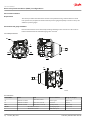
Danfoss RDM L is a reverse displacement motor with a cartridge mount, designed for use in a variety of applications. It features a compact design, high efficiency, and low noise levels. The motor is available in a range of sizes and configurations to meet the specific requirements of your application.
Some of the key features of the Danfoss RDM L include:
- Compact design for easy installation in tight spaces
- High efficiency for reduced energy consumption
- Low noise levels for a quieter operating environment
- Variety of sizes and configurations to meet your specific needs
The Danfoss RDM L is ideal for use in a wide range of applications, including:
Danfoss RDM L is a reverse displacement motor with a cartridge mount, designed for use in a variety of applications. It features a compact design, high efficiency, and low noise levels. The motor is available in a range of sizes and configurations to meet the specific requirements of your application.
Some of the key features of the Danfoss RDM L include:
- Compact design for easy installation in tight spaces
- High efficiency for reduced energy consumption
- Low noise levels for a quieter operating environment
- Variety of sizes and configurations to meet your specific needs
The Danfoss RDM L is ideal for use in a wide range of applications, including:



















-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
Danfoss RDM L User guide
- Type
- User guide
- This manual is also suitable for
Danfoss RDM L is a reverse displacement motor with a cartridge mount, designed for use in a variety of applications. It features a compact design, high efficiency, and low noise levels. The motor is available in a range of sizes and configurations to meet the specific requirements of your application.
Some of the key features of the Danfoss RDM L include:
- Compact design for easy installation in tight spaces
- High efficiency for reduced energy consumption
- Low noise levels for a quieter operating environment
- Variety of sizes and configurations to meet your specific needs
The Danfoss RDM L is ideal for use in a wide range of applications, including:
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
Related papers
-
Danfoss RDM K User guide
-
Danfoss E-MOPI-TI003-E Installation guide
-
Danfoss Series 20 Pumps 70cc Service guide
-
Danfoss Series 20 Axial Piston Pumps Service guide
-
Danfoss K Frame Series User guide
-
Danfoss S90 M Installation guide
-
Danfoss S45 User guide
-
Danfoss Hot Wire Cutter Installation guide
-
Danfoss M-MFB15-15 Fixed Inline Piston Motor User manual
-
Danfoss OSP Neutral Position Springs Tech Note User guide
Other documents
-
Craftsman D302140 Malay
-
Craftsman 91pc Tool List
-
 Continental Hydraulics Vane Pump Installation guide
Continental Hydraulics Vane Pump Installation guide
-
Aigo E063 Datasheet
-
Toro Groundsmaster 4700-D Rotary Mower User manual
-
 Haldex G1204C5A300N00 Owner's manual
Haldex G1204C5A300N00 Owner's manual
-
ESAB RDM-2000 Robotic Deflection Mount Installation guide
-
Power Fist 8339822 Owner's manual
-
Atos F003 Owner's manual
-
Ashcroft KM41 Installation guide


























