Insys i-modul ISDN HIX Designer’s Guide
- Category
- ISDN access devices
- Type
- Designer’s Guide

Designer's Guide
i-modul ISDN HIX V4


Copyright © July 12 INSYS MICROELECTRONICS GmbH
Any duplication of this manual is prohibited. All rights on this documentation and
the devices are with INSYS MICROELECTRONICS GmbH Regensburg.
Trademarks
The use of a trademark not shown below is not an indication that it is freely avail-
able for use.
MNP is a registered trademark of Microcom Inc.
IBM PC, AT, XT are registered trademarks of International Business Machine Cor-
poration.
INSYS®, e-Mobility LSG® and e-Mobility PLC® are registered trademarks of INSYS
MICROELECTRONICS GmbH.
Windows™ is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Publisher:
INSYS MICROELECTRONICS GmbH
Hermann-Köhl-Str. 22
D-93049 Regensburg, Germany
Phone: +49 941 58692 0
Fax: +49 941 58692 45
E-mail: [email protected]
Internet: http://www.insys-icom.com
Date: Jul-12
Item: 31-22-04.028
Version: 1.0
Language: EN

Content
1 Technical Data .........................................................................................6
1.1 Physical Features...................................................................................................6
1.2 Technological Features..........................................................................................7
1.3 Certifications..........................................................................................................7
2 Connections.............................................................................................8
2.1 PCB Layout............................................................................................................8
2.2 Pin Layout Terminal Strip P1 .................................................................................9
2.3 Pin Layout Terminal Strip P2 .................................................................................9
2.4 Pin Layout Terminal Strip P3 ...............................................................................10
2.5 PIN Specifications................................................................................................11
2.5.1 Reset input ............................................................................................. 11
2.5.2 Indication Signals ................................................................................... 11
2.6 Connection Example for Serial Interface..............................................................12
2.7 Connection Example for Codec Interface ............................................................13
3 Function Overview.................................................................................14
4 Meaning of the Symbols and the Formatting in this Manual..................15
5 Operating Principle ................................................................................16
5.1 Operation with the Terminal Program..................................................................16
6 Functions ...............................................................................................18
6.1 Establishing or Accepting a Data Connection......................................................18
6.1 Querying the Alarm Inputs...................................................................................20
6.2 Automatic Call .....................................................................................................21
6.2.1 Configuring an Automatic Call ............................................................... 21
6.2.2 Disabling an Automatic Call ................................................................... 24
6.3 Data flow control .................................................................................................25
6.3.1 Hardware Data Flow Control (RTS/CTS)................................................. 25
6.3.2 Software Data Flow Control with XON/XOFF ........................................ 26
6.4 Remote Configuration..........................................................................................27
6.4.1 Remotely Configuring the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 ................................... 27
6.4.2 Configuring the Remote Configuration Number .................................... 28
6.4.3 Configuring the Remote Configuration Password ................................. 28
6.4.4 Configuring the Permitted Callers for Remote Configuration ................ 29
6.5 Connection Configuration of the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 at the ISDN Basic Access
............................................................................................................................30
6.5.1 Configuration at Multipoint Interface (PMP, Point-to-Multipoint).......... 30
6.5.2 Configuration at Point-to-Point Interface (PTP, Point-to-Point).............. 30
6.6 Control Outputs ...................................................................................................31
6.7 TA+Configurator..................................................................................................32
6.8 Configuring the Transfer Protocol........................................................................33
6.9 Outputting CLIP of Incoming Calls ......................................................................34
6.10 Resetting the Device............................................................................................35
4 Jul-12

Contents
Jul-12 5
7 ISDN Error Messages.............................................................................36
7.1 Extended Error Messages with ISDN...................................................................38
8 Maintenance ..........................................................................................42
9 Firmware History ...................................................................................44
10 AT Command Reference........................................................................45
11 Special ISDN Parameters .......................................................................53
12 S Register ..............................................................................................55
13 TA+Configurator Command Reference..................................................56
14 Special AT Commands for Voice Functions ...........................................58
14.1 AT Commands for Accepting Voice Connections ................................................58
14.2 AT Commands for Controlling Voice Connections...............................................60
14.3 Responses of AT Commands for Voice Connections...........................................62
14.4 AT Commands for DTMF Detection.....................................................................65
15 Voice Connections at the Point-To-Point Connection.............................66
15.1 Incoming Voice Call.............................................................................................66
15.2 Outgoing Voice Call.............................................................................................66
16 Example for Handling Connections........................................................67
16.1 Initiating and Ending an Outgoing Data Connection............................................67
16.2 Initiating and Ending an Outgoing Voice Connection ..........................................67
16.3 Accepting an Incoming Voice Connection...........................................................68
16.4 Holding Connections ...........................................................................................69
17 CE/EMC Compliant Integration ..............................................................70
17.1 Your Application ..................................................................................................70
17.2 Application Interface / Terminal Strip P1 .............................................................70
17.3 Network Interface / Terminal Strip P2 (for Modem /ISDN)...................................70
17.4 Antenna Connection (if equipped) .......................................................................71
17.5 Further Recommendations ..................................................................................71
17.6 Reference Documents .........................................................................................71
18 Declaration of Conformity......................................................................72
19 Tables and Diagrams..............................................................................73
19.1 List of Tables .......................................................................................................73
19.2 List of Diagrams ..................................................................................................73
20 Index......................................................................................................74

Technical Data i-modul ISDN HIX V4
1 Technical Data
1.1 Physical Features
All specified data was measured with nominal input voltage, at full load, and an
ambient temperature of 25 °C. The limit value tolerances are subject to the usual
variations.
Physical Feature Value
Operation voltage VCC +5 V (± 5%) DC
HIGH level alarm input VIH > 2 V (max. VCC)
LOW level alarm input VIL < 0.8 V
HIGH level alarm output VOH
(3.3 V CMOS compatible)
> 2.4 V
LOW level alarm output VOL < 0.4 V
Input current of GND to internal VCC Typical 0.5 mA
Maximum output current for state
LOW IOLmax
1.6 mA
Maximum output current for state
HIGH IOHmax
100 μA
Total current consumption in idle approx. 25 mA
Total current consumption in active
state
approx. 60 mA
Total maximum current consumption max. 110 mA
Weight approx. 18 g
Dimensions (Length x Width x Height) 56.4 mm x 56.4 mm x 13.1 mm
Height of the terminal strip above PCB 6.5 mm
PCB thickness 1.6 mm
Temperature range 0°C – 70°C
Maximum permissible humidity 95% non-condensing
Table 1: Physical Features
6

i-modul ISDN HIX V4 Technical Data
1.2 Technological Features
Technological Feature Description
Transmission speed in B channel: 64000 bps
Transmission speed in D channel: 9600 bps (X31-D)
Transmission standards B channel V.110, V.120, X75, X31/X25, HDLC
(transparent), PPP sync-async,
BAP/BACP/ML-PPP, bit-transparent
Transmission standards D channel DSS1
Command sets Hayes dial (AT command set), V25bis
async. Hotline 108 DTR
SMS Sending T-Mobile, Vodafone, E-Plus
I/O 2 inputs, 2 outputs
Voice functionality yes
Table 2: Technological Features
1.3 Certifications
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 has the following license number for the connection to
the PSTN: CE-0682 for Europe (EC), Switzerland and Norway. The i-modul ISDN
HIX V4 is conform to the European safety requirements IEC 60 950.
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 has been developed in compliance with the following
guidelines and standards:
R&TTE 1999/5/EG
DIN EN 55022 Class B
DIN EN 61000-6-2
DIN EN 60950-1
CTR3
7

Connections i-modul ISDN HIX V4
2 Connections
2.1 PCB Layout
P3
P2
P1
Figure 1: PCB layout, terminal strip and fixing hole position
Figure 2: PCB layout, height profile
Item Type Description
P1 SAMTEC TW series 2-row 2 mm
pitch or Fischer SLY 6 / 81 20 Z
Serial interface, inputs and outputs
P2 SAMTEC TW series 2-row 2 mm
pitch or Fischer SLY 6 / 81 6 Z
Phone network interface
P3 SAMTEC TW series 2-row 2 mm
pitch or Fischer SLY 6 / 81 6 Z
Codec interface
Table 3: Specification and assignment of the terminal strips
8

i-modul ISDN HIX V4 Connections
2.2 Pin Layout Terminal Strip P1
Pin Type Signal Description
1 GND Ground of supply voltage (ground)
2 Supply VCC 5V DC supply voltage
3 GND Ground of supply voltage (ground)
4 Input TXD Transmit signal from the terminal of the RS232 line; TTL
level
5 GND Ground of supply voltage (ground)
6 Output RXD Receive signal from the RS232 line; TTL level
7 Output ID-PIN2 Reserved for 2. ID PIN
8 Input RTS~ Request to Send; TTL level (RS232 signal)
9 Output ID-PIN1 VCC (internal pull-up 10 kOhm)
10 Output CTS~ Clear To Send; TTL level (RS232 signal)
11 Input RESET~ RESET, TTL level, tmin = 3 s
12 Input DTR~ Data Terminal Ready; TTL level (RS232 signal)
13 Output OH~ Off Hook
14 Output DCD~ Data Carrier Detect; TTL level (RS232 signal)
15 Output RI~ Ring Signal TTL level (RS232 signal)
16 Output DSR~ Data Set Ready; TTL level (RS232 signal)
17 Output UA Switch output; TTL level
18 Input UE Alarm input; TTL level
19 Output UA2 Switch output 2; TTL level
20 Input UE2 Alarm input 2; TTL level
Table 4: Terminal strip connections description, terminal strip P1
The tilde "~" behind the signal description indicates that this signal is
"low active".
2.3 Pin Layout Terminal Strip P2
Pin Type Signal Description
1 Input SRB / RX- RJ45-Pin 5
2 Output STB / TX- RJ45-Pin 6
3 Input SRA / RX+ RJ45-Pin 4
4 Output STA / TX+ RJ45-Pin 3
5 Output Rx (BRA
ps)
Not connected
6 Output Tx (BRA
ps)
Not connected
Table 5: Terminal strip connections description, terminal strip P2
9

Connections i-modul ISDN HIX V4
2.4 Pin Layout Terminal Strip P3
Please observe further data from the Motorola MC145484 data sheet for imple-
menting the codec interface (refer to www.motorola.com)
Pin Type Signal Description
1 Output NF Out Codec analog output
max. output voltage: 1.575 Vpk
load capacity: Cmax = 500 pF
output current: Imin = ± 1.0 mA
load resistance: Rmax = 1 kOhm
output impedance: 1 Ohm
2 Output GND OUT Ground for output
3 Input NF IN Codec analog input
max. input voltage: 1.575 Vpk
input resistance: Rmin = 10 MOhm
input current: Ityp = 0.1 µA
input capacity: Cmax = 10 pF
4 Input GND IN Ground for input
Table 6: Terminal strip connections description, terminal strip P3
10

i-modul ISDN HIX V4 Connections
2.5 PIN Specifications
All following specifications are based on a supply voltage of VCC = 5 V ± 5%.
2.5.1 Reset input
Pin Signal Type Description
11 Reset Input Normal state: 1 (internal pull-up resistor)
Reset: 0 (against GND)
A minimum time of 3 s for activation is recommended to trigger the
reset safely
Table 7: PIN specifications - Reset input
2.5.2 Indication Signals
Pin Signal Type Description
13 OH Output
This output indicates Off-Hook of the modem.
Signaling:
Normal state: High (hung up)
Off-Hook: Low (off-hook)
15 RI Output
The ring indicator indicates an incoming connection attempt.
Signaling:
Normal state: High
Ring: Low
Table 8: PIN specifications - indication signals
Figure 3: Connection example of the OH signal
11

Connections i-modul ISDN HIX V4
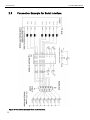
2.6 Connection Example for Serial Interface
Figure 4: Connection example of the serial interface
12

i-modul ISDN HIX V4 Connections
2.7 Connection Example for Codec Interface
Figure 5: Connection example for codec interface
Figure 6: Connecting the codec interface with electret microphone
13

Function Overview i-modul ISDN HIX V4
3 Function Overview
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 provides you with the following functions:
Operation at ISDN point-to-point and multipoint interface
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 can be operated at ISDN point-to-point
interfaces as well as at multipoint interfaces.
Different transfer protocols
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 supports different transfer protocols, like
e.g. X.75, V.110 and HDLC (for PPP connections).
Data buffering for serial transmission
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 provides send and receive buffers to adjust
the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 to the data processing speed of the
application.
Hardware and software data flow control
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 can interrupt the data flow of the
application via the control lines of the serial interface, if the buffers of
the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 exceed a certain level. An application can
also prompt the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 via a control line to interrupt the
data flow. As an alternative, the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 can control the
data flow via XOFF/XON characters in the data stream.
Automatic call
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 can initiate an automatic call either
depending on the DTR signal or independent of a status line.
Control outputs, controllable locally and remote
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 has two potential-free control outputs,
which can be used to switch other functions in an application.
Remote configuration
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 can be configured remotely using another
INSYS ISDN device and a terminal program.
Voice functionality
The voice functionality allows to establish voice connections with
other phones using a connected phone receiver for example. This
provides an easy communication with the service personnel at the
site. Moreover, the module also allows to accept voice calls.
14

i-modul ISDN HIX V4 Meaning of the Symbols and the Formatting in this
Ml
4 Meaning of the Symbols and the Formatting in
this Manual
This section describes the definition, formatting and symbols used in this manual.
The various symbols are meant to help you read and find the information relevant
to you. The following text is structured like a typical operating instruction of this
manual.
Bold print: This will tell you what the following steps will result in
After that, there will be a detailed explanation why you could perform the
following steps to be able to reach the objective indicated first. You can
decide whether the section is relevant for you or not.
An arrow will indicate prerequisites which must be fulfilled to be able to
process the subsequent steps in a meaningful way. You will also learn
which software or which equipment you will need.
1. One individual action step: This tells you what you need to do at this
point. The steps are numbered for better orientation.
A result which you will receive after performing a step will be marked
with a check mark. At this point, you can check if the previous steps
were successful.
Additional information which you should consider are marked with a
circled "i". At this point, we will indicate possible error sources and tell
you how to avoid them.
Alternative results and steps are marked with an arrow. This will tell
you how to reach the same results performing different steps, or what
you could do if you didn't reach the expected results at this point.
15

Operating Principle i-modul ISDN HIX V4
5 Operating Principle
This chapter describes the basic procedures to operate and configure an i-modul
ISDN HIX V4. In general, the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 is configured and operated via
AT commands. You can enter these commands yourself with the help of a terminal
program and the AT command reference.
5.1 Operation with the Terminal Program
In general, any terminal program can be used. We recommend the program
TeraTerm by T. Teranishi under Windows. It is available free of cost on the
Internet at http://hp.vector.co.jp/authors/VA002416/teraterm.html. You can
use the program "minicom" if you work in a Linux environment.
Caution!
Damage of the serial interface!
A possible direct connection of the serial interface of the i-
modul ISDN HIX V4 with a typical RS232 interface of a PC
overloads components of the module due to the higher
voltage levels.
Use an RS232 level converter (e.g. MAX232) to adjust both
interface types correctly.
Configuring and operating the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 with a terminal program
How to configure and operate the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 with a terminal
program.
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 is connected to the PC and supplied with power.
A terminal program is installed on the PC.
1. Start your terminal program.
2. Select the serial port, to which your i-modul ISDN HIX V4 is
connected.
COM1 under Windows corresponds to /dev/ttyS0 under Linux.
3. Type the character string AT into the terminal program. Complete the
entry by pressing the Enter key.
Each command input starts with AT and is completed with the Enter
key.
The
OK.
i-modul ISDN HIX V4 replies with
16

i-modul ISDN HIX V4 Operating Principle
If the i-modul ISDN
probable reasons:
a) the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 is switched off or
b) the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 is not in configuration mode or
c) the i-modul ISDN
HIX V4 does not respond, this may have three
HIX V4 is connected to another serial port. Check
it and repeat step 3.
mmands can be found in the chapter "AT
d
i-
at all
settings are stored safely and are available for the next restart.
4. Configure the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 using AT commands.
A reference of the AT co
Command Reference".
5. Save your entries with AT&W.
Not all configurations at the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 need to be save
actively by entering AT&W. Some settings are automatically saved
immediately. We still recommend sending the command AT&W to the
modul ISDN HIX V4 as your last configuration step to ensure th
17

Functions i-modul ISDN HIX V4
6 Functions
6.1 Establishing or Accepting a Data Connection
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 can call another ISDN TA (ISDN Terminal Adapter) via the
phone line and establish a data connection. After dialling a phone number, the i-
modul ISDN HIX V4 synchronises with the called TA and opens a data connection.
All incoming characters are transmitted to the other (called) TA during the active
data connection. Therefore, AT commands are not processed during a connection.
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 must be changed to command mode again using an
"Escape sequence" that it processes AT commands again during an active
connection. Then, the local i-modul ISDN HIX V4 processes the entered characters
as AT commands and does not transmit them to the remote terminal.
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 can accept an incoming connection in the same way. For
this, the "application" or the PC with the terminal program must support the
hardware data flow control at the serial interface, otherwise, the i-modul ISDN HIX
V4 does not accept the incoming connection. In this case, the hardware data flow
control must be disabled in the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 that a connection is accepted
regardless of the status of the application. The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 answers after
the configured number of ring tones and opens a connection.
This hardware data flow control is activated by default.
Configuration with AT commands
In order to establish a data
connection with the i-modul ISDN
HIX V4, use the command
Replace <number> with the phone
number of the remote terminal.
ATD<number>
In order to configure the data
connection protocol, use the
command
Refer to the AT command
reference for protocol details.
ATB
In order to configure the data
connection protocol, use the
alternative command
Refer to the AT command
reference for protocol details.
AT**PROT
18

i-modul ISDN HIX V4 Functions
If the remote terminal accepts the
connection, the i-modul ISDN HIX
V4 indicates
CONNECT
If the remote terminal is busy, the i-
modul ISDN HIX V4 indicates BUSY
If no connection can be
established, the i-modul ISDN HIX
V4 indicates
NO CARRIER
if the i-modul ISDN HIX V4 cannot
start a dial-up procedure, it
indicates
NO DIALTONE
In order to change to command
mode during a data connection,
use the escape sequence
No data must be transmitted for 1
second before and after that the i-
modul ISDN HIX V4 changes to
command mode.
+++
In order to change from command
mode to normal data transmission
again, use the command
ATO
In order to accept an incoming
connection, use the command ATA
In order to configure the number of
ring tones after which the i-modul
ISDN HIX V4 answers and accepts
the connection, use the command
Replace <n> with the number of
ring tones.
ATS0=<n>
In order to terminate a connection
and cause the i-modul ISDN HIX V4
to hang up, use the command
ATH
19

Functions i-modul ISDN HIX V4
6.1 Querying the Alarm Inputs
The i-modul ISDN HIX V4 provides two digital inputs, which trigger an alarm
condition when connecting to ground. The status of these alarm inputs can be
queried via the respective S register using an AT command. The i-modul ISDN HIX
V4 can send a message in case of an alarm. This message can be sent via data
connection, as SMS or as e-mail via a service provider. The i-modul ISDN HIX V4
evaluates a connection of the input to ground as alarm. If no positive edge is
counted at least 4 seconds after the negative edge, an alarm will be processed. A
pause of at least 5 seconds is necessary after resetting the input before a new
alarm can be triggered.
Figure 7: Pulse evaluation
Configuration with AT commands
In order to query the condition of
alarm input 1, use the command ATS17?
In order to query the condition of
alarm input 2, use the command ATS18?
The value "1" indicates an open
input and the value "0" indicates
a closed input. The response on
the right indicates an open input
for example.
001
OK
20
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
Insys i-modul ISDN HIX Designer’s Guide
- Category
- ISDN access devices
- Type
- Designer’s Guide
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
Related papers
-
Insys i-modul ISDN HUT Designer’s Guide
-
Insys 2G (GSM) 4.2 Owner's manual
-
Insys Socket ISDN basic Designer’s Guide
-
Insys Pocket ISDN Owner's manual
-
Insys ISDN Owner's manual
-
Insys ISDN 19″ Modem Owner's manual
-
Insys 2G (GPRS) 5.0 Ethernet Owner's manual
-
Insys Powerline Quick Installation Guide
-
Insys i-modul GPRS serial Designer’s Guide
-
Insys ETSM / ETSU Quick Installation Guide
Other documents
-
Cisco CISCO887GW-GN-E-K9 Datasheet
-
Cisco 887V Datasheet
-
Cisco 880 Series Datasheet
-
Cisco C888 EFM Datasheet
-
Cisco CISCO886-K9 Datasheet
-
IFM O2D550 User guide
-
 Hix HT-400e Owner's manual
Hix HT-400e Owner's manual
-
Cisco CISCO887VA-M-K9 Datasheet
-
Cisco 867VAE Datasheet
-
Amprobe AM50, AM53, AM55 & AM56 Digital Multimeters User manual












































































