ESAB HW-9 is a TIG welding torch designed for precision welding applications. It features a hard body, silicone rubber body, and flexible head models. The torch is suitable for a variety of welding tasks, including:
- General welding
- Pipe welding
- Aerospace welding
- Automotive welding
- And more
The HW-9 torch is known for its durability, flexibility, and ease of use. It is a popular choice for welders of all skill levels.
Here are some of the key features of the ESAB HW-9 TIG welding torch:
- Durable construction: The HW-9 torch is made from high-quality materials that are designed to withstand the rigors of welding.
ESAB HW-9 is a TIG welding torch designed for precision welding applications. It features a hard body, silicone rubber body, and flexible head models. The torch is suitable for a variety of welding tasks, including:
- General welding
- Pipe welding
- Aerospace welding
- Automotive welding
- And more
The HW-9 torch is known for its durability, flexibility, and ease of use. It is a popular choice for welders of all skill levels.
Here are some of the key features of the ESAB HW-9 TIG welding torch:
- Durable construction: The HW-9 torch is made from high-quality materials that are designed to withstand the rigors of welding.
















-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
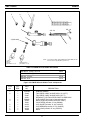 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
ESAB HW-9 is a TIG welding torch designed for precision welding applications. It features a hard body, silicone rubber body, and flexible head models. The torch is suitable for a variety of welding tasks, including:
- General welding
- Pipe welding
- Aerospace welding
- Automotive welding
- And more
The HW-9 torch is known for its durability, flexibility, and ease of use. It is a popular choice for welders of all skill levels.
Here are some of the key features of the ESAB HW-9 TIG welding torch:
- Durable construction: The HW-9 torch is made from high-quality materials that are designed to withstand the rigors of welding.
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
in other languages
- français: ESAB HW-9 Manuel utilisateur
Related papers
-
ESAB PT-32 Plasma Arc Cutting Torch User manual
-
ESAB Genuine Heliarc HW-90 & HW-90 Pencil Tig Welding Torches Troubleshooting instruction
-
ESAB 350mpi POWER SOURCE User manual
-
ESAB 350mpi POWER SOURCE User manual
-
ESAB GENUINE Heliarc HW-17 User manual
-
ESAB MIG-35 Solid/Cored Wire Feeder Troubleshooting instruction
-
ESAB PCM-150 Plasma Arc Cutting/Gouging Packages Installation guide
-
ESAB MT-150 Mig Welding Torch Troubleshooting instruction
-
ESAB PCM-1125 Plasma Arc Cutting Package User manual
-
ESAB & HW-26F Tig Welding Torches User manual
Other documents
-
Miller MF000000L Owner's manual
-
Miller WP-18SC TORCH Owner's manual
-
Miller W-225 TORCHES Owner's manual
-
Miller MF000000L Owner's manual
-
Miller MC000000L Owner's manual
-
Miller MF000000L Owner's manual
-
Miller MC000000L Owner's manual
-
Miller MF000000L Owner's manual
-
Miller MF000000L Owner's manual
-
Miller MC000000L Owner's manual















