
OVERVIEW
As more micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) are being used for
automotive and consumer electronics, engineers need a robust MEMS and
mixed-signal co-design flow that enables both system-on-chip (SoC) and system-
in-package (SiP) approaches. A clear-cut interface between a MEMS design sub-
flow and the conventional mixed-signal sub-flow is necessary. Cadence
®
VCAD
Services has developed an IP for handling the special requirements for a MEMS
methodology (for both SoC and SiP applications) called SIMPLI. The IP ensures
efficient handling of concurrent design/optimization of the MEMS and electronics
while handling engineering change orders between the two domains.
The MEMS design sub-flow adopts a top-down approach starting
with behavioral modeling down to finite-element simulation. For
MEMS design, a Cadence-based design sub-flow is readily
available, yet the flow is equally portable to many third-party
MEMS tools through the use of SIMPLI (VCAD Productivity IP).
The MEMS design sub-flow is demonstrated by 18 design tasks.
An x-axis MEMS accelerometer design demonstrates these design
tasks from specifications to publishing.
CADENCE MIXED-SIGNAL / MEMS
CO-DESIGN METHODOLOGY
MIXED-SIGNAL / MEMS CO-DESIGN
METHODOLOGY
The Cadence Mixed-Signal / MEMS Co-Design Methodology
comprises three sub-flows:
• MEMSdesign
• MEMSIPpublishingandimporting
• Mixed-signaldesign
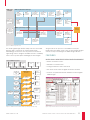
Figure 1: Cadence Mixed-Signal / MEMS Co-Design Methodology
MEMS IP
Analog / Mixed-Signal
and Digital Components
Single Monolithic
CMOS-MEMS
MEMS
Inter-Digitized
Sensor
Clock
Tree
C-to-V
Signal
Proc
ADC
C-to-V
Inter-Digitized
Sensor IP
Methods for efficent use of EDA and FEM
Foundry Design Kit
IC System Specificaions
MEMS Design Sub-Flow
Electro-Mechanical
Simulation
Physical Design
SIMPLI
Functional
Validation
Physical
Integration
Mixed-Signal/MEMS Design
Sub-Flow
Electrical
Simulation
Physical Design
Electro-Mechanical
Top-Down Top-Down Bottom-up
MEMS
Specifications
Analog
(Mixed-Signal) Digital
Integration/
Publishing

2
www.c ad en ce .c om
CADEN CE MIX E D-SIG N AL / M EMS C O -DESI G N MET H ODOLO G Y
The mixed-signal design sub-flow adopts a meet-in-the middle
approach and is a variant of the Cadence AMS Design
Methodology. This decreases the entry barrier for the mixed-
signal design team to integrate the MEMS structure. In addition,
most of the steps that require handling by the mixed-signal
designer (due to the presence of the MEMS structure) are
handled from the SIMPLI cockpit. Thus, the mixed-signal designer
will not need special training on the MEMS design sub-flow.
FEATURES
MIXED-SIGNAL / MEMS SPECIFICATION-DRIVEN ENVIRONMENT
• EnablesvericationIPreuse
• Automatesvericationtasks
• Testingenvironmentcanbehierarchical
• Usemodelcanbesimilartodigitalfunctionalverication
• Performsco-optimizationandRFsimulationformixed-signal/
MEMS designs
MEMS Top-Down Functional Design
MEMS Design
Data Input
1A
MEMS Design
Specifications
1B
Foundry Design
Kit (180nm)
5A
Nominal Finite-
Element
Verification
6
Geometrical/
Mechanical
Models
Enhancement
7A
Nominal/
Statistical
Verification
with Enhanced
Models
8A
Finite-Element
Signoff
8B
N-DOF
Reduced-Order
Model
Generation
7B
Geometrical/
Mechanical
Design
Optimization
3A
MEMS
Topology
Selection
4A
Geometrical/
Mechanical
Nominal Design
2A
MEMS
Executable
Specifications
Creation
2B
MEMS
Design
Validation
Strategy
5B
MEMS Block
Early Design
Rule Checking
7C
MEMS Layout/
Abstract Final
Design
Generation
8C
MEMS Block
Final Design
Rule Checking
8B
MEMS Block
Electrical
Parasitic
Extraction
3B
PCell
Creation
4B
MEMS Layout
Nominal Design
Generation
2C
Auxiliary DRC
Rules Creation
9
MEMS IP
Packaging
MEMS Top-Down Physical Design
Figure 2: MEMS design sub-flow
Figure 3: SIMPLI interface handles MEMS IP publishing and importing
Specification
Files
Abstract
LEF Files
Layout
GDSII File
CDL Netlist
Spice, Spectre
Coupled C
Netlists
Required MEMS IP Input Files
Target
PDK
Symbol
View
Spice
Black-Box
CDL
Black-Box
Functional
View
Encrypted
Functional
File
SIMPLI Library
Processor
Symbol
Generation
DRC
Coupled C
Extraction
Abstract
Generation
Black-
boxing
Auxiliary Virtuoso not shipped
Layout
Generation
Functional
View
GDSII
Files
Functional
Description
Files
Measurement
Files
LEF
Files
Layout
View
Abstract
View
Spectre
Black-Box
Assura
Customization
,
-
Testbench bank and
simulation analysis
definition
Global variables
Specifications captured
as expressions,
waveforms, or
post-processing scripts
Specification
boundaries
Figure 4: Specification-driven environment using Virtuoso technology

3
www.c ad en ce .c om
CADEN CE MIX E D-SIG N AL / M EMS C O -DESI G N MET H ODOLO G Y
SIMPLI INTERFACE DEDICATED TO MEMS DOMAIN
One challenge in the co-design of MEMS and mixed-signal
portions of a chip is that they might not necessarily be sharing
the same flow. Moreover, the information required by the mixed-
signal design team might not be readily available from the MEMS
tools.
An extra layer is necessary to automate the generation of all the
necessary information from the MEMS tools while still allowing IP
protection.
The Cadence Mixed-Signal / MEMS Co-Design Methodology uses
a SIMPLI interface dedicated to the MEMS domain. SIMPLI is a
type of VCAD productivity IP that operates on standard inputs
and generates views required for mixed-signal design within the
Cadence Design Framework. Moreover, SIMPLI automates the
extraction of parasitic coupling capacitances at the interface with
thereleasedMEMSstructure.UsingtheSIMPLIinterface,
designers have the flexibility to export their layout as an abstract
view, and their behavioral or reduced-order models in a 128-bit
RSA encrypted format, while ensuring that the information is
useful for simulation by the mixed-signal design group.
FULL-CHIP SIMULATION EARLY IN THE DESIGN CYCLE
To figure out conceptual problems in the design, an early
co-simulation of the whole system needs to be available. The
Mixed-Signal / MEMS Co-Design Methodology enables testbench
reuse and provides different configurations, which allows full-
chip verification while the design is being developed, thus
lowering design costs.
PCELL-DRIVEN MIXED-SIGNAL / MEMS PHYSICAL
CO-DESIGN
The Mixed-Signal / MEMS Co-Design Methodology demonstrates
a Pcell approach for laying out complicated MEMS structures,
such as accelerometers. Early design-rule checks (DRC) are
implemented directly in the Pcell. A motion-aware Pcell is
demonstrated for the purpose of electrical parasitic extraction of
the MEMS structure.
An FEM-aware Pcell allows for easy communication with a
portion of the Pcell for simulation with FEM tools. All the Pcells
are linked to the behavioral models through Cadence Virtuoso
®
technologies.
Foundry PDK library name
Tabs configuring information
of views to be generated
SIMPLI run mode:
• Release - for MEMS designer to
release a MEMS component
• Integration - for SoC designer to
integrate a MEMS
Output
directory
containing all
generated files
and views
Switches
specifying
which views
to be
created
Table containing
cells found in
various input files
Figure 5: SIMPLI interface
System output
Paramerterizable accelerometer
suitable for both simulation
optimization and schematic-
driven layout
Accelerometer
mechanical inputs
stimuli through
inherited connections
Switched-cap
sampling clock
Figure 6: Early co-simulation of the full chip, including the MEMS
Figure 7: Pcell approach to laying out complex MEMS structures
Mechanical ports expressed in
VHDL-AMS displacement type
Parameters governing
accelerometer geometrical
dependancies
MEMS electical ports
corresponding to silicon ports
Substrate connection
port name

4
www.c ad en ce .c om
CADEN CE MIX E D-SIG N AL / M EMS C O -DESI G N MET H ODOLO G Y
EXECUTABLE SCENARIOS
MEMS design
• Conceptvalidation
• Functionalverication
• Physicaldesign
• Post-layoutandsignoff
MEMS IP publishing and importing
• MEMSIPpublishingusingSIMPLI
• MEMSIPimportingusingSIMPLI
Mixed-signal design
• Conceptvalidation
• Functionalverication
• Full-chipassembly
• Post-layoutandsignoff
• Full-chipco-optimization
PRODUCT INTEGRATION
• VirtuosoMulti-ModeSimulation
• VirtuosoAMSDesignerSimulator
• VirtuosoAnalogDesignEnvironment
• VirtuosoSchematicEditor
• VirtuosoLayoutSuite
• Assura
®
Design Rule Checker (DRC)
• AssuraLayoutvs.Schematic(LVS)Verier
• AssuraParasiticExtraction(RCX)
• SIMPLI(VCADProductivityIP)
List of nets that
are completed
routed
Readout as
plain footprint
MEMS accelerometer
as abstract
Opened MEMS
connections
Set of global variables from
MEMS and electronics that
satisfy conflicting specifications
simultaneously
Best global optimization results
arranged in descending order
Figure 8: Virtuoso layout technology links all Pcells to behavioral models
Figure 9: Full-chip co-optimization

© 2009 Cadence Design Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cadence, the Cadence logo, Assura, and Virtuoso are registered trademarks of Cadence Design
Systems, Inc. All others are properties of their respective holders..
21057 06/09 MK/MVC/DM/PDF
For more information
contact Cadence sales at:
+1.408.943.1234
or log on to:
www.cadence.com/
contact_us
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
Cadence CADENCE MIXED-SIGNAL Overview
- Type
- Overview
- This manual is also suitable for
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
Related papers
Other documents
-
 OpenLink Software Server 4.5 User manual
OpenLink Software Server 4.5 User manual
-
Texas Instruments Low-Power Pedometer Using an MSP430 MCU Application Note
-
Telit Wireless Solutions JF2 Hardware User's Manual
-
Maestro A2100-B User manual
-
Maestro A2100-A/B User manual
-
Murata MEMS User manual
-
STMicroelectronics STM32Cube Quick start guide
-
Silicon Labs UG309 User guide
-
Silicon Labs UG250 User guide
-
Sierra RedySmart User manual





