................................
LTO 160: TRANSISTOR BOARD AP02 28.............................................
LTO 160: TRANSISTOR BOARD AP03 30.............................................
LTO 250: TRANSISTOR BOARD AP02 32.............................................
LTO 250: TRANSISTOR BOARD AP03 34.............................................
MOSTEST ER 36.....................................................................
LTO 160: SOFT STARTING 37........................................................
LTO 250: SOFT STARTING 38........................................................
SUPPRESSION BOARD AP07 39.....................................................
LTO 160: SUPPRESSION BOARD AP08 40...........................................
LTO 250: SUPPRESSION BOARD AP08 40...........................................
MOTHER BOARD AP12 42...........................................................
ROTATION AP13 46.................................................................
WIRE FEED AP14 48................................................................
POWER SUPPLY AP15 50...........................................................
CONNECTOR BOARD AP16 52.......................................................
CONNECTOR BOARD AP17 53.......................................................
PULSE GENERATOR INTERFACE BOARD AP18 54....................................
CONTROL BOX E01 56..............................................................
Display board 57...................................................................
Microprocessor board 58............................................................
Battery replacement 61.............................................................
FAULT/ERROR MESSAGES ON THE DISPLAY 62......................................
Faults in the power electronic circuits of the machine 62.................................
Memory errors/faults 62.............................................................
Communication faults/errors 63......................................................
Errors in the course of welding 63....................................................
Errors in the course of sequential running 64...........................................
Blocking messages 64..............................................................

-- 3 --conte
DISASSEMBLY / REASSEMBLY 65....................................................
Removal of transistor circuit boards AP02 and AP03 65.................................
Refitting the transistor circuit board 65................................................
Assembling the diode modules 66....................................................
Fitting the main transformer , TC02 67................................................
TECHNICAL DATA 68................................................................
LOAD CHARACTERISTICS 69........................................................
INSTRUCTIONS 71..................................................................
SAFETY 71........................................................................
INTRODUCTION 72.................................................................
General 72........................................................................
INSTALLATION 73..................................................................
Lifting instructions 73...............................................................
Mains voltage connection 73.........................................................
Connection of a complete welding system 74..........................................
OPERATION 76.....................................................................
Controls and connections 76.........................................................
Overheating protection 77...........................................................
MAINTENANCE 77..................................................................
Check--up and cleaning 77..........................................................
CONTROL BOX 77..................................................................
ACCESSORIES 78..................................................................
SPARE PARTS LIST 81..............................................................
NOTES 96..........................................................................
Rights reserved to alter specifications without notice.

-- 4 --
clto0de1
READ THIS FIRST
Maintenance and repair work should be performed by an experienced person, and electrical
work only by a trained electrician. Use only recommended replacement parts.
This service manual i s intended for use by t echnicians with electrical/electronic training for
help in connection with fault--tracing and repair.
All component names in the connection diagram are listed in the component description.
This manual contains details of all design changes that have been made up to and including
February 2000.
The LTO 160 and LTO 250 are designed and tested in accordance with European
standard EN 60974--1 and EN 50199.
On completion of service or repair work, it is the responsibility of the person(s) etc.
performing the work to ensure that the product does not depart from the requirements
of the above standard.
WARNING
READ AND UNDERSTAND THE INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE INSTALLING OR OPERATING.
ARC WELDING AND CUTTING CAN BE INJURIOUS TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS. TAKE PRECAU -
TIONS WHEN WELDING. ASK FOR YOUR EMPLOYER’S SAFETY PRACTICES WHICH SHOULD BE
BASED ON MANUFACTURERS’ HAZARD DATA.
ELECTRIC SHOCK -- Can kill
S Install and earth the welding unit in accordance with applicable standards.
S Do not touch live electrical parts or electrodes with bare skin, wet gloves or wet clothing.
S Insulate yourself from earth and the workpiece.
S Ensure your working s tance is s afe.
FUMES AND GASES -- Can b e dangerous to health
S Keep your head out of the fumes.
S Use ventilation, extraction at the arc, or both, to keep fumes and gases from your breathing zone and
the general area.
ARC RAYS -- Can injure eyes and burn skin.
S Protect your eyes and body. Use the correct welding screen and filter lens and wear protective
clothing.
S Protect bystanders with suitable screens or curtains.
FIRE HAZARD
S Sparks (spatter) can cause fire. Make sure therefore that there are no inflammable materials nearby.
NOISE -- Excessive noise can damage hearing
S Protect your ears. Use ear defenders or other hearing protection.
S Warn bystanders of the risk.
MALFUNCTION -- Call for expert assistance in the event of malfunction.
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS!

-- 5 --clto0de1
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
This component description refers to the connection diagrams.
The LTO 160 and LTO 250 are primary--switched power units, using parallel--connected
MOSFET--transistors as the switching elements.
The power units are p rogrammable and provided with a memory so that different welding
programs can be set and stored by means of a control box. The welding programs can be
divided into sectors with different sets of parameters. The division into sectors is
time--controlled.
They are designed both for manual and mechanized welding.
WARNING !
STATIC ELECTRICITY can damage circuit
boards and electronic components.
S
SS
S Observe precautions for handling electrostatic
sensitive devices.
S
SS
S Use proper static--proof bags and boxes.
ESD
AP01 The main circuit board with control electronics. See block diagram on
page 12 and description on page 14.
AP02 Circuit board with power transistors for the positive pole, see description
for the LTO 160 on page 28 and for the LTO 250 on page 32.
WARNING! the transistors are connected to mains voltage potential.
AP03 Circuit board with power transistors for the negative pole, see description
for the LTO 160 on page 30 and for the LTO 250 on page 34.
WARNING! the transistors are connected to mains voltage potential.
AP07 Interference suppression circuit board: see circuit diagram on page 39.
AP08 Interference suppression circuit board, prevents mains--borne interference.
See circuit diagram on page 40.
AP10 Circuit board shunt amplifier, see description on page 16.
AP11 HF generator.
AP12 Circuit board. See description on page 42.
AP13 Circuit board, motor control, rotation. See description on page 46.
AP14 Circuit board, motor control, wire feed speed. See description on page 48.
AP15 Circuit board, voltage supply for rotation and wire feed. See description on
page 50.
AP16 Circuit board, distribution board for AP14. See diagram on page 52.
AP17 Circuit board, distribution board for AP15, see diagram on page 53.

-- 6 --
clto0de1
AP18 Circuit board, interface for pulse generator. See description on page 54.
C01 Capacitor, 0.1←F, 1000 VDC, transient protection.
C02, C03 Capacitor, 1000←F, buffer/smoothing capacitor.
Time to discharge after turning off the unit: about two minutes.
Capacitor C03 is only mounted in the LTO 250.
C04 Decoupling capacitor, 0.1←F, 1000 VDC, protects against HF.
C05 2 -- capacitors, 4.7←F, see L02.
C06--C09 Capacitor, 0.1←F.
C10 LTO 160: 2 -- capacitors, 12 nF. Protection against transient voltages.
LTO 250: 2 -- capacitors, 1 nF. Protection against transient voltages.
E01 Control box. See description on page 56.
EV01 Fan, 24 VDC.
EV02 Fan, 24 VDC. Only monted in the LTO 250.
FU01 Fuse 315 mA, slow blow.
FU02 Fuse 630 mA, slow blow.
FU03 Fuse 1 A, slow blow.
FU04 Fuse 800 mA, slow blow.
FU06, FU07 Fuse 0.5 A, slow blow.
FU08, FU09 Fuse 1.25 A, slow blow.
HL01 Lamp, 28 V, white, lights when mains power is on.
L01 Secondary inductor.
L02 Inductor, forms an LC circuit with C05 and V06 to reduce the risk of arc
extinction at low welding currents.
When V03 conducts, the LC circuit charges up. The circuit is capable of
temporarily maintaining a high arc voltage at low current, thus reducing the
risk of arc extinction.
Diode V06 prevents capacitor C05 from going negative.
L03 LTO 160: Primary inductor, improves the machine’s form factor, i.e.
reduces the mains load.
LTO 250: Ferrite ring core, transient protection.
L04, L05 Ferrite ring core, transient protection. Only mounted in the LTO 250.
QF01 Mains power supply switch.
R01 Resistor, 3.9 kτ 5W.
R02 -- R05 Current limit resistor, 3 τ 10 W.
R06 -- R07 Current limit resistor, 10 τ 10 W.

-- 7 --clto0de1
RS01 LTO 160: Shunt, 119 mV at 140 A
LTO 250: Shunt, 119 mV at 250 A
ST01 LTO 160:
Thermal overload cutout, for overload protection, mounted on the main
transformer (TC02) winding. Breaks at 130 _C and resets at 100 _C.
LTO 250:
Thermal overload cutout, for overload protection, mounted on the winding
of inductor L01. Breaks at 130 _ C and resets at 100 _C.
TC01 Control power transformer. Secondary output voltages: 9, 20, 26 and 42V.
TC02 Main transformer. For fitting instructions, see page 67.
TC03 Control power transformer for motor regulators.
TC04 Transformer for water cooler. Only mounted in the LTO 250.
TV01 HF transformer.
V01, V02 Mains rectifier bridge, 35 A, 1200 V. Af ter replacing the rectifier bridges,
the machine must be soft--started: see instructions on page 37.
Rectifier bridge V02 is only mounted in the LTO 250.
V03, V04 Rectifier and freewheel diodes.
V03 r ectifies the welding current.
During the time interval between two voltage pulses from transformer
TC02, the freewheel diode V04 maintain the welding current from inductor
L01.
On the cooling fins one respectively three diode modules are mounted.
Each diode module consists of two diodes.
For installation instructions, see page 66.
V05 LED, yellow. Lights when thermal cutout ST01 operates (breaks) as a
result of high temperature.
V06 Diode, see L02.
X.. Terminal block.
XP . . Pin connector.
XS . . Sleeve connector.
XS04 26--pole ribbon cable connector .
XS12 2--pole Cannon connector.
XS13--XS14 Welding current terminal, OKC type.
XS20 26--pole connector for ribbon cable.
XS32 Connector for voltage supply to cooling unit.
YV01 Solenoid valve.

-- 8 --
clto0de1
CONNECTION DIAGRAM LTO 160

-- 9 --clto0de1

-- 1 0 --
clto0de1
CONNECTION DIAGRAM LTO 250

-- 1 1 --clto0de1

-- 1 2 --
clto0de2
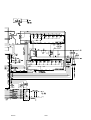
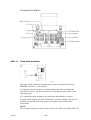
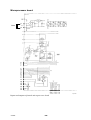
BLOCK DIAGRAM, CIRCUIT BOARD AP01
1 Power supply
2 +5 V Power supply monitoring
3 Start / Stop input
4 Gas valve
5 Shunt input with amplifier AP10
6 Arc voltage sensing

-- 1 3 --clto0de2
7 HF unit
9 Machine type selection
10 Thermal overload switch
11 Welding process control
12 Interface circuits for motor control
13 Pulse width modulator
14 Gate circuit

-- 1 4 --
clto0de2
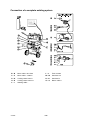
DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION, CIRCUIT BOARD AP01
This description refers to the block diagram on page 12 and to the components position
diagram on page 27.
Only those parts connected to the board’s inputs and outputs are described here. If the circuit
board is faulty, it must be replaced.
After replacing the circuit board, the machine must be soft--started. See the instructions
on page 37 och 38.
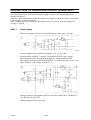
AP01:1 Power supply
The power supply to the board can be divided into three parts; a, b and c.
cltn0e06
Voltage regulator VR2 stabilises the supply to +5 ¦0.25 V DC.
Resistors R126 and R127, capacitor C104 and diode D27 form a voltage
monitoring circuit for the unregulated supply to voltage regulator VR2.
The voltage from potential divider R126/R127 is connected to pin 9 of IC7: see
AP01:2) below. The voltage is about 2.5 V.
Voltage regulator VR4 supplies fan EV01 and EV02 with +28V. Fan EV02 is
only fitted in the LTO 250.
Voltage regulator VR3 is not used.

-- 1 5 --clto0de2
Voltage regulator VR1 produces an output voltage of +20 ¦1.0 V, which
supplies the pulse width modulator output stage (Block AP01:13).
Potential divider R100/R101 supplies 2.6 V to the processor in Block AP01:11.
This provides a signal that the power supply is available.
The +27 V supplies relay RE1 in Block AP01:7 and indicating lamp HL01.
The analogue circuits on the board are supplied by +15V and --15V. The
microprocessor monitors the --15V supply by a signal from the right--hand side
of resistor R54.
AP01:2 + 5 V Power supply monitoring
A voltage of about 2.5 V is supplied to IC7, pin 9, from power supply circuit 1a.
If this voltage drops below the threshold voltage of 1.3 V, pin 10 of IC7 goes
low, providing the processor with a low power supply voltage signal.
If the +5 V supply to pin 3 of I C7 drops below 4.65 V, pin 15 goes low and
inhibits the pulse width m odulator in block AP 01:13, the processor also receives
a reset signal.

-- 1 6 --
clto0de2
AP01:3 Start / Stop input
The output signal from IC14, pin 4, goes high (+5 V) when the torch contact
switch is not activated, and low (0 V) when it is activated.
AP01:4 Gas valve
Operating the torch trigger switch causes semiconductor relay RE2 to conduct
and energise solenoid valve YV01. C82 and R111 form an HF filter.
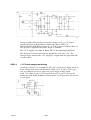
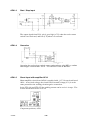
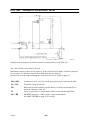
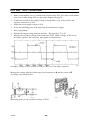
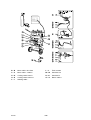
AP01:5 Shunt input with amplifier AP10
Shunt amplifier circuit board AP10 is supplied with ¦15 V fr om circuit board
AP01. At no--load voltage, the circuit board’s neutral voltage (0 V) is at the
same potential as the welding circuit negative connection.
In the LTO 160 and LTO 250 the welding current can be set in 1 A steps. The
lowest current that can be set is 3A.
cltn0e28
Component positions, AP10

-- 1 7 --clto0de2
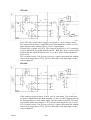
LTO 160
cltn0e12
In the LTO 160, 119mV shunt voltage cor responds to 140 A welding current.
The signal from the shunt is amplified by the shunt amplifier, so that a 119 mV
input signal from the shunt produces a 6.66 V output signal.
Transistor Q1 is turned on by IC8. This connects resistor R9 to 0 V, connecting
resistors R8 and R9 in parallel with R6 and R7. With R10, these resistors form a
potential divider which divides the 6.66 V to 1.48 V, which is then supplied to
pin3ofIC2.
IC2 is a buffer circuit. The processor receives a signal representing the welding
current from output pin 6 of IC2. Resistor R4 connects the shunt signal to the
control amplifier.
LTO 250
250A welding current produces 119mV ±1mV at the shunt. The signal from
the shunt is amplified by the shunt amplifier, so that a 119 mV input signal from
the shunt produces a 6.66V output signal. Resistors R10, R6 and R7 on circuit
board AP01 divide this voltage to 2.65V, which is then supplied to pin 3 of IC2.
IC2 is a buffer circuit. The processor receives a signal representing the welding
current from output pin 6 of IC2. Resistor R4 connects the shunt signal to the
control amplifier.

-- 1 8 --
clto0de2
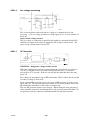
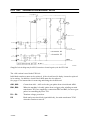
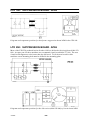
AP01:6 Arc vo ltag e monitoring
cltn0e13
This circuit measures and scales the arc voltage to a suitable level for the
processor. 64 V arc voltage produces a voltage signal of 5.1 V at the cathode of
diode D3.
Open--circuit voltage control
The arc voltage is connected to input D2 and supplied to potential divider R29
and R30, the output from which is supplied to the voltage control circuit. The
open--circuit voltage must be about 70V.
AP01:7 HF Generator
WARNING: Dangerous voltages in this circuit.
When the welding torch switch is operated, and the open--circuit arc voltage is
over 50 V, relay RE1 closes and turns on HF generator AP11. It remains
activated for 0.75 seconds. If the arc has not str u ck within this time, the relay
drops off.
The voltage on the primary side of HF transformer TV01 is about 400 V, and the
secondary voltage is about 8 kV.
From serial number xxx--006--xxxx a new type of HF generator is used, see the
spare parts list. This generator produces about 500 V on the primary side of the
HF transformer and about 10 kV on the secondary side.
The new HF generator replaces the old type. When fitting the new generator to
older m achines, three new mounting holes for the generator must be drilled. Fit
the generator with the connection terminal turned towards the base plate.

-- 1 9 --clto0de2
AP01:9 Machine type indicator
As the same circuit boards are used in other machines, it is necessary for the
processor to know what type of machine it is controlling. A link is therefore
provided connector G to short out a pull--up resistor. In the LTO 160 the link
connects G1 -- G4, and in the LTO 250 it connects G1--G3.
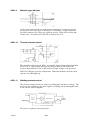
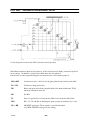
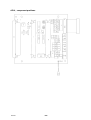
AP01:10 Thermal overload cutout
cltn0e19
The thermal overload switch, ST01, is normally closed, which means that input
K2 is at 10 V. This voltage is dropped by the potential divider formed by
resistors R31 and R32 to 4.8 V, and used as an input voltage to the processor.
LED V05 indicates excessive temperature. When the thermal overload cutout
operates, the LED lights up.
AP01:11 Welding process con t rol
The processor inputs are the set values of welding data and the arc voltage. The
processor also calculates a set value signal for welding current and supplies this
to the current control amplifier.
The process regulator control principle

-- 2 0 --
clto0de2
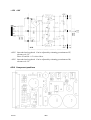
AP01:12 Motor control interface circuits
The reference voltages for rotation and wire feed are generated on circuit board
AP01. The +15 V and 5 V voltages are power supplies for the galvanic
separation of the speed and direction signals on circuit board AP12.
Potentiometers R102, R104, R107 and R109 are adjusted and set at the time of
manufacture of the circuit board. They can be checked as described below:
Rotation
1 Remove circuit board AP07 and fit test board 0740 859 001 in its place.
2 Measure the voltage between B7 and B26.
3 Set a rotation speed of 100% on the control unit.
4 Adjust R109 to produce a voltage of --10.0 V 0.005 V.
5 Stop t he rotation and adjust R107 until the voltage is 0 V +0.001 V.
6 Repeat points 4 and 5 until the values are within the tolerance limit.
Wire feed
1 Remove circuit board AP07 and fit test board 0740 859 001 in its place.
2 Measure the voltage between B4 and B26.
3 Set the wire feed speed at 2.2 m/min.
4 Adjust R102 to produce a voltage of --7.8 V 0.005 V.
5 Stop the wire feed and adjust R104 until the voltage is 0 V +0.001 V.
6 Repeat points 4 and 5 until the values are within the tolerance limit.
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
Related papers
Other documents
-
Poly Planar MA7020 Installation guide
-
Mircom LT-6060 Installation guide
-
Conceptronic CLHDMIHOOK Datasheet
-
Poly Planar MA4052 User guide
-
Poly Planar MA7050 Installation guide
-
Poly Planar MA7065 Installation guide
-
sako SUNSEE Owner's manual
-
Audioplex PRE-B1 Installation guide
-
TECPHILE AP11 Wireless Magnetic Keyboard Case User manual
-
Conceptronic C02-001 Datasheet

































































































