
DMR System Planner


Copyright Information
Hytera is the trademark or registered trademark of Hytera Communications Co., Ltd.
(the Company) in PRC and/or other countries or areas. The Company retains the
ownership of its trademarks and product names. All other trademarks and/or product
names that may be used in this manual are properties of their respective owners.
The product described in this manual may include the Company’s computer
programs stored in memory or other media. Laws in PRC and/or other countries or
areas protect the exclusive rights of the Company with respect to its computer
programs. The purchase of this product shall not be deemed to grant, either directly
or by implication, any rights to the purchaser regarding the Company’s computer
programs. Any of the Company’s computer programs may not be copied, modified,
distributed, decompiled, or reverse-engineered in any manner without the prior
written consent of the Company.
Disclaimer
The Company endeavors to achieve the accuracy and completeness of this manual,
but no warranty of accuracy or reliability is given. All the specifications and designs
are subject to change without notice due to continuous technology development. No
part of this manual may be copied, modified, translated, or distributed in any manner
without the express written permission of us.
If you have any suggestions or would like to learn more details, please visit our
website at: http://www.hytera.com.
Software Version
All the features in the system planner is based on R5.0 or above.

Revision History
Version Date Description Remarks
R1.0 November 21, 2012 Initial release

1
Contents
1 DMR Introduction................................................................................................ 5
1.1 Analog Communication VS Digital Communication......................................... 6
1.2 Hytera DMR Technology Introduction.............................................................. 7
1.3 Hytera DMR Technology Highlights................................................................. 8
2 Brief Introduction of DMR Functions ................................................................... 9
2.1 Basic Parameter Introduction .......................................................................... 9
2.2 Voice Services................................................................................................11
2.2.1 Group Call ......................................................................................................11
2.2.2 Private Call.....................................................................................................11
2.2.3 All Call ........................................................................................................... 12
2.2.4 Phone............................................................................................................ 12
2.3 Data Service.................................................................................................. 16
2.3.1 Text Message ................................................................................................ 16
2.3.2 GPS............................................................................................................... 17
2.4 General Services........................................................................................... 18
2.4.1 Supplementary Service ................................................................................. 18
2.4.2 One Touch Call.............................................................................................. 20
2.4.3 Encrypt .......................................................................................................... 21
2.4.4 Telemetry....................................................................................................... 24
2.4.5 VOX............................................................................................................... 28
2.5 Emergency Alarm.......................................................................................... 30
2.5.1 Alarm............................................................................................................. 31
2.5.2 Emergency Call ............................................................................................. 32
2.5.3 Alarm with Call .............................................................................................. 32
2.5.4 Lone Worker.................................................................................................. 33
2.5.5 Man Down ..................................................................................................... 34

Hytera DMR System Planner
2
2.6 Scan .............................................................................................................. 36
2.6.1 Scan List ....................................................................................................... 38
2.6.2 Scan Stay Condition...................................................................................... 39
2.6.3 Channel Scan Order...................................................................................... 40
2.7 Roaming........................................................................................................ 43
2.7.1 Roaming Methods ......................................................................................... 44
2.7.2 Configuring the RSSI Threshold.................................................................... 47
2.7.3 Setting Beacon Duration and Beacon Interval............................................... 51
2.7.4 Performance while Roaming ......................................................................... 54
2.8 Hytera Patented Features ............................................................................. 55
2.8.1 Pseudo Trunk ................................................................................................ 55
2.8.2 Priority Interrupt............................................................................................. 62
2.9 Analog function ............................................................................................. 72
2.10 Back-to-Back................................................................................................. 74
2.10.1 Mobile Radio Accessory Pin ...................................................................... 74
2.10.2 Repeater Accessory Pin ............................................................................ 75
2.11 Hytera DMR Application Protocol .................................................................. 77
2.11.1 Radio Registration Service (RRS) ............................................................. 78
2.11.2 Positioning System(LP)......................................................................... 80
2.11.3 Radio Control Service(RCP)................................................................. 82
2.11.4 Text Message Service (TMP)..................................................................... 83
2.11.5 Data Transmission Service (DTP).............................................................. 84
2.11.6 Telemetry Service (TMP) ........................................................................... 85
2.11.7 Real-time Transport Service (RTP)............................................................ 86
3 Components of DMR System ........................................................................... 87
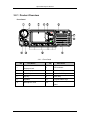
3.1 Portable Radio............................................................................................... 88
3.1.1 Product Overview.......................................................................................... 89
3.1.2 Basic Operations........................................................................................... 92
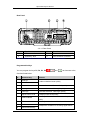
3.2 Mobile Radio ................................................................................................. 95
3.2.1 Product Overview.......................................................................................... 96

Hytera DMR System Planner
3
3.2.2 Basic Operations........................................................................................... 99
3.3 Repeater ..................................................................................................... 103
3.3.1 Introduction ................................................................................................. 104
3.3.2 Basic Operations......................................................................................... 106
3.4 RDAC (Repeater Diagnostics and Control) ..................................................110
3.4.1 Diagnose ......................................................................................................111
3.4.2 Control..........................................................................................................112
3.4.3 Repeater Configuration ................................................................................113
4 DMR System Topologies..................................................................................117
4.1 Direct Mode..................................................................................................118
4.1.1 Back-to-Back Mobile Radio Application in Direct Mode................................119
4.1.2 Further Development Functions in Direct Mode .......................................... 123
4.1.3 Telemetry..................................................................................................... 124
4.2 Repeater Mode ........................................................................................... 127
4.2.1 Back-to-back Repeaters.............................................................................. 128
4.2.2 Radio Dispatch............................................................................................ 133
4.2.3 Telemetry..................................................................................................... 133
4.3 IP Multi-site ................................................................................................. 135
4.3.1 Network Topology of IP Multi-site Connect .................................................. 137
4.3.2 Local Area Network ..................................................................................... 137
4.3.3 Wide Area Network (WAN) .......................................................................... 138
4.3.4 WAN and LAN ............................................................................................. 140
4.3.5 Broadband Wireless Access........................................................................ 141
4.3.6 Digital Functions Supported in IP Multi-site Connect Mode......................... 146
4.4 Access Management................................................................................... 147
4.4.1 Local Access Management ......................................................................... 148
4.4.2 Multi-site Access Management.................................................................... 149
4.5 Repeat request priority ................................................................................ 152
4.6 Super Master............................................................................................... 152
4.6.1 Star Network Architecture............................................................................ 153

Hytera DMR System Planner
4
4.6.2 Double-layer Network Architecture.............................................................. 154
4.7 Phone Interconnect ..................................................................................... 155
4.7.1 Phone Applications in Local Mode .............................................................. 155
4.7.2 Phone Applications in IP Multi-site Connect Mode ...................................... 158
5 DMR System Considerations.......................................................................... 159
5.1 Important notes of R4.0 update................................................................... 159
5.1.1 Subscriber ................................................................................................... 159
5.1.2 Repeater ..................................................................................................... 159
5.1.3 Interaction between Subscriber and Repeater ............................................ 160
5.2 Important notes of R4.5 update................................................................... 160
5.2.1 Subscriber ................................................................................................... 160
5.2.2 Repeater ..................................................................................................... 160
5.2.3 Interaction between Subscriber and Repeater ............................................ 160
5.3 Function interaction..................................................................................... 161
5.3.1 Phone Interconnect ..................................................................................... 161
5.3.2 Encryption ................................................................................................... 162
5.3.3 Pseudo Trunking ......................................................................................... 162
5.3.4 Priority Interrupt........................................................................................... 163
5.3.5 Roaming...................................................................................................... 165
5.3.6 IP Multi-site Connect ................................................................................... 166
5.3.7 Telemetry..................................................................................................... 169
6 DMR System Documentation and Applications............................................... 171
6.1 Documentation ............................................................................................ 171
6.2 CPS............................................................................................................. 172
6.3 Tuner........................................................................................................... 173
A. Appendix......................................................................................................... 175
A.1 Abbreviation ................................................................................................ 175
A.2 Hytera Official Website ................................................................................ 176

5
1 DMR Introduction
This chapter mainly introduces the Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) standards, focusing
on the protocol principles and tendency of the digital technology.
DMR is an open digital radio standard for professional mobile radio users published
by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in 2004. This
standard aims to achieve a high-efficient professional wireless communication
system with less complexity and low cost.
DMR standard covers three tiers:
Tier I: This tier is for license-free use in the 446MHz band. It utilizes 6.25kHz
FDMA technology, targeted at the business market. Updated recently, Tier I
supports trunking system and becomes available for the professional market.
Tier II: This tier is for conventional communication. It adopts two-slot 12.5kHz
TDMA technology and targets the professional market.
Tier III: This tier is for trunking and simulcast communication. Besides two-slot
12.5kHz TDMA technology, it also supports network management applications.
This tier is targeted at professional market.
Digital technology presents a predictable tendency of the wireless communication,
which delivers products of better communication quality, higher security, more
spectrum resource and richer functions compared with analog products.
Hytera adopts the DMR technology and develops the digital radio compatible with
analog work mode. Hytera DMR radios can convert analog signals into digital
signals, and transmits both data and voice. Digital signals can be enhanced via the
gain and transmitted in a wider coverage. Based on TDMA technology, digital radios
accommodate much more subscribers.

Hytera DMR System Planner
6
1.1 Analog Communication VS Digital
Communication
Analog communication has poor privacy protection. The signal transmitted by an
analog radio can be received by any other analog radio on the same channel. Thus
interference easily occurs in analog communication. However, digital
communication employs some technologies such as color code, which significantly
enhance the interference resistance.
In analog communication, the signal becomes weakened gradually, and thus affects
the coverage. In digital communication, however, the signal can be encrypted and
transmitted in a wider coverage. Signal interference also has a great impact on the
communication coverage: the more the signal interference occurs, the smaller the
coverage becomes.
In analog communication, the transmitting radio transmits on a specified channel
and the receiving radio has to receive the signals on the same channel. In digital
communication, the TDMA technology allows to divide the 12.5kHz channel into two
slots, which can serve as an independent channel. The transmitting radio transmits
on one slot (while the other slot stays idle), and the receiving radio detects the
signaling on both slots and receives signal on the active slot.
In analog communication, the FDMA technology allows multiple subscribers
simultaneously access a channel. However, with TDMA technology, one 12.5kHz
channel is divided into two 6.25kHz slots, and thus the spectrum resource is
expanded; moreover, the RF performance remains the same even though the
channel is divided. Compared with analog products, DMR products can
accommodate more subscribers and thus increases the system scope.

Hytera DMR System Planner
7
1.2 Hytera DMR Technology Introduction
Hytera adopts the DMR technology and makes developments in compliance with
the ETSI DMR Tier II standards.
Hytera DMR radio collects the audio signals at the microphone, converts the audio
signals to analog signals, and then converts the analog signals to digital signals. In
addition, the sampling signal should be strong enough to ensure high audio quality,
so certain techniques are required to compress the signal.
After sampling, the radio processes the signal through coding technology, to filter
the unwanted noises and make signal compression.
The encoded signal (audio or data) is then transmitted in frames. The signal with
signaling can generate a digital data packet, which consists of the header (mainly
the control and air interface information) and payload (encoded audio or data) and
can be transferred over IP network. The header information repeats periodically
during transmission, which makes the signal more reliable and realizes the late
entry function.
The framing signal gets encoded for FM transmission. The bits contained in the
digital packets are encoded as symbols representing the amplitude and phase of the
modulated carrier frequency. Finally, the signal gets amplified and then transmitted.

Hytera DMR System Planner
8
1.3 Hytera DMR Technology Highlights
Hytera DMR technology has many advantages compared with analog technology,
especially in aspects such as spectrum resource, capacity, coverage and
encryption.
The DMR technology divides one channel into two alternative slots, and thus allows
twice the channels based on the same spectrum resource. This is a big help to
relieve the stress of increasing shortage in spectrum resource. The 2-slot
technology doubles the repeater functions, which greatly reduces the cost and
minimizes the configuration complexity. Furthermore, its compatibility with analog
mode makes the transition cost-effective and smooth. The radio transmits on the
two slots alternatively, which can reduce the transmission time length and thus
ensure a longer endurance.
With Hytera DMR radios, it becomes possible to use two slots simultaneously. For
example, you can receive audio and data simultaneously on both slots, or transmit
audio on one slot while receive signaling to realize special functions, such as Priority
Interrupt, on the other slot. The audio transmission will not be affected by data
reception. In this way, users can experience a more efficient and swift
communication.
With DMR technology, the communication has a larger coverage and better
reliability. Analog signal is transmitted in sine waveform which may be subject to
more interference; while digital signal is transmitted in rectangular waveform that
can be optimized easily. In addition, digital signals can be transmitted very far by
either repeater or IP network. However, analog signal cannot be sent through IP
network.
During analog transmission, the signal can be received once the frequency is known,
and it can be decrypted easily even scrambler is applied. This is far from enough for
users who require reliable security. However, the digital signal can be encrypted
through special mechanisms, in which keys are applied to make the signal
inaccessible to anyone except those possessing the same key, so as to achieve
communication privacy.

9
2 Brief Introduction of DMR Functions
DMR digital communications system realizes voice services (such as group call,
private call, all call, etc.), data services (such as text message, GPS data, ect.) and
supplement services.
This chapter mainly introduces some basic functions and their parameter
configurations of DMR conventional system.
2.1 Basic Parameter Introduction
DMR configurations involve some basic parameters which determine the basic
attributes of DMR equipment.
The main parameters are as follows:
Radio ID: The unique identification information of each radio. You must designate an
ID to the radio for other users to identify it when making a private call or sending
messages. The private call ID is the Radio ID.
Group Call ID: Used to identify a particular group. The group members must define
the group call ID, or they cannot receive the corresponding call.
Alias: The alias of a radio, private call contact and group call contact. It is
configurable for you so that it is more convenient to find the contact to call.
Channel: The channel provides communication services using the DMR digital
signaling. There is at least 1 digital channel and at most 1,023 digital channels that
can be established.
Color Code: This is used to identify a system. Users who wish to communicate with
each other in the same system are assigned with the same color code. A radio
ignores the channel activity which does not match the preset color code in this field,
as it is assuming the activity belongs to other system. In case that there are multiple
systems to be monitored, then different color codes must be assigned to the
corresponding channels. Range of the color code: 0 – 15.
Tx/Rx Frequency: The Tx/Rx frequency of the current channel. Both the frequencies
of the communicating parties must be matched.
Tx Admit: This is used to control the Tx authority of the radio. The administrator
can authorize different levels of users to different Tx rights: the low level users
can be authorized to Channel Free or Color Code Free; as for the high level
ones, they are set to Always Allow.

Hytera DMR System Planner
10
Tx Admit: This is used to prevents you from transmitting on channels that are
already in use.
Always Allow: The radio can transmit via the PTT key any time regardless of the
channel.
Channel Free: The radio is allowed to transmit when the channel is free.
Code Color Free: The radio can transmit only when the channel is free or the
color code is not matched.
Group Call Hang Time: The time in which the radio still hangs in the group call after
the call is over. In other words, a member's PTT operation can call back the group
directly without contact list selection.
Private Call Hang Time: The time in which the radio still hangs in the private call
after the call is over. Within this period, either of the communication parties can call
back the other directly by holding the PTT key without contact list selection or
Acknowledge.
Time Slot: DMR applies TDMA scheme to divide the 12.5kHz channel into two
consecutive slots. Either slot can be used for communication or data transmission.
Slot 1: Slot 1 is used for transmitting and receiving in Repeater mode, as well as
receiving signals from repeater in Direct mode.
Slot 2: Slot 2 is used for transmitting and receiving in Repeater mode, as well as
receiving signals from repeater in Direct mode.
Pseudo Trunk: Both slots can be used simultaneously for communication or
data transfer in Direct and Repeater modes. And in Repeater mode, the slot is
alternative.
Note: Pseudo Trunk is one of the Hytera patents. Generally, in Repeater mode,
DMR standard protocol defines radios to transmit in the fixed slot. If the slot is
occupied, the radio has to wait for it instead of another free slot, wasting the
frequency band resources. However, the Pseudo Trunk feature allows two different
calls to be made simultaneously in Direct mode, as well as the dynamic slot
distribution in Repeater mode. This brings great convenience and efficiency to the
communications.

Hytera DMR System Planner
11
2.2 Voice Services
DMR voice services support group call, private call and all call. It means that you
can make a call with a group, a person and all users in the system.
2.2.1 Group Call
A group call is transmitted to a group by a user. Each member in the group can hear
the others. The configuration of the group call contacts via the CPS is prior to make
a group call. After the configuration, you can make a group call by holding down PTT.
All the group members must be in the same slot on the same channel, and have the
matched Tx and Rx frequency and color code.
Parameter Configuration
The radio can only receive the group calls from the groups included in the Rx Group
List. Thus, to receive a group call, the available groups must be added into the Rx
Group List via the CPS. To make a group call, there must be available group
members in the contact list. In addition, the group call ID must be set.
Group Call Hang Time: Within this period, the group members can hold down PTT to
call any time without selecting the group from the contact list.
Tx Admit: The group call making radio shall not be set to “Rx Only”. Also, it must be
authorized to transmit group call prior to the call making.
Temporary Group Call
A user out of the group can make a temporary group call by the keypad, but such
calls will not be recorded into the call logs. In the temporary group call hang time,
the members can call back.
2.2.2 Private Call
A private call is made between two individual radios only. Both parties must be in the
same slot on the same channel and have the matched Tx and Rx frequency and
color code.
To make a private call, the radio must be designated with an ID. Then the call maker
will need to select the ID or alias of the called party to make a call.
Parameter Configuration
The ID of both the calling party and the called party must be configured before the

Hytera DMR System Planner
12
call making. You may add the ID or alias of the contacts into the contact list via the
CPS or the radio menu. Even if you do not add the ID or alias, you can also enter the
call ID of a contact for calling.
Private Call Hang Time: Within this period, both parties can hold down PTT to talk
without selecting the other again.
Tx Admit: The private call making radio shall not be set to “Rx Only”. Also, it must
be authorized to transmit private call prior to the call making.
2.2.3 All Call
All Call is a call from an individual radio to all radios in the system. All Calls do not
communicate through special time slots or channels within the system. Only the
user with the high authority can make an all call. This is especially significant when
you need to communicate with all users in the entire channel. Both parties must be
in the same slot on the same channel and have the matched Tx and Rx frequency
and color code.
The all call maker must be authorized first via the CPS.
Parameter Configuration
Call ID value: 16777215 (not editable), An all call user should be with high authority.
The system administrator needs to set the all call user based on actual
requirements.
Tx Admit: The all call making radio shall not be set to “Rx Only”.
2.2.4 Phone
The Phone feature fullfils the communications between radio and phone via DTMF
signaling and the PSTN system.
With the Phone feature, the radio can be connected to the local PSTN gateway
device via the repeater, and then connected to the phone system, to realize the
communications. Besides, the radio can be connected to the remote PSTN gateway
device through the multi-site network to establish the communications. See the
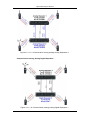
following two figures.
The Phone feature is supported in both analog mode and digital mode. If you use
the multi-site network to realize the remote Phone feature, you should use the radio
and the repeater both in digital mode. The Phone feature only supports a call
between a radio of the system and a phone at a time, instead of multiple phones.

Hytera DMR System Planner
13
Figure 2.2.4-1: Phone Network System via Local PSTN Gateway
Figure 2..2.4-2: Phone Network System with Multi-site PSTN Gateway
The Phone feature realizes the connection between the repeater and the PSTN
network by transmitting a call and DTMF signaling, so as to achieve the
communications between the radio and the phone. Phone interconnection, a special
form of the DTMF signaling application, is exclusively used for the communications
between radio and phone. Its operation is like this: the radio encodes two specific
tones into the DTMF code to represent for the digital symbols, loads the carrier with
the DTMF code and transmits it to the repeater. When the repeater is connected to
the radio, it will transfer the received DTMF code to the PSTN gateway device for
the communication with the phone. The call and the DTMF code are transmitted
together in this process: the radio transmits a call and an access code to connect to

Hytera DMR System Planner
14
the repeater and the public switched telephone network (PSTN) respectively,
achiving its communications with a specific phone. The call ends when the radio
sends the de-access code or when the phone is hung up. Like the call between
the radios, the call between the radio and the phone is subject to time limit.
The DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) encoding technology uses two sepcific
tones (high and low) to represent a number (as shown in the following figure), so as
to realize some features. It is often designed with 16 keys (numeric keys 0~9 and
function keys *, #, A, B, C and D). As the DTMF code consists of a high frequency
(f1) and a low frequency (f2), the equation of corresponding signal is:
F(t)=A.sin(2.pi.f1.t)+A.sin(2.pi.f2.t).
Figure 2.2.4-3: Tone Combination for DTMF
Note: A, B, C, D, and the pause code (“P”) only can be input via the CPS.
There are two dialing methods including live dial and buffer dial.
Live Dial: During the voice transmission via PTT, the radio will send the
corresponding DTMF code immediately after you enter a digit via the keypad, like
dialing the number on the phone. When you release PTT, the radio will stop the
transmission. When making Live Dial operation, press the programmed key to
transmit the access code.
Buffer Dial: Enter the needed DTMF code and then hold down PTT to transmit it,
like dialing on the mobile phone. This method works only when you enable the
DTMF keypad mode. You can enable the DTMF keypad via the CPS or the radio
menu.
In analog mode, the radio will load the carrier with the DTMF code and transmit the
Low frequency
High frequency

Hytera DMR System Planner
15
code directly. The repeater will transfer the received DTMF code to the PSTN
gateway to connect the phone system for communications between the radio and
the phone. When a call is received from the phone, the radio needs to send the
DTMF code to put through the call. During the call, the phone can receive the voices
transmitted by any other radio in the system. Likewise, the voice transmitted by the
phone will be received by any radio in the system.
In digital mode, the radio will transmit signalings and the DTMF code to the repeater.
Then the repeater will transfer the DTMF code to the PSTN gateway device to
connect the phone system and put through the call. When the buffer dial is used, the
radio call type matches the type of the transmitting contact on the channel. If a
private call contact is selected as the transmitting contact, the radio will make a
private call to the phone. The radio can receive call from the phone and private calls
from other radios simultaneously. If a group call contact is selected, the radio will
make a group call to the phone. All group members can communicate with the
phone upon establishing this call. If an all call contact is selected, the radio will make
an all call to the phone. All radios in the system can communicate with the phone
upon establishing this call. During live dialing, the call type depends on which kind of
call is initiated upon holding down PTT, but is not necessarily associated with the
transmitting contact on the channel. During buffer dialing, the call type is consistent
with the type of the transmitting contact when you make a call from the contact list.
Generally, what kind of call the phone initiates to the radio is subject to the type of
the transmitting contact in the repeater. However, if the radio makes a private call
whose ID is the repeater’s ID, the call type has no bearing on the type of the
transmitting contact in the repeater.
After a radio sends the Access Code and talks with the phone, the phone will receive
voice from other radios in the system. In this case, interference may occur if several
radios send voice simultaneously. The voice from radio with strong RSSI will replace
one from radio with weak RSSI.

Hytera DMR System Planner
16
2.3 Data Service
DMR data services include text message, GPS, supplement services, etc. In this
chapter, we mainly introduce text message and GPS services.
2.3.1 Text Message
With DMR technology, you can send, receive, forward and save text messages
using your radio. For your convenience, you can preset the regular text messages
and save them in the radio in advance. Then you can send a preset message
directly or after you edit it. In the radio with display, you can enter any text message
via the keypad, save it in the radio and send it. As for the radio without display, you
can only preset the message via the CPS, and send it by the programmed key.
However, you are not able to check or edit it through the radio. You can use a
Hytera DMR radio to send text message to an individual user, a group or the control
station, and reply or forward the message to other radios.
Text messages are applied in:
Communication of sensitive information;
Noisy environment where it is hard to hear the voice clearly;
The radio with problem in voice services.
Text message include two categories: private message and group message.
Private message: text message sent between two radios.
Group message: text message sent by a radio to a group of radios. The group
message differs from the private message in that it is a point-to-many service
without acknowledge.
Parameter configuration
The same as private call, text message needs such parameter configurations: ID,
color code, frequency and slot, and it is subject to Tx Admit.
As private message is sent between two radios, it does not involve a third party ID.
Both parties must be in the same slot on the same channel and have the consistent
Tx and Rx frequency and color code.
To send private message, you need to set the ID first. You may search for the
receiver by the ID or the alias.
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
 97
97
-
 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
-
 125
125
-
 126
126
-
 127
127
-
 128
128
-
 129
129
-
 130
130
-
 131
131
-
 132
132
-
 133
133
-
 134
134
-
 135
135
-
 136
136
-
 137
137
-
 138
138
-
 139
139
-
 140
140
-
 141
141
-
 142
142
-
 143
143
-
 144
144
-
 145
145
-
 146
146
-
 147
147
-
 148
148
-
 149
149
-
 150
150
-
 151
151
-
 152
152
-
 153
153
-
 154
154
-
 155
155
-
 156
156
-
 157
157
-
 158
158
-
 159
159
-
 160
160
-
 161
161
-
 162
162
-
 163
163
-
 164
164
-
 165
165
-
 166
166
-
 167
167
-
 168
168
-
 169
169
-
 170
170
-
 171
171
-
 172
172
-
 173
173
-
 174
174
-
 175
175
-
 176
176
-
 177
177
-
 178
178
-
 179
179
-
 180
180
-
 181
181
-
 182
182
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
Related papers
-
 Hytera BD502i Owner's manual
Hytera BD502i Owner's manual
-
Hytera BD352i Owner's manual
-
Hytera BD352i Owner's manual
-
 Hytera BD61X User guide
Hytera BD61X User guide
-
Hytera MD622i Owner's manual
-
 Hytera BD302i Owner's manual
Hytera BD302i Owner's manual
-
 Hytera PD605 Owner's manual
Hytera PD605 Owner's manual
-
 Hytera BP56X Digital Portable Radio User manual
Hytera BP56X Digital Portable Radio User manual
-
 Hytera BP51X Digital Portable Radio User manual
Hytera BP51X Digital Portable Radio User manual
-
 Hytera HP68X User guide
Hytera HP68X User guide
Other documents
-
 Titan Radio TR2X Owner's manual
Titan Radio TR2X Owner's manual
-
Titan TR3X Digital Portable Radio User manual
-
Raven M4x FlexGate Quick Reference Manual
-
Kirisun PT8000 User manual
-
 DV Development Group DV4mini User manual
DV Development Group DV4mini User manual
-
AnyTone AT-D878UV Operating instructions
-
Kirisun DP480 User manual
-
Alinco DJ-MD5X User manual
-
RCA BR200DV User manual
-
Alinco DJ-MD5 User manual






























































































































































































