EnGenius Technologies 802.11b User manual
- Category
- Routers
- Type
- User manual
This manual is also suitable for
EnGenius Technologies IEEE 802.11b Outdoor Wireless Client Bridge
The EnGenius Technologies IEEE 802.11b Outdoor Wireless Client Bridge is a fully interoperable, IEEE 802.11b compliant Outdoor Wireless Last-mile product. The Wireless Client Bridge operates in remote bridge mode, and connects Outdoor Wireless Router Bridge to construct point-to-point as well as point-to-multipoint topologies, for maximum flexibility in configuring building-to-building networks to WISP.
Key Features
- 9dBi patch directional antenna
- Support 24VDC 0.8A Power-over-Ethernet
- NAT/NAPT and Virtual Server Mapping support
EnGenius Technologies IEEE 802.11b Outdoor Wireless Client Bridge
The EnGenius Technologies IEEE 802.11b Outdoor Wireless Client Bridge is a fully interoperable, IEEE 802.11b compliant Outdoor Wireless Last-mile product. The Wireless Client Bridge operates in remote bridge mode, and connects Outdoor Wireless Router Bridge to construct point-to-point as well as point-to-multipoint topologies, for maximum flexibility in configuring building-to-building networks to WISP.
Key Features
- 9dBi patch directional antenna
- Support 24VDC 0.8A Power-over-Ethernet
- NAT/NAPT and Virtual Server Mapping support




















-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
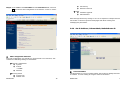 8
8
-
 9
9
-
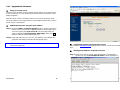 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
 16
16
-
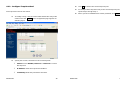 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
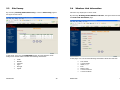 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
EnGenius Technologies 802.11b User manual
- Category
- Routers
- Type
- User manual
- This manual is also suitable for
EnGenius Technologies IEEE 802.11b Outdoor Wireless Client Bridge
The EnGenius Technologies IEEE 802.11b Outdoor Wireless Client Bridge is a fully interoperable, IEEE 802.11b compliant Outdoor Wireless Last-mile product. The Wireless Client Bridge operates in remote bridge mode, and connects Outdoor Wireless Router Bridge to construct point-to-point as well as point-to-multipoint topologies, for maximum flexibility in configuring building-to-building networks to WISP.
Key Features
- 9dBi patch directional antenna
- Support 24VDC 0.8A Power-over-Ethernet
- NAT/NAPT and Virtual Server Mapping support
Ask a question and I''ll find the answer in the document
Finding information in a document is now easier with AI
Other documents
-
Allnet ALL0199AP User manual
-
Senao International SL-2511BG PLUS User manual
-
 IMC Networks XI-1500-IH User manual
IMC Networks XI-1500-IH User manual
-
Ruby Tech OW-1000 User manual
-
 Eusso UOW2000-AP67 User manual
Eusso UOW2000-AP67 User manual
-
Dlink DWL-1750 User manual
-
Buffalo N150 User manual
-
Allnet ALL0358N Owner's manual
-
Repotec RP-WR1201G Owner's manual
-
Dlink DWL-1700AP Owner's manual




























