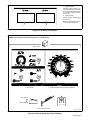
Miller Dimension 812 Owner's manual
- Category
- Welding System
- Type
- Owner's manual
This manual is also suitable for

cover 5/94 − ST-800 091 PRINTED IN USA
1994 MILLER Electric Mfg. Co.
Read and follow these instructions and all
safety blocks carefully.
Have only trained and qualified persons
install, operate, or service this unit.
Call your distributor if you do not understand
the directions.
Give this manual to the operator.
For help, call your distributor
or: MILLER Electric Mfg. Co., P.O. Box 1079,
Appleton, WI 54912 414-734-9821
OWNER’S
MANUAL
October 1994 Form: OM-278
Effective With Serial No. KE634255
CC/CV DC, 100% Duty Cycle Welding Power Source
For Multiple Welding Processes And CAC-A Cutting/Gouging
650 Amperes At 44 Volts DC
Uses Three-Phase Input Power (See Rating Label)
Overheating And Short Circuit Protection
14-Pin Remote Control Receptacle And Remote Control Terminal Strip
115 Volts AC 15 Amperes Auxiliary Power Receptacle
Dimension 652Dimension 652

OM-278 − 10/94
EMF INFORMATION
The following is a quotation from the General Conclusions Section of
the U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, Biological
Effects of Power Frequency Electric & Magnetic Fields −
Background Paper, OTA-BP-E-53 (Washington, DC: U.S.
Government Printing Office, May 1989): “. . . there is now a very large
volume of scientific findings based on experiments at the cellular
level and from studies with animals and people which clearly
establish that low frequency magnetic fields can interact with, and
produce changes in, biological systems. While most of this work is
of very high quality, the results are complex. Current scientific
understanding does not yet allow us to interpret the evidence in a
single coherent framework. Even more frustrating, it does not yet
allow us to draw definite conclusions about questions of possible risk
or to offer clear science-based advice on strategies to minimize or
avoid potential risks.”
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the following
procedures:
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them.
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cables around the body.
4. Keep welding power source and cables as far away as practical.
5. Connect work clamp to workpiece as close to the weld as
possible.
About Pacemakers:
The above procedures are among those also normally
recommended for pacemaker wearers. Consult your doctor for
complete information.
Considerations About Welding And The Effects Of Low Frequency Electric And
Magnetic Fields
NOTE
mod10.1 4/93
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 − SAFETY INFORMATION 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 2 − SPECIFICATIONS 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-1. Volt-Ampere Curves 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2-2. Duty Cycle 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 3 − INSTALLATION 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-1. Typical Process Connections 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-2. Selecting A Location And Moving Welding Power Source 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-3. Installing Gas Supply 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-4. 115 Volts AC Duplex Receptacle 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-5. Selecting And Preparing Weld Output Cables 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-6. Connecting To Weld Output Terminals 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-7. Remote 14 Receptacle Information And Connections 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-8. Terminal Strip 1T Information And Connections 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-9. Connecting Input Power 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 4 − OPERATION 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 5 − MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-1. Routine Maintenance 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-2. Overload Protection 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-3. Troubleshooting 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 6 − ELECTRICAL DIAGRAMS 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SECTION 7 − TUNGSTEN ELECTRODE 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7-1. Selecting Tungsten Electrode 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7-2. Preparing Tungsten 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
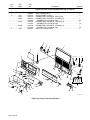
SECTION 8 − PARTS LIST 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 8-1. Main Assembly 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
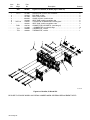
Figure 8-2. Panel, Front w/Components 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
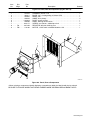
Figure 8-3. Rectifier, Si Diode SR1 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Figure 8-4. Panel, Rear w/Components 33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .

OM-278 Page 1
SECTION 1 − SAFETY INFORMATION
mod1.1 2/93
Read all safety messages throughout this manual.
Obey all safety messages to avoid injury.
Learn the meaning of WARNING and CAUTION.
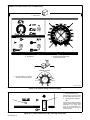
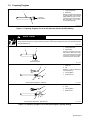
1 Safety Alert Symbol
2 Signal Word
WARNING means possible death
or serious injury can happen.
CAUTION means possible minor
injury or equipment damage can
happen.
3 Statement Of Hazard And Re-
sult
4 Safety Instructions To Avoid
Hazard
5 Hazard Symbol (If Available)
6 Safety Banner
Read safety blocks for each sym-
bol shown.
7 NOTE
Special instructions for best oper-
ation − not related to safety.
2
NOTE
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch live electrical parts.
• Disconnect input power before
installing or servicing.
WARNING
READ SAFETY BLOCKS at start of
Section 3-1 before proceeding.
WARNING
5
4
6
7
1 2
CAUTION
MOVING PARTS can injure.
• Keep away from moving parts.
• Keep all panels and covers closed
when operating.
3
Turn Off switch when using high frequency.
Figure 1-1. Safety Information
SECTION 2 − SPECIFICATIONS
Table 2-1. Welding Power Source
Specification Description
Type Of Output CC/CV DC (Constant Current/Constant Voltage Direct Current)
Rated Weld Output NEMA Class I (100) − 650 Amperes, 44 Volts DC At 100% Duty Cycle (See Section 2-2)
Type Of Input Power Three-Phase; 230, 460, Or 575 Volts AC; 60 Hz
Input Amperes At Rated Output 126 A At 230 V, 63 A At 460 V, 50.4 A At 575 V
Input Amperes While Idling 3.8 A At 230 V, 1.9 A At 460 V, 1.4 A At 575 V
KVA/KW Used At Rated Output 50 kVA/34.8 kW
KVA/KW Used While Idling 1.52 kVA/0.76 kW
Max. Open-Circuit Voltage CC Mode: 72 Volts DC; CV Mode: 70 Volts DC
Welding Processes Shielded Metal Arc (SMAW), Gas Tungsten Arc (GTAW), Gas Metal Arc (GMAW), Flux Cored Arc
(FCAW), And Submerged Arc Welding (SAW); Air Carbon Arc Cutting And Gouging (CAC-A)
Overall Dimensions See Figure 3-3
Weight Net: 545 lb (247 kg); Ship: 561 lb (254 kg)

OM-278 Page 2
2-1. Volt-Ampere Curves
ssb1.1* 10/91 − ST-168 916 / ST-168 917
The volt-ampere curves show the
minimum, mid, and maximum volt-
age and amperage output capabili-
ties of the welding power source.
Curves of other settings fall be-
tween the curves shown.
A. CC Mode B. CV Mode
Figure 2-1. Volt-Ampere Curves
2-2. Duty Cycle
CAUTION
WELDING LONGER THAN RATED DUTY CYCLE can damage unit and void warranty.
• Do not weld at rated load longer than shown below.
warn7.1 8/93
Duty Cycle is percentage of 10
minutes that unit can weld at
rated load without overheating.
Continuous Welding
sb1.1 8/93 − Ref. ST-168 918
0
10
Minutes
100% Duty Cycle At 650 Amperes
Definition Chart
Figure 2-2. Duty Cycle

OM-278 Page 3
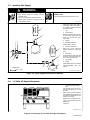
SECTION 3 − INSTALLATION
3-1. Typical Process Connections
See also operator booklet on unit for additional process connection information.
NOTE
Welding
GMAW
Power Source
Work
Welding
GTAW
Power Source
Work
HF Unit
Welding
GMAW
Power Source
Work
Push-Pull
Feeder
Wire Feeder
14 Pin
Remote
Control
Welding
SMAW
Power Source
Work
14 Pin
14 Pin
POLARITY
TYPICAL
Figure 3-1. Typical Process Connections

OM-278 Page 4
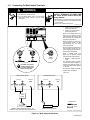
3-2. Selecting A Location And Moving Welding Power Source
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch live electrical parts.
• Disconnect input power conductors from deener-
gized supply line BEFORE moving welding power
source.
FIRE OR EXPLOSION can result from
placing unit on, over, or near combus-
tible surfaces.
• Do not locate unit on, over, or near combustible sur-
faces.
• Do not install unit near flammables.
FUMES can be hazardous; LACK OF
FRESH AIR AND PROPER VENTILA-
TION can be harmful.
• Do not breathe welding fumes.
• Place unit only where there is a good fresh air supply
and proper ventilation.
FALLING EQUIPMENT can cause seri-
ous personal injury and equipment
damage.
• Use lifting eye to lift unit only, NOT running gear, gas
cylinders, or any other accessories.
• Use equipment of adequate capacity to lift the unit.
swarn11.1* 3/93
1 Lifting Eye
2 Lifting Forks
Use lifting eye or lifting forks to
move unit.
If using lifting forks, extend forks
beyond opposite side of unit.
3 Rating Label (Under Access
Door)
Use rating label to determine input
power needs.
4 Line Disconnect Device
Locate unit near correct input pow-
er supply.
OR
1
3
Movement
Location And Airflow
2
18 in
4
(460 mm)
18 in
(460 mm)
ssb9.1 12/93 − ST-800 402 / ST-800 091
Figure 3-2. Movement And Location Of Welding Power Source
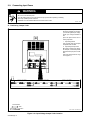
Overall dimensions (A, B, and C) include lifting eye, handles, hardware, etc.
NOTE
Ref. ST-153 556-A
B
A
C
Inches Millimeters
A 27-1/4 692
B 22-1/4 565
C 36 914
D 33 838
E 1-1/2 38
F 20 508
G 1-1/8 29
H 7/16 Dia 11 Dia
4 Holes 4 Holes
D
E
F
G
H
Figure 3-3. Overall Dimensions And Base Mounting Hole Layout

OM-278 Page 5
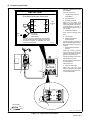
3-3. Installing Gas Supply
WARNING
CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
• Keep cylinders away from welding and other
electrical circuits.
• Never touch cylinder with welding electrode.
• Always secure cylinder to running gear, wall, or
other stationary support.
BUILDUP OF SHIELDING GAS can harm
health or kill.
• Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
warn4.1 9/91
Obtain gas cylinder and chain to
running gear, wall, or other station-
ary support so cylinder cannot fall
and break off valve.
1 Cap
2 Cylinder Valve
Remove cap, stand to side of valve,
and open valve slightly. Gas flow
blows dust and dirt from valve.
Close valve.
3 Cylinder
4 Regulator/Flowmeter
Install so face is vertical.
5 Gas Hose Connection
Fitting has 5/8-18 right-hand
threads. Obtain and install gas
hose.
6 Flow Adjust
Typical flow rate is 20 cfh (cubic feet
per hour). Check wire manufactur-
er’s recommended flow rate.
7CO
2
Adapter
8 O-Ring
Install adapter with O-ring between
regulator/flowmeter and CO
2
cylinder.
ssb3.1* 6/93 − ST-158 697-A
Tools Needed:
5/8, 1-1/8 in
CO
2
Gas
7 8
3
1
2
4
5
6
1
2
3
Argon Gas
OR
Figure 3-4. Typical Regulator/Flowmeter Installation
3-4. 115 Volts AC Duplex Receptacle
Ref. ST-800 101-B
1 115 Volts AC Duplex Recep-
tacle
This welding power source sup-
plies up to 15 amperes of 115 volts
ac power.
Power output is shared between
this receptacle and the Remote 14
receptacle or terminal strip 1T (see
Sections 3-7 and 3-8).
Receptacle is protected from over-
load by circuit breaker CB1 (see
Section 5-2).
Close door.
1
Figure 3-5. Connecting To 115 Volts AC Duplex Receptacle

OM-278 Page 6
3-5. Selecting And Preparing Weld Output Cables
sb6.5 11/92 − S-0752
1 Weld Output Cable
Determine total cable length in weld
circuit and maximum welding am-
peres. Use Table 3-1 to select prop-
er cable size.
Use shortest cables possible.
Do not use damaged cables.
2 Terminal Lug
Use lugs of proper amperage
capacity and hole size for connect-
ing to work clamp, wire feeder or
electrode holder, and weld output
terminals.
3 Wire Feeder
4 Insulated Electrode Holder
5 GTAW Torch
Install according to manufacturer’s
instructions.
6 Work Clamp
Install onto work cable.
Tools Needed:
10 ft (3 m)
1
Total Cable
Length In Weld
Circuit = 20 ft (6 m)
10 ft (3 m)
For Example,
2
6
3
2
54
OR OR
Figure 3-6. Selecting And Preparing Weld Output Cables
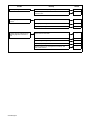
Table 3-1. Weld Cable Size*
Total Cable (Copper) Length In Weld Circuit Not Exceeding
100 ft (30 m) Or Less
150 ft
(45 m)
200 ft
(60 m)
250 ft
(70 m)
300 ft
(90 m)
350 ft
(105 m)
400 ft
(120 m)
Welding
Amperes
10 To 60%
Duty Cycle
60 Thru 100%
Duty Cycle
10 Thru 100% Duty Cycle
100 4 4 4 3 2 1 1/0 1/0
150 3 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 3/0
200 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 4/0
250 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-2/0
300 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-3/0
350 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-3/0 2-4/0
400 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-4/0 2-4/0
500 2/0 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-4/0 3-3/0 3-3/0
600 3/0 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-4/0 3-3/0 3-4/0 3-4/0
700 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-4/0 3-3/0 3-4/0 3-4/0 4-4/0
800 4/0 2-2/0 2-3/0 2-4/0 3-4/0 3-4/0 4-4/0 4-4/0
*Weld cable size (AWG) is based on either a 4 volts or less drop or a current density of at least 300 circular mils per ampere. S-0007-D

OM-278 Page 7
3-6. Connecting To Weld Output Terminals
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch live electrical parts.
• Turn Off welding power source, and disconnect
input power before making any weld output
connections.
USING BOTH POSITIVE (+) WELD
OUTPUT TERMINALS AT SAME TIME
can cause serious electric shock and
arcing hazards.
• Both positive (+) terminals are live at the same time.
• Do not use both positive (+) weld output terminals at
the same time.
• Remove any cable not being used.
swarn12.1* 2/93
Ref. ST-800 101-B / ST-162 508-A
1 Positive (+) High Inductance
Weld Output Terminal
2 Positive (+) Low Inductance
Weld Output Terminal
While in the GMAW mode (see
Figure 4-4), use positive (+) weld
output terminal that provides the
best welding arc and weld puddle
properties for application.
When connected to Low terminal,
low inductance results in a stiff,
fast-responding arc, and small,
fast-freezing puddle.
When connected to High terminal,
high inductance results in a soft,
slower-responding, low spatter arc,
and more fluid weld puddle.
While in SMAW mode (see
Figure 4-4), use positive (+) High
Inductance weld output terminal.
3 Negative (−) Weld Output Ter-
minal
For Electrode Positive (DCEP),
connect work cable to negative (−)
terminal and electrode holder or
wire feeder cable to proper positive
(+) terminal.
For Electrode Negative (DCEN),
reverse cable connections.
Close door.
1
Tools Needed:
3/4 in
Use ONLY one positive
(+) weld output terminal
at a time. Remove any
cable not being used.
POSITIVE
2
NEGATIVE
3
Wire
Feeder
Workpiece Workpiece
Welding Power Source
GMAW or SAW Connections (DCEP) − For
SMAW Connections (DCEP)
POSITIVE
NEGATIVE
Welding Power Source
POSITIVE
NEGATIVE
FCAW Use Low Inductance Weld Output Terminal
Figure 3-7. Weld Output Connections

OM-278 Page 8
3-7. Remote 14 Receptacle Information And Connections
sb7.1* 12/93 − ST-800 693-A / Ref. S-0004-A / S-0750
1 Remote 14 Receptacle RC8
(See Table 3-2)
2 Keyway
3 Plug
4 Threaded Collar
To connect to receptacle, align
keyway, insert plug, and tighten
threaded collar. Close door.
If remote control plug does not fit
receptacle, go to Figure 3-9 to wire
cord to terminal strip 1T.
3
4
OR
AJ
B
K
I
C
L
NH
D
M
G
E
F
12
Figure 3-8. Remote 14 Connections
Table 3-2. Remote 14 Socket Information
A 24 volts ac. Protected by circuit breaker CB2.
B Contact closure to A completes 24 volts ac contactor control circuit.
I 115 volts ac. Protected by circuit breaker CB1.
J Contact closure to I completes 115 volts ac contactor control circuit.
G Circuit common for 24 and 115 volts ac circuits.
C Command reference; CV: +10 volts dc or CC: 0 to +10 volts dc.
D Remote control circuit common.
E 0 to +10 volts dc input command signal from remote control.
K Chassis common.
F Current feedback; 0 to +10 volts dc, 1 volt per 100 amperes.
H Voltage feedback; 0 to +10 volts dc, 1 volt per 10 arc volts.
Socket Information
*The remaining sockets are not used.
Socket*

OM-278 Page 9
3-8. Terminal Strip 1T Information And Connections
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill; UNEXPECTED OUTPUT can cause serious injury.
• Do not touch live electrical parts.
• Turn Off welding power source, and disconnect input power before making any internal inspection or connections.
• Do not connect to Remote 14 receptacle and terminal strip at the same time.
Output (Contactor) can be energized from either the receptacle or terminal strip. Use only one remote control method.
Terminal Information:
Remote Contactor
A, B Contact closure completes the 24 volts ac contactor control circuit. Protected by circuit breaker CB2.
Remote Amperage/Voltage Control
C Command reference; CV: +10 volts dc or CC: 0 to +10 volts dc.
D Control circuit common.
E Input command signal (potentiometer wiper or 0-10 volts dc source); 0 to +10 volts dc.
115 Volts AC
I, J Contact closure completes the 115 volts ac contactor control circuit. Protected by circuit breaker CB1.
Remote Power On/Off
K GND (chassis common).
L, M Remote power on/off connections.
Remote Voltage Sensing Signal
N Voltage sensing signal from Negative (−) weld output terminal.
P Voltage sensing signal from Positive (+) weld output terminal.
Ref. ST-800 170-C
Turn Off welding power source.
1 Remote Control Cord
2 Terminal Strip Access Panel
Remove screws and tip access
panel forward.
3 Strain Relief (Customer
Supplied)
Install strain relief. Route leads
through strain relief.
4 Terminal Strip 1T
5 Terminal Strip Label
Connect leads to 1T using terminal
information below.
Secure cord in strain relief. Rein-
stall and secure access panel.
Close door.
Tools Needed:
1
2
3
4
5
In some cases, Terminal Strip 1T letter designators
do not match Remote 14 Receptacle RC8. Read
descriptions below before making connections.
Turn Off power before
opening terminal strip
cover.
C
REMOTE
OUTPUT
CONTROL
115 VAC 24VAC
REMOTE
REMOTE
VOLTAGE
SENSE
GND REMOTE
POWER ON/OFF
S-162 895-B
EDI J ABNPK ML
REMOTE
CONTACTOR CONTACTOR
Figure 3-9. Terminal Strip 1T Connections

OM-278 Page 10
3-9. Connecting Input Power
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch live electrical parts.
• Turn Off welding power source, and disconnect input power before inspecting or installing.
• Have only qualified persons install unit.
• Installation must meet National Electrical Code and all other codes.
swarn3.1 2/93
A. Positioning Jumper Links
ssb5.1* 2/92 − ST-800 104-A
Jumper links allow operation on dif-
ferent input voltages and are facto-
ry set for the highest input voltage.
Check input voltage available at
site.
Open rear panel access door to
check jumper links.
1 Input Voltage Label
Look at jumper links and compare
link position with unit label.
2 Input Voltage Jumper Links
Move links to match input voltage.
For example, use 230 volts position
when 230 volts input power is avail-
able.
Close rear panel access door or go
on to Figure 3-11.
Tools Needed:
3/8 in
3/8 in
21
230 VOLTS
S-168 940
460 VOLTS 575 VOLTS
Figure 3-10. Input Voltage Jumper Links Location

OM-278 Page 11
B. Connecting Input Power
Have only qualified persons make
this installation.
Open rear access door.
1 Line Disconnect Device Of
Proper Rating
2 Input Conductors
3 Grounding Conductor
Select size and length using
Table 3-3. Conductor rating must
comply with national, state, and lo-
cal electrical codes. Use lugs of
proper amperage capacity and cor-
rect hole size.
4 Strain Relief Connector
Insert conductors through strain
relief.
5 Line Terminals
6 Welding Power Source
Ground Terminal
Connect grounding conductor to
ground terminal on base of unit first.
Then connect input conductors to
contactor.
7 Disconnect Device Ground
Terminal
Install and connect grounding
conductor and input conductors in
conduit or equivalent to deener-
gized line disconnect device.
Connect grounding conductor first,
then line input conductors.
Be sure grounding conductor goes
to an earth ground.
Close access door.
8 Overcurrent Protection
Select type and size using
Table 3-3. Install into deenergized
line disconnect device (fused dis-
connect switch shown).
ssb2.4* 1/94 − ST-800 103-A
L1
S-162 681
IMPORTANT
Three-Phase Input Power Connections
GND/
3
Green Or
Green With
Yellow Stripe(s)
PE
Input
Contactor
W
L2
L3
Cut All Conductors To Same Length, And Loop Back
Excess Grounding Conductor. Always Connect Input
Grounding Conductor To GND/PE Stud Near
Contactor On Base First.
Tools Needed:
3/8 in
3/8 in
25
3
6
8
1
4
7
Figure 3-11. Input Power Connections

S-0092-G
OM-278 Page 12
Table 3-3. Electrical Service Requirements*
Input Voltage
230 460 575
Input Amperes At Rated Output
126 63 51
Recommended Standard Fuse Or Circuit Breaker
Rating In Amperes
1
200 90 80
Input Conductor Size In AWG/Kcmil
2
1 6 6
Max Input Conductor Length In Feet (Meters)
3
180 (55) 284 (87) 444 (135)
Grounding Conductor Size In AWG/Kcmil
4
6 8 8
*
These values are calculated from the 1993 edition of the National Electrical Code (NEC).
1 Recommended fuse or circuit breaker size is that closest to 150% of rated input amperage of the welding power source. Article 630-12(a) of NEC
allows fuse or circuit breaker sizing up to 200% of rated input amperage.
2 Input conductor size is for insulated copper wire with 75°C rating with not more than three single current-carrying conductors in a cable or raceway
(Table 310-16 of NEC).
3 Maximum length is to prevent more than a 3% voltage drop between service entrance and input terminals of the welding power source (Articles
210-19(a) and 215-2(b) of NEC).
4 The grounding conductor shall be colored or identified as specified in the NEC. Grounding conductor size for copper wire is not required to be larger
than input conductor (Article 250-95 of NEC).
SECTION 4 − OPERATION
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Always wear dry insulating gloves.
• Insulate yourself from work and ground.
• Do not touch live electrical parts.
• Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous
to your health.
• Keep your head out of the fumes.
• Ventilate area, or use breathing device.
• Read Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) and
manufacturer’s instructions for material used.
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
• Do not weld near flammable material.
• Watch for fire; keep extinguisher nearby.
• Do not locate unit over combustible surfaces.
• Do not weld on closed containers.
• Allow work and equipment to cool before handling.
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin;
NOISE can damage hearing.
• Wear welding helmet with correct shade of filter.
• Wear correct eye, ear, and body protection.
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
• Keep away from moving parts.
• Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards closed
and securely in place.
MAGNETIC FIELDS FROM HIGH CUR-
RENTS can affect pacemaker operation.
• Pacemaker wearers keep away.
• Wearers should consult their doctor before going
near arc welding, gouging, or spot welding opera-
tions.
See Safety Precautions at beginning of manual for ba-
sic welding safety information.
swarn6.1 10/91
1 Output (Contactor) Switch
2 Arc Force (Dig) Control
3 Remote Amperage/Voltage
Control Switch
4 Process Selector Switch
5 Amperage/Voltage Adjustment
Control
6 Digital Voltmeter
7 Digital Ammeter
8 Power Switch/Pilot Light
9 High Temperature Shutdown
Light
34267
8
9
5
Ref. ST-800 101-B
1
Figure 4-1. Controls

OM-278 Page 13
Wear the following while welding:
1 Dry, Insulating Gloves
2 Safety Glasses With Side
Shields
3 Welding Helmet With Correct
Shade Of Filter (See ANSI
Z49.1)
sb3.1 1/94
123
Figure 4-2. Safety Equipment
1 Work Clamp
Connect work clamp to a clean,
paint-free location on workpiece, as
close to weld area as possible.
Use wire brush or sandpaper to
clean metal at weld joint area. Use
chipping hammer to remove slag
after welding.
sb4.1 2/93
Tools Needed:
1
Figure 4-3. Work Clamp
1 Process Selector Switch
Use switch to select type of weld
output. Use SMAW (Hot Start On)
position for Shielded Metal Arc
Welding and Air Carbon Arc Cut-
ting/Gouging processes. Use
GMAW position for Gas Metal Arc
and Flux Cored Arc Welding pro-
cesses. Use SMAW (Hot Start Off)
position for Gas Tungsten Arc
Welding process.
Switch position determines opera-
tion of Amperage/Voltage Adjust-
ment control (see Figure 4-5) and
Arc Force (Dig) control (see
Figure 4-6).
With switch in SMAW (Hot Start
On) position, unit automatically pro-
vides a starting amperage higher
than set value.
Ref. ST-162 500-A
1
Figure 4-4. Process Selector Switch

OM-278 Page 14
1 Amperage/Voltage Adjustment
Control
2 Volts Scale
3 Amps Scale
Use Process Selector switch (see
Figure 4-4) to select weld amper-
age or voltage. Use Volts scale for
GMAW and FCAW processes. Use
Amps scale for SMAW and GTAW
processes.
4 Remote Amperage/Voltage
Control Switch
Use switch to select way of control-
ling amperage and voltage adjust-
ment.
For front panel control, place switch
in the Panel position.
For remote control, place switch in
Remote position. See Examples in
Figure 4-9 and Figure 4-10.
1
2
3
4
V
12
16
20
24
28
32
36 40
44
48
52
56
60
Figure 4-5. Amperage/Voltage Adjustment Control And Switch
1 Arc Force (Dig) Control
This control is used for SMAW,
SAW, or CAC-A, and only works
when Process Selector switch (see
Figure 4-4) is in the SMAW (Hot
Start On) position.
Control increases short-circuit am-
perage to help start an arc or make
vertical or overhead welds.
When set at 0, short-circuit amper-
age is the same as normal welding
amperage.
As setting increases, short-circuit
amperage increases to help arc
starting. See Figure 2-1.
Select setting best suited for appli-
cation. Numbers around control are
for reference only.
Turn control to 0 (zero) for GTAW process.
1
Figure 4-6. Arc Force (Dig) Control
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch live electrical parts.
• Do not touch weld output terminals when contactor is energized.
• Do not touch electrode and work clamp at the same time.
swarn7.1 10/91
1 Output (Contactor) Switch
Use switch to select way of control-
ling unit output.
For weld output, place switch in On
position.
For remote output control, connect
to Remote 14 receptacle or terminal
strip as instructed in Sections 3-7
and 3-8, and place switch in Re-
mote position.
Weld output terminals are
energized when switch is
On and Power is On.
1
Figure 4-7. Output (Contactor) Switch

OM-278 Page 15
1 Digital Voltmeter
Voltmeter displays voltage (to 0.1
volt) at the weld output terminals,
but not necessarily the welding arc
due to cable resistance, poor con-
nections, etc.
2 Digital Ammeter
Ammeter displays weld amperage
output of unit.
Both meters hold last weld value for
5 seconds after welding ends.
12
Figure 4-8. Voltmeter And Ammeter
4. Adjust Remote Control
2. Set Switches
1. Set Process
Ref. ST-162 500-A
EXAMPLE Of Combination Remote Amperage Control For GTAW Welding
Min (0 A DC)
Max (450 A DC)
V
12
16
20
24
28
32
36 40
44
48
52
56
60
3. Set Desired Maximum Amperage For Application
Figure 4-9. Remote Amperage Control Example

OM-278 Page 16
2. Set Switches
1. Set Process
3. Front Panel Amperage/Voltage
Control Does Not Work
REMOTE VOLTAGE
Min
(0 V)
Max
EXAMPLE Of Full Remote Voltage Control For GMAW Welding
V
12
16
20
24
28
32
36 40
44
48
52
56
60
(60 V)
Ref. ST-162 500-A
4. Set Percentage On Remote
Voltage Control Of Wire Feeder
Figure 4-10. Remote Voltage Control Example
1 Power Switch/Pilot Light
Use switch to turn unit on and off.
The switch lights when power is on.
2 High Temperature Shutdown
Light
Lights when unit internal tempera-
ture has reached maximum rated
temperature. Unit output shuts
down, but thermostatically con-
trolled fan motor runs as long as
cooling is needed.
2
1
Figure 4-11. Power Switch/Pilot Light, And High Temp Light

OM-278 Page 17
WARNING
BUILDUP OF SHIELDING GAS can harm health or kill.
• Shut off shielding gas supply when not in use.
warn1.1 9/91
1 Shielding Gas Cylinder
2 Valve
3 Gun Trigger
4 Foot Control
5 Finger Tip Control
Open valve on cylinder just before
welding.
Gun trigger, finger tip control, or foot
control turns weld output and gas
flow on and off.
Close valve on cylinder when fin-
ished welding.
sb5.2* 2/92 − S-0621-C
2
1
3
4
5
Figure 4-12. Shielding Gas
Begin Welding
ssb7.1 9/92
Install &
Connect
Equipment
Select
Electrode
Put On
Personal Safety
Equipment
Set Controls
Insert
Electrode
Into Holder
Turn On
Welding Power
Source
Figure 4-13. Sequence Of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Begin Welding
ssb6.1 9/92
Install &
Connect
Equipment
Install & Prepare
Wire Feeding
System
Put On
Personal Safety
Equipment
Set Controls
Turn On
Shielding Gas
Turn On Feeder
And Welding
Power Source
Figure 4-14. Sequence Of Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Install &
Connect
Equipment
Install & Prepare
Wire Feeding
System
Put On
Personal Safety
Equipment
Set Controls
Turn On Feeder
And Welding
Power Source
Begin Welding
ssb6.1* 9/92
Figure 4-15. Sequence Of Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Install &
Connect
Equipment
Install & Prepare
Wire Feeding
System
Install & Prepare
Flux System
Begin Welding
Turn On
Flux System
Put On
Personal Safety
Equipment
Set Controls
Turn On Feeder
And Welding
Power Source
Figure 4-16. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)

OM-278 Page 18
Turn On
Shielding Gas
ssb8.1 12/92
Install &
Connect
Equipment
Install & Connect
High-Frequency
Unit
Select
Tungsten
(See Section 7)
Insert
Tungsten
Into Torch
Put On
Personal Safety
Equipment
Set Controls
Turn On
High-Frequency
Unit
Turn On
Welding Power
Source
Begin Welding
Figure 4-17. Sequence Of Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Install &
Connect
Equipment
Begin
Cutting Or
Gouging
Turn On
Welding Power
Source
Turn On
Compressed Air
Supply
Connect
Compressed Air
Supply
Select
Carbon Electrode
Put On
Personal Safety
Equipment
Set Controls
Insert Electrode
Into Torch
Figure 4-18. Air Carbon Arc Cutting And Gouging (CAC-A)
SECTION 5 − MAINTENANCE & TROUBLESHOOTING
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
• Do not touch live electrical parts.
• Turn Off welding power source, and disconnect
input power before inspecting, maintaining, or
servicing.
HOT PARTS can cause severe burns.
• Allow cooling period before maintaining or servicing.
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
• Keep away from moving parts.
Maintenance to be performed only by qualified persons.
swarn8.1 2/93
5-1. Routine Maintenance
Turn Off all power before maintaining.
3 Months
Clean
And
Tighten
Weld
Terminals
Replace
Unreadable
Labels
6 Months
Tape Or
Replace
Cracked
Weld
Cable
OR
During Heavy Service,
Clean Monthly
Blow Out
Or
Vacuum
Inside
ST-800 091
Figure 5-1. Maintenance Schedule
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
Page is loading ...
-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
Miller Dimension 812 Owner's manual
- Category
- Welding System
- Type
- Owner's manual
- This manual is also suitable for
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
Related papers
-
Miller DIMENSION 652 Owner's manual
-
Miller MC010301U Owner's manual
-
Miller DIMENSION 652 Owner's manual
-
Miller DIMENSION 652 Owner's manual
-
Miller MA400469U Owner's manual
-
Miller 812 Owner's manual
-
Miller DIMENSION 652 Owner's manual
-
Miller DIMENSION 652 Owner's manual
-
Miller LE128450 Owner's manual
-
Miller DIMENSION 652 Owner's manual
Other documents
-
Hobart CYBER FLEX User manual
-
ESAB Inverter Arc Welder Model 300GMS CC/CV User manual
-
ESAB Inverter Arc Welder Model 300GMS CC/CV User manual
-
HobartWelders STICKMATE LX Owner's manual
-
 METAL MAN FC125 Specification
METAL MAN FC125 Specification
-
Intermatic FM1D20A Installation guide
-
Miller Electric DC 650 User manual
-
Hobart Beta Mig 135 P Owner's manual
-
Pyramid PS52KX User manual
-
Miller Electric SSW-2020 ATT User manual






































